Higher Methane Emissions from Energy Sector
Prelims: General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change
Why in News?
Aaccording to the recent International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Global Methane Tracker 2025, the energy sector contributed around 145 million tonnes (Mt) of methane emissions in 2024.
Methane (CH4) is a greenhouse gas responsible for around 30 % of the rise in global temperatures since the Industrial Revolution. Its levels in atmosphere are growing faster than other greenhouse gases, with its concentration being 2-and-a-half times higher than the preindustrial era.
- 3 main sources of methane – Agriculture, energy and waste sectors.
- Oil, natural gas, coal and bioenergy-based sectors accounts for more than 35 % of methane emissions from human activity.
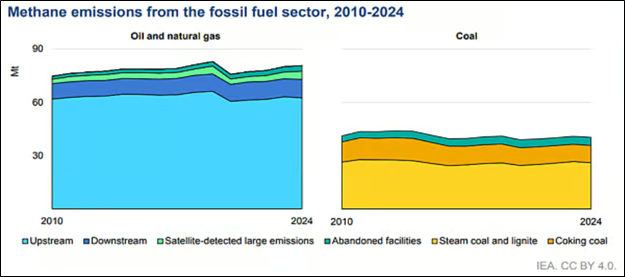
- Methane Emissions by sectors in decreasing order
- In Energy sector - Oil operations>Natural Gas Operations> Abandoned Wells
- Overall – Oil operations> Coal> Natural Gas Operations> Bioenergy
- Emissions from abandoned facilities - IEA estimated around 8 million abandoned onshore oil and gas wells are present globally, as well as a large number of abandoned coal mines.
- Both sources, it added, would be the world’s 4th largest emitter of fossil fuel methane.
- Emitting countries - China leads the world in methane emissions from fossil fuel operations, followed by United States, Russia, Iran, Turkmenistan, India, Venezuela and Indonesia.
- Measures – Global Methane Pledge (GMP) launched in 2021, aims to collectively reduce global methane emissions by at least 30 % from 2020 levels by 2030.
- Oil and Gas Decarbonization Charter was launched in 2023, aims to reduce the greenhouse gas pollution of 50 major oil and gas companies.
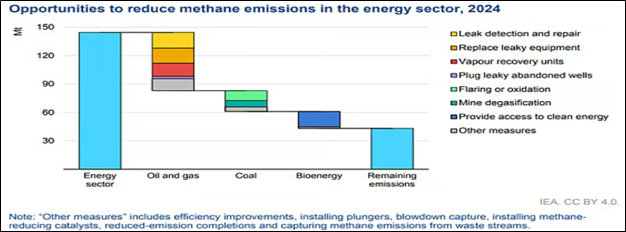
With current technologies, around 70 % of methane emissions from the fossil sector can be reduced.
- Challenges - Existing pledges would cut fossil-fuel methane emissions by 40 % by 2030.
- Only few countries or companies have developed real implementation plans for these commitments.
- Most of the coal industry has not committed to reducing its methane emissions.
- IEA Recommendations – Fossil fuel companies should bear the primary responsibility for abating methane emissions.
- Significance of emission reduction - Deploying targeted methane mitigation solutions in the fossil fuel sector would prevent a roughly 0.1°C rise in global temperatures by 2050 according to IEA.
Reference
Down To Earth| Higher Methane Emissions from Energy Sectors
Related News| Global Methane Tracker | MethaneSAT
Report on India’s Priority Corridors for Zero-Emission Trucking
Prelims: General issues on Environment| Sustainable Development | Current events of national and international importance.
Why in News?
Recently, Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India released a report on India’s Priority Corridors for Zero-Emission Trucking.
|
Zero-Emission Trucking (ZET)
|
- Need – Nearly 40% of fuel consumption and transport emissions in India originate from long-distance trucks.
- It is crucial for decarbonising the logistics sector, reducing air pollution, and strengthening India’s energy security.
- Zero-Emission Trucks (ZETs) – Thay are vehicles powered by clean energy sources like electricity or hydrogen, producing no tailpipe emissions.
- They can lower carbon emissions by 44% to 79% compared to diesel trucks and are more sustainable transport mode.
- It can help India improve logistics efficiency, lower costs, improve air quality, and reduce environmental impact.
|
- Report – It is the result of a rigorous, data-driven assessment designed to support India's vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat and economic goals.
- Developed with the support of - Centre of Excellence for Zero Emission Trucking (CoEZET) - IIT Madras, Rocky Mountain Institute, and pManifold as knowledge partners.
- Objectives – To guide future investments in charging infrastructure, public-private partnerships, and regulatory support mechanisms.
- Selection of ZETs corridors – The report identifies the top 10 high-impact corridors most suited for early ZET deployment, laying the groundwork for a dedicated national ZET infrastructure network.
- They were identified through a 3-phase process by a quantitative and qualitative assessment using parameters such as
- Toll traffic data and mapping of supply/demand centres
- Stakeholder consultations
- Detailed field research
- It also considered factors such as high freight traffic, industrial activity, availability of ancillary services, grid infrastructure readiness, corridor length relative to battery range, and strategic stakeholder inputs.
- Significance – It will serve as a strategic guide for policymakers and industry actors with comprehensive insight into the three-part corridor identification process.
- By strategically targeting these corridors, India can accelerate its transition to a zero-emission freight sector while boosting competitiveness and resilience.
- It can also serve as a reference for the PM E-DRIVE scheme.
PM E-DRIVE scheme was launched in 2024 by the Ministry of Heavy Industries to promote the adoption of zero-emission transport (ZET) solutions.
Reference
PIB| Release of Report on India’s Priority Corridors for ZETs
Related News – PM E-DRIVE Scheme
Decline in MMR and IMR
Prelims: Demographics | Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
As per recent report by Sample Registration System (SRS) Report & United Nation Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group (UN-MMEIG) India sees a decline in MMR and IMR.
- Sample Registration System (SRS) Report 2021 - The report was recently released by the Registrar General of India (RGI) shows that India has continued to witness a significant improvement in key maternal and child health indicators.
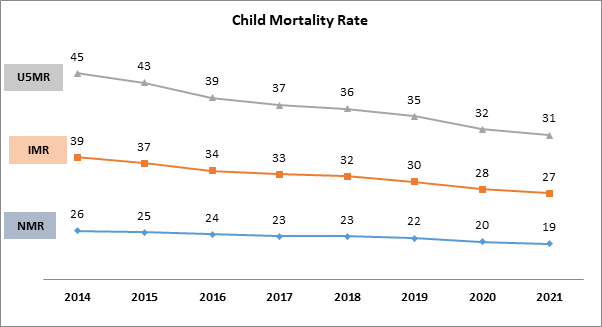
Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR) 0-28 days /1,000 live births.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) – 0-11 months /1000 live births.
Under five Mortality rate (U5MR) – 0- 5years /1000 live births.
|
Indicator
|
2014
|
2021
|
|
Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
|
130 per lakh live births
|
93 per lakh live births
|
|
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
|
39 per 1000 live births
|
27 per 1000 live births
|
|
Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR)
|
26 per 1000 live births
|
19 per 1000 live births
|
|
Under-Five Mortality Rate (U5MR)
|
45 per 1000 live births
|
31 per 1000 live births
|
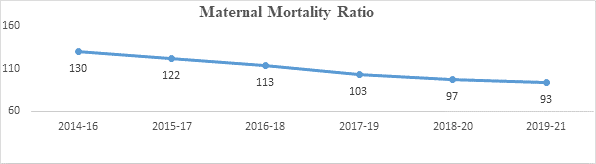
The U.N.’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim at reducing global MMR to less than 70 per 100,000 live births.
- Eight States have already attained SDG target of MMR (<=70 by 2030).
- Twelve States/UT have already attained SDG target of U5MR (<=25 by 2030).
- Six States/ UT have already attained SDG target of NMR (<=12 by 2030).
- UN-MMEIG Report 2000-2023 - India’s MMR has reduced by 23 points from 2020 to 2023.
UN-MMEIG is an international collaboration focused on tracking global maternal mortality. The group was established to provide consistent and comparable estimates of maternal mortality worldwide.
- India's MMR declined by 86% from 1990 to 2023, compared to global reduction of only 48%.
- India achieved a 78% decline in U5MR, surpassing the global reduction of 61%.
- NMR in India declined by 70%, compared to global reduction of only 54%.
- India recorded a 71% decline in IMR, outperforming the global reduction of 58%.
Reference
PIB| India Witnesses a Downward Trend in Mortality Rates
GLEX (Global Conference on Space Exploration)
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
Recently Union minister of science and technology inaugurated the 12th edition of the Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX 2025) from 7th to 9th May 2025 in New Delhi.
- GLEX - It is an international platform to share knowledge, innovations, and collaborative strategies in the field of space exploration.
