Mains Syllabus: GS II - Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Recently many states are focussing on early childhood care and education.
Early child development encompasses physical, socio-emotional, cognitive and motor development between 0-8 years of age.
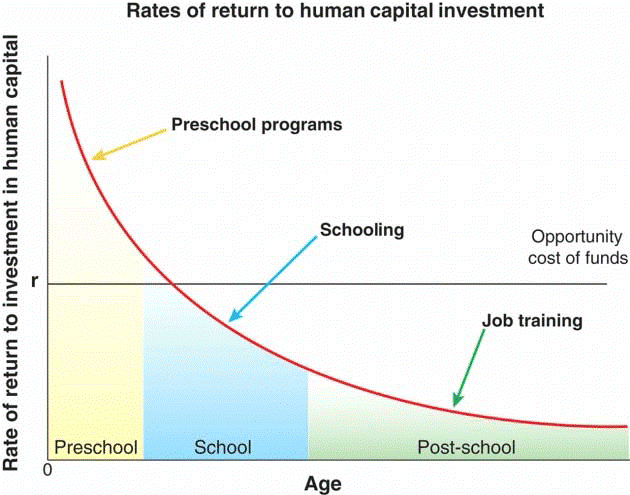
The Heckman curve was a powerful economic model that provided a simple yet profound insight — of the relationship between age and the rate of return on investments in human capital.
2% of three-year-olds, 5.1% of four-year-olds, and nearly one-fourth of five-year-olds are enrolled directly in Class one.
|
Government Initiatives on ECCE |
|
The Hindu | Rewriting the script of early childhood education