Highest Forex Sales by RBI in FY25
Prelims: Economic and Social Development| Current events of national and international importance.
Why in news?
The Reserve Bank of India sold a record $398.71 billion of foreign currency in 2024-25 on a gross basis as the Indian central bank stepped up its defence of the rupee amid a volatile global environment.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves – They are external assets held by a country’s central bank.
- These typically include:
- Foreign currency assets (FCA) like U.S. Treasury securities,
- Gold reserves,
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) from the IMF,
- Reserve Tranche Position in the IMF.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) manages India’s forex reserves on behalf of the Government of India.
- Management falls under RBI’s broader mandate of maintaining monetary and financial stability, particularly exchange rate stability.
Importance of Forex Reserves
- Currency stability – To stabilize the rupee against excessive volatility in forex markets.
- Crisis buffer – To provide a cushion against external shocks, such as oil price spikes or geopolitical instability.
- Investor confidence – High reserves boost global investor confidence in India’s macroeconomic health.
- Debt management – To help in managing and servicing foreign debt obligations.
- Import cover – To ensure sufficient import cover, typically desirable to be at least 6 months of imports.
- Current forex reserve – At the end of FY25 (March 2025), India’s total foreign exchange reserves stood at just under $625 billion.
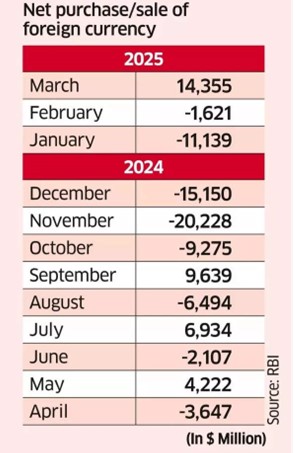
- For the FY25 with net forex sales of $34.51 billion.
- This was the second-highest net annual sale since FY09 ($34.92 billion) during the global financial crisis.
- It marks only the seventh time in 30 years that RBI sold more than it bought.
- This is mainly due to weakening rupee in second half of FY25 which dropped to all-time low of Rs 87.95/USD in February 2025.
In December 2024, RBI allowed banks to raise interest rates on FCNR deposits by 150 basis points to attract dollar deposits from NRIs.
FCNR (Foreign Currency Non-Resident) deposit is a type of term deposit account offered by Indian banks to NRIs.
Reference
The Indian Express| RBI sold nearly $400 billion of Forex in FY25
Governing Council of NITI Aayog
Prelims: Polity and Governance| Constitutional Bodies | Current events of national and international importance.
Why in news?
Recently 10th Governing Council Meeting of NITI Aayog is held on 24th May 2025 at New Delhi.
- Governing Council of NITI Aayog – The Governing Council is the apex body for cooperative federalism and policy coordination between Centre and states.
- Composition
- Prime Minister (Chairman)
- Chief Ministers of all States and Union Territories (UTs),
- Lieutenant Governors of UTs,
- Union Ministers,
- Vice Chairman and senior officials of NITI Aayog.
- Functions – To discuss national development priorities, multi-state issues and reviews policy implementation.
10th Governing Council Meet (May 2025)
- Venue – Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi
- Theme - "Viksit Rajya for Viksit Bharat @2047"
- Objectives:
- To prepare state wise long-term, inclusive vision documents that align with national priorities but tailored to local contexts.
- To ensure grassroots transformation for people-centric development.
- To review and implement the recommendations from the 4th National Conference of Chief Secretaries.
The 4th National Conference of Chief Secretaries (Dec 2024) focused on “Promoting Entrepreneurship, Employment and Skilling – Leveraging the Demographic Dividend.
Strategic Priorities for States
- Human development – Health, education, and nutrition.
- Sustainable growth – Green energy, climate resilience, and circular economy.
- Governance reforms – ICT-based monitoring, accountability, and real-time project evaluation.
- Economic drivers – Localized manufacturing, digital economy, MSMEs.
- Technology & data – Emphasis on data-driven governance and outcome-based planning.
|
Quick Facts
|
- NITI Aayog – National Institution for Transforming India
- NITI Aayog Policy think tank of the Government of India
- Formed On – 1st January 2015 by replacing erstwhile Planning Commission (1950–2014).
- Composition
- Chairperson – Prime Minister
- Vice chairperson - Shri Suman Bery
- CEO - B. V. R. Subrahmanyam
- Full time members – Appointed by PM
- Ex-Officio members – Minister of Finance, Defence, Home Affairs, Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Key Bodies within NITI Aayog
- Governing Council
- Regional Councils
- Team India Hub
- Knowledge and Innovation Hub
|
Reference
PIB| 10th Governing Council Meeting of NITI Aayog at New Delhi
National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR)
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance.
Why in News?
Recently Union Minister of Earth Sciences inaugurated "Sagar Bhavan" and "Polar Bhavan" at the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) in Goa.
- NCPOR – It serves as the nodal agency for India's polar and ocean research.
- Location – Vasco da Gama, Goa
- Nodal Ministry – Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Established – 1998
- Functions – It undertakes and coordinates scientific expeditions to:
- Antarctica
- Arctic
- Himalayas
- Southern Ocean
- It leads India’s Deep Ocean Mission under the Blue Economy initiative
- It maintains Indian research stations,
- Maitri and Bharati in Antarctica
- Himadri in the Arctic
- Himansh in the Himalayas
- It plays a crucial role in cryosphere studies, climate science, sea level rise monitoring, and India’s polar diplomacy
New Facilities Inaugurated
Polar Bhavan
- It is an integrated facility for polar and ocean research on,
- Cryosphere and ocean research
- Climate monitoring
- Weather pattern studies
- It hosts Science on Sphere (SOS) a 3D visualization platform.