- Theme - Reaching New Worlds: A Space Exploration Renaissance
- Organized by - The event is organized by the International Astronautical Federation (IAF).
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) (host)
- Astronautical Society of India (ASI) (co-host)
International Astronautical Federation (IAF) is a global body promoting dialogue and cooperation among stakeholders in the space sector.
Objectives
- To share technical, policy, and programmatic updates in global space exploration.
- To assess progress since GLEX 2021 and chart future directions.
- To discuss collaborative solutions, challenges, and lessons learnt.
- To explore how space investments benefit humanity.
- To promote international cooperation and innovation in space missions.
Role of India in Global Space Conference
- It is the first major global space conference in India in recent years.
- India will showcase its achievements in space science and technology through ISRO and private players.
- Opportunity for India to strengthen its role as a leader in the Global South in space diplomacy.
- Promotes India's emerging commercial space ecosystem and technological capabilities.
- Facilitates bilateral and multilateral space cooperation initiatives with major space powers.
References
- PIB| India hosts GLEX 2025
- IAF| Global Space Exploration Conference 2025
UNFF20 – United Nations Forum on Forests (2025)
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
Recently the 20th session of the United Nations Forum on Forests was held at UN Headquarters, New York, from May 5 to 9, 2025.
- United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) - It is a functional body under the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
- Establish – 2000
- Objectives – To promote the management, conservation, and sustainable development of all types of forests.
- To strengthen long-term political commitment to forest-related goals globally.
United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating global economic, social, and environmental issues.
UNFF-20 Objectives
- To review progress toward the Global Forest Goals.
- To assess countries’ Voluntary National Contributions (VNCs) toward forest conservation.
- To promote discussions on forest financing, forest fires, certification, climate resilience, and ecosystem valuation.
- To integrate Country-Led Initiatives (CLIs) into global decision-making.
Country-Led Initiatives (CLIs) are voluntary initiatives hosted by individual UN member countries in support of the work of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF).
India on UNFF-20
India now has 25.17% forest and tree cover of its total geographical area as per India State of Forest Report.
- Restoring Degraded Forest Landscapes - The event showcased India’s experience in integrated forest restoration through policy innovation, convergence of resources, community engagement, and use of technology for monitoring and evaluation.
- Valuing Forest Ecosystems - India called for ecosystem service valuation in national forest policy planning.
Ecosystem Service Valuation refers to the process of identifying, quantifying, and assigning economic, social, or environmental value to the benefits humans receive from ecosystems.
- India presented studies from Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, and tiger reserves.
- These studies quantified ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water provisioning, and biodiversity conservation.
Reference
PIB| 20th Session of the United Nations Forum on Forests
|
One Liners 12-05-2025
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
Revival of Ancient Ayurvedic Texts
Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS) has recently successfully revived two significant Ayurvedic manuscripts: Dravyaratnākara Nighaṇṭu and Dravyanamākara Nighaṇṭu.
- Ayurvedic Manuscripts - Are ancient texts preserving medicinal knowledge, including plant names, therapeutic uses, and formulations. Nighaṇṭus are traditional lexicons detailing the properties of medicinal substances.
- Dravyaratnākara Nighaṇṭu - Authored by Mudgala Paṇḍita in 1480 AD, this 18-chapter text provides in-depth information on drug synonyms, actions, and compositions, referencing earlier Nighaṇṭus and introducing new therapeutic substances.
- Dravyanamākara Nighaṇṭu - Attributed to Bhisma Vaidya, this post-Dhanvantari text serves as a specialized appendix, comprising 182 verses focused on homonyms in drug names, crucial for Ayurvedic pharmacology.
- Significance for Ayurvedic Science - The revival of these texts enriches the understanding of Ayurvedic pharmacology, offering clarity on drug identification and usage, particularly benefiting fields like Rasashastra and Bhaishajya Kalpana.
|
|
Russia Honours Biju Patnaik
Russia has paid tribute to Biju Patnaik by installing a memorial plaque at its embassy in New Delhi, recognizing his significant role during the Battle of Stalingrad (1942–43).
- Biju Patnaik - Born in Cuttack in 1916, Biju Patnaik was a distinguished freedom fighter, skilled aviator, and influential politician. He joined the Royal Indian Air Force in 1936 as a transport and rescue pilot.
- Aid to Russia in WWII - During the crucial Battle of Stalingrad, Patnaik flew perilous supply missions, braving German air defenses to deliver essential arms and supplies to the besieged Soviet Red Army.
