Mains Syllabus: GS I - Population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues; GS II – International Issues.
Why in the News?
Recently, Global Report on Internal Displacement 2025 was released by the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) and the Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC).
What is the global displacement crisis?
Internally displaced people are those who have been forced to flee their homes as a result of conflict, violence, