7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
|
State of Economy – Data Points |
|
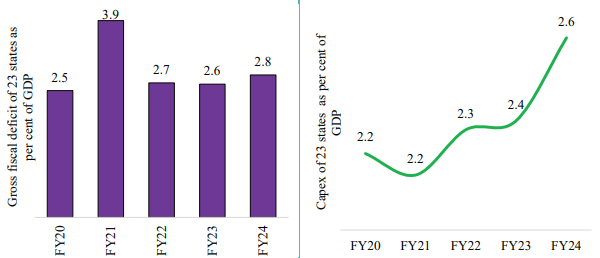
According to Economic Survey 2023-24, India is projected as a high-growth and low-inflation economy.
Macroeconomic vulnerability index is an index constructed by combining India’s fiscal deficit, Current Account Deficit and inflation.
|
Source |
Year/ Period |
Forecast |
|
IMF |
2024-25 |
7.0 |
|
ADB |
FY25 |
7.0 |
|
Economic Survey |
Current FY |
6.5-7.0 |
|
Monetary Policy Committee |
Current FY |
7.2 |
|
World Bank |
FY25 |
6.6 |
|
SBI |
FY25 |
8.0 |