- Role in India's Independence - Patnaik also actively supported India's Quit India Movement by undertaking secret flights for nationalist leaders and played a key role in aiding Indonesia's struggle for independence.
- The Pivotal Battle of Stalingrad- The Battle of Stalingrad (July 1942 – February 1943) was a major and bloody WWII confrontation between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union for control of Stalingrad, a strategic city on the Volga.
- Turning Point of WWII - The Soviet victory in Stalingrad marked a crucial turning point in World War II, halting the German advance and leading to their eventual retreat from the Eastern Front.
|
|
Polity & Governance
|
|
CBI Director's Tenure Extended
Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC) has granted a one-year extension to CBI Director Praveen Sood, a Karnataka cadre IPS officer, beyond his scheduled retirement date.
- About Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) – It is India's top agency for investigating high-profile corruption, economic offenses, and serious crimes. It derives its authority from the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946.
- Historical Origins and Formation - Roots trace back to the Special Police Establishment (SPE) formed in 1941.
- Officially established as - CBI on April 1, 1963, following recommendations from the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption.
- Headed by a Director - An IPS officer of DGP rank.
- Appointment – Director is appointed by 3 member selection committee, including the PM, Leader of Opposition, and the Chief Justice of India or their nominee, with a tenure extendable up to five years.
- Investigative Functions - Primary functions include investigating anti-corruption cases, economic offenses like fraud and money laundering, and special crimes referred by states or courts. It also serves as India's Interpol nodal agency.
- Role in Law Enforcement - Beyond investigations, the CBI maintains criminal records, compiles crime statistics, and facilitates coordination among state police forces, playing a crucial role in India's law enforcement framework.
|
|
Kerala's Demand for Animal Birth Control (ABC) Rule Changes
Amid rising stray dog attacks and rabies cases, Kerala is advocating for modifications to the existing (ABC) Rules.
- Understanding the ABC Rules - Enacted under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960, focus on sterilisation and immunization for stray dog population control, prohibiting culling.
- Local Bodies' Responsibilities - The rules mandate local bodies to establish sterilisation centres and ensure humane capture, neutering, vaccination, and release of stray dogs.
- The ABC Process Explained - Trained personnel humanely capture stray dogs, which then undergo sterilisation, vaccination against rabies, and are subsequently released back into their original localities following Supreme Court directives.
- Importance of ABC Measures - ABC programs are significant for preventing stray dog overpopulation while respecting animal rights and simultaneously protecting public health by reducing rabies occurrences.
- Promoting Ethical Animal Management - These rules promote a scientific and ethical approach to managing stray animals, offering an alternative to inhumane culling practices.
|
|
Cashless Treatment for Accident Victims
May 5, 2025, India launched a scheme ensuring cashless medical treatment up to Rs 1.5 lakh for road accident victims, aiming for timely care.
- Scheme Applicability and Benefits - Any person injured in a road accident on Indian roads is eligible for cashless treatment at designated hospitals for up to seven days post-accident.
- Implementation by National Health Authority (NHA) - NHA oversees the scheme, collaborating with police, hospitals, and state agencies. Non-designated hospitals offer stabilization before transfer.
- Monitoring and Government Oversight - A steering committee led by the Road Secretary monitors the scheme's effectiveness, building on a prior pilot program.
- Availing Cashless Treatment - Victims should seek immediate care at designated hospitals (list available via State Road Safety Council or NHA portal) and inform the police.
- Financial Coverage and Duration - Treatment up to Rs 1.5 lakh is cashless for seven days. Hospitals handle claims with the NHA. Keeping records and the police report is advised.
|
|
International Relations and Issues
|
|
Balochistan Independence Declaration
On May 9, 2025, Mir Yar Baloch announced Balochistan's independence from Pakistan.
- International Support - Baloch urged India to grant recognition and establish an embassy in New Delhi. It also appealed to the UN for peacekeeping forces and demanded the Pakistani Army's withdrawal.
- Balochistan - A Southwestern Province of Pakistan. Largest province by area, shares borders with Iran and Afghanistan and has a coastline along the Arabian Sea. Its capital is Quetta.
- Geography and Demographics - Characterized by arid, rugged terrain and a desert climate, Balochistan is sparsely populated despite its rich mineral resources.
- Dominant ethnic group - Is the Baloch people, with Pashtuns and Brahuis also present.