- It also has India’s first Polar and Ocean Museum,
Sagar Bhavan
- It is a storage facility dedicated to archiving and processing polar samples.
- It supports cryosphere and oceanographic research.
- It enables high-precision analysis of polar and deep-sea samples.
- It enhances India’s capacity in,
- Climate change research
- Sea-level monitoring
- Marine and polar geochemistry
Significance
- It supports Blue Economy, climate resilience, and ocean geopolitics.
- It is expected to make NCPOR a global hub for integrated polar and ocean science.
- It helps India participate more actively in international climate initiatives.
Reference
PIB| Union Minister inaugurated Sagar Bhavan and Polar Bhavan
Fall in Net FDI
Prelims: Economic and Social Development| Current events of national and international importance.
Why in News?
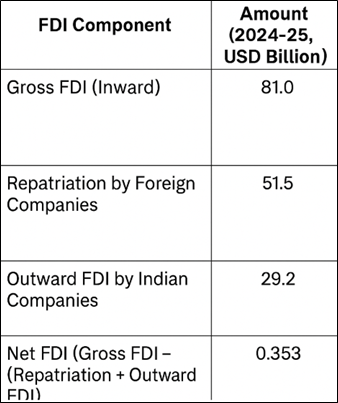
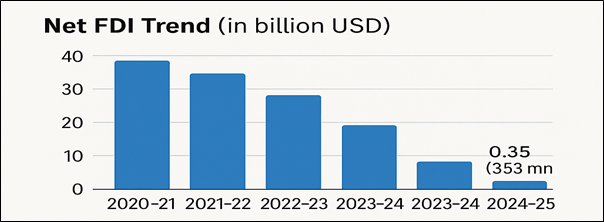
Recent data released in RBI reveals that Net FDI into India fell by over 96% to $353 million in 2024–25 from $10.1 billion in 2023–24.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) – It refers to an ownership stake in a foreign company or project made by an investor, company, or government from another country.
- FDI investors typically take controlling positions in domestic firms or joint ventures and are actively involved in their management.
- Top sector-wise Gross FDI Inflows for 2024–25
- Manufacturing
- Financial services
- Electricity and energy
- Communication services
- Top countries contributing to India’s Gross FDI
- Singapore
- Mauritius
- UAE
- Netherlands
- USA
- OFDI (Outward Foreign Direct Investment) - It refers to investments made by Indian companies in foreign countries — through acquisitions, establishing subsidiaries, joint ventures, or branches.
- In 2024–25 over $29.2 billion were invested abroad by Indian companies.
- Indian OFDI mainly into Singapore, USA, UAE, Mauritius, Netherlands.
- Net FDI – It is the difference between Gross FDI and Outward direct investments by Indian firms and repatriation by overseas entities.
- Net FDI = Gross FDI inflows − (OFDI by Indian firms +Repatriation by foreign firms)
Repatriation refers to the profits, dividends, or capital from foreign companies gained from India that were sent back to their home countries.
- Net FDI reflects the net capital retained within India after outflows.
Reason for fall in net FDI Fall
- Highest Repatriation - $51.5 billion repatriated in 2024–25 which is the highest in last decade.
- Rise in OFDI - Indian firms invested $29.2 billion abroad which is a 75% increase from previous year.
- Pandemic Trend – Net FDI has been consistently declining declined post-pandemic.
Reference
The Hindu| India’s Net FD crashed by more than 96%
Tyre Particle Pollution from Electric Vehicles
Prelims – Environment and Ecology, Science and Technology
Mains – General Studies-III (Environment and Ecology – Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation; Science and Technology – Developments and their Applications and Effects in Everyday Life)
Why in news?
A recent study published by researchers from TIFR, IIT Bombay, and Columbia University reveals that electric vehicles (EVs) may worsen air pollution through increased tyre wear and plastic particle emissions.
Tyre Particle Pollution
- Tyre particle pollution refers to the release of tiny bits of rubber and plastic from vehicle tyres as they wear down during driving.
- These particles become a part of air pollution.
- Tyres release particles of broadly two sizes:
- Smaller Particles (1-10 micrometres): These are very tiny.
- Larger Particles (more than 100 micrometres): These are bigger.
- The study found that EVs are heavier, experience more friction and wear on their tyres compared to regular petrol or diesel cars.
- EVs release substantially larger amounts of particle sizes into the atmosphere.
- These plastic particles can have harmful effects on both human health and the environment.
Impacts of tyre Particle Pollution from Electric Vehicles
- Increased Tyre Wear – EVs, being heavier due to their batteries and reinforced frames, put more stress on their tyres, leading to accelerated wear.
- Microplastic Release – The increased tyre wear results in the release of tiny plastic and rubber particles (microplastics) into the air.
- Health and Environmental Risks – These airborne microplastics can be inhaled, posing respiratory and other health problems. They also contribute to microplastic contamination in ecosystems.
- Increasing Airborne Pollutants – The smaller particles, being lighter, remain suspended in the air for longer durations, thereby increasing the concentration of airborne pollutants.
- Primary Fragmentation – Heavy EVs experience more sudden tyre wear from rapid acceleration, braking, and road irregularities.
- This process, known as primary fragmentation, primarily produces the smaller, more problematic particles that remain airborne.
Way forward
- Technological Solutions – Development of sturdier tyres specifically designed for heavier EVs.
- Research into particle capture systems that prevent tyre fragments from entering atmosphere.
- Innovation in tyre materials to reduce particle generation.
- Policy Interventions – Expansion of air quality regulations to include smaller tyre particles.
- Updated emission standards accounting for non-exhaust emissions.
- Stricter manufacturing standards for tyre durability and composition.
- Infrastructure Improvements – Better road quality to reduce some types of tyre wear.
- Limited effectiveness on smaller particles that cause air pollution.
Reference
The Indian Express


