Mains Syllabus: GS II - Government Policies and Interventions for Development in various sectors and Issues arising out of their Design and Implementation.
Over the last decade, the Ministry of Women and Child Development has strengthened access to nutrition, education, legal safeguards, and essential entitlements.
Mains Syllabus: GS II - Important International Institutions, agencies and fora - their Structure, Mandate.
Recently Union Finance Minister advocates for reforms in international financial architecture to ensure MDB funds are used for development purposes.
|
Key components of the IFA |
|
Prelims : Current events of national importance and international importance
Why in News?
INS Tabar takes part in a rescue mission as it responds to a distress call from Pulau-flagged MT Yi Cheng 6, in the Gulf of Oman, which caught a fire in the engine room and total power failure onboard.
Reference
Prelims: Current events of National and International Importance
Why in News?
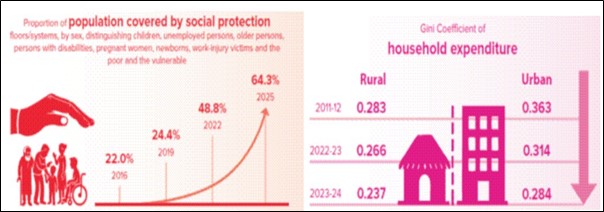
Recently, on the occasion of 19th Statistics Day (29th June), the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released various publications on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The Gini index, or Gini coefficient, measures income inequality in nations by determining how income is distributed across their populations.
Reference
Prelims : Current events of National and International Importance
Why in News?
Recently, 19th Statistics day was celebrated to commemorate 132nd Birth Anniversary of Prof. P. C. Mahalanobis with the theme ‘75 Years of National Sample Survey’.
National Statistics Day is celebrated on June 29th every year in India.
|
Recent launches of NSS |
|
Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis (1893-1972)
Reference
Prelims: Current events of National and International Importance
Why in news?
Recently 36 workers were killed at the factory in the explosion of the Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) drying unit at Sigachi Industries, Hyderabad.
Chemically inert means that a substance has very low reactivity and does not readily form chemical bonds with other substances.
Key Applications
Reference
Prelims: Current events of National and International Importance| Agriculture
Why in news?
Recently National Statistics Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the annual publication of “Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agriculture and Allied Sectors (2011-12 to 2023-24).
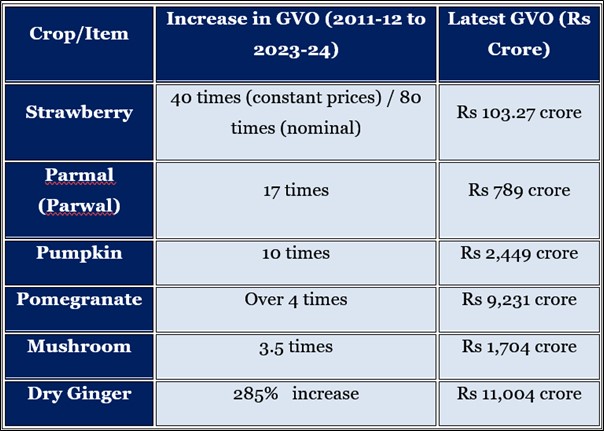
Major Trends in Fruits and Vegetables
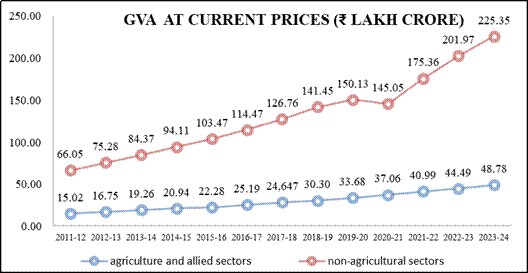
Gross Value of Output (GVO) represents the total value of production of goods in agriculture and allied sectors, before deducting the cost of inputs.
Changing food consumption patterns
Reference
Prelims: Current events of national importance and international importance
Why in News?
INS Tabar takes part in a rescue mission as it responds to a distress call from Pulau-flagged MT Yi Cheng 6, in the Gulf of Oman, which caught a fire in the engine room and total power failure onboard.
Reference
Prelims: Current events of National and International Importance
Why in News?
Recently, on the occasion of 19th Statistics Day (29th June), the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released various publications on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The Gini index, or Gini coefficient, measures income inequality in nations by determining how income is distributed across their populations.

Reference
PIB| SDG National Indicator Framework Progress Report, 2025
National Sample Survey (NSS)
Prelims: Current events of National and International Importance
Why in News?
Recently, 19th Statistics day was celebrated to commemorate 132nd Birth Anniversary of Prof. P. C. Mahalanobis with the theme ‘75 Years of National Sample Survey’.
National Statistics Day is celebrated on June 29th every year in India.
|
Recent launches of NSS |
|
Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis (1893-1972)
Reference
PIB| 75 Years of National Sample Survey
Why in news?
Recently 36 workers were killed at the factory in the explosion of the Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) drying unit at Sigachi Industries, Hyderabad.
Chemically inert means that a substance has very low reactivity and does not readily form chemical bonds with other substances.
Key Applications
Reference
The Hindu | Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC)
Prelims: Current events of National and International Importance| Agriculture
Why in news?
Recently National Statistics Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the annual publication of “Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agriculture and Allied Sectors (2011-12 to 2023-24).
Major Trends in Fruits and Vegetables

Gross Value of Output (GVO) represents the total value of production of goods in agriculture and allied sectors, before deducting the cost of inputs.

Changing food consumption patterns
Reference