7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims – General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change.
Mains – General Studies-III (Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment)
Why in news?
A recent study published in the journal Earth's Future has explored an innovative approach to SAI, specifically by investigating low-altitude aerosol delivery, aiming to reduce costs and potentially bring it closer to implementation despite opposition.
Advantages of Low-Altitude Injection
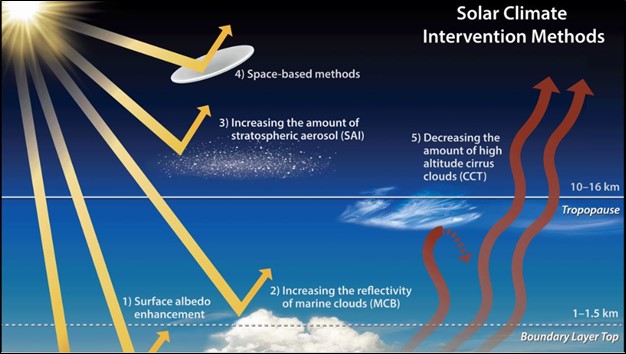
Risks and Side Effects
Reference