- Strategic Significance and Resources - The region holds substantial reserves of natural gas, coal, copper, and gold. Gwadar port is a crucial component of CPEC, granting China access to the Arabian Sea. India has expressed concerns over human rights in the region.
- History of Insurgency - Various Baloch nationalist groups have been engaged in insurgency, seeking greater autonomy or independence, and frequently targeting CPEC infrastructure and Pakistani security forces.
|
|
India-Maldives HADR Exercise
INS Sharda's arrival at Maafilaafushi Atoll in the Maldives signifies India's participation in a joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) exercise.
- Maldivian Archipelago- Located in the north-central Indian Ocean, the Maldives comprises around 1,200 low-lying coral islands within 26 atolls, with Malé as its capital.
- Language and Faith - Dhivehi is the official language, and Islam is the state religion. Arabic, Hindi, and English are also spoken.
- Diverse Ethnic Roots - The Maldivian ethnic group has ancestry from Tamils, Sinhalese, Arabs, and traders from Africa and Southeast Asia.
- Strategic Indian Ocean Location - Positioned on key global shipping routes, the Maldives holds considerable strategic importance in the Indian Ocean.
- Importance for India's Maritime Vision - It is a crucial partner for India's SAGAR and MAHASAGAR doctrines, enhancing India's regional maritime security and outreach.
|
- UN Charter's Article 51: Right to Self-Defence
Article 51 of the UN Charter (1945) enshrines the inherent right of member states to individual or collective self-defence against armed attacks until Security Council intervention.
- Foundation of International Law - The UN Charter, signed in 1945 and effective that year, is a legally binding international treaty outlining core principles of international relations, including state sovereignty and the prohibition of force.
- Context and Purpose of Self-Defence - Established to provide a legal basis for self-preservation, Article 51 acknowledges states' fundamental right to defend against aggression, crucial for national sovereignty and collective security.
- Key Elements of Article 51 - The article permits self-defence if an armed attack occurs, mandating immediate reporting of such actions to the Security Council to prevent misuse of this right.
- Application in Interstate Conflicts - Primarily invoked in cases of direct state-on-state aggression, responses under Article 51 must be proportional and necessary to the threat.
- Controversies in Counterterrorism - The use of Article 51 in counterterrorism against non-state actors is debated, with critics questioning if such actions meet the threshold of an "armed attack."
- India, Pakistan, and Article 51 - The India-Pakistan conflict, with India's Operation Sindoor and Pakistan's invocation of Article 51, highlights the complex interpretation and application of self-defence in contemporary security challenges.
|
|
Security
|
|
HAROP Drone in 'Operation Sindoor'
Reports suggest India utilized Israeli HAROP loitering munitions on May 8, 2025, during its retaliatory 'Operation Sindoor'.
- HAROP: A Loitering Munition - Developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), HAROP is an advanced loitering munition, functioning as both a missile and a UAV. It loiters, selects a target, and self-destructs with an explosive payload.
- Against High-Value Targets - Designed to neutralize critical assets like radars, command posts, tanks, and SAMs, HAROP can even engage moving targets.
- Operational Features - Unlike conventional missiles, HAROP can search, track, and engage targets dynamically using its electro-optical sensor for real-time visual identification.
- Key Technical Specifications - With an endurance of up to 9 hours, it allows for extensive area scanning and deep strikes. It can be launched from various platforms and operate in GPS-denied environments, offering both autonomous and manual attack modes.
|
|
Science
|
|
Soviet Venus Probe Kosmos 482 Set for Re-entry
over five decades in Earth orbit, the Soviet spacecraft Kosmos 482 is predicted to re-enter the atmosphere around May 10, 2025.
- Failed Venus Mission - Launched in March 1972 as part of the Venera program, its intended destination was Venus. However, an upper rocket stage malfunction prevented its escape from Earth's orbit.
- Stuck in Low Earth Orbit - Despite the failure, the lander module separated but remained trapped in low Earth orbit instead of proceeding to Venus.
- Lander Module Details - The spherical lander module measures about one metre in diameter and weighs roughly 500 kilograms.
- Durable Construction - Built with robust materials and a heat shield designed for Venus' harsh environment, some fragments may survive atmospheric re-entry.
- Uncontrolled Re-entry and Risk Assessment - The uncontrolled nature of its descent means the landing location is unpredictable, potentially anywhere between 51.7° north and south latitude. Experts, however, consider the risk of harm to be minimal.
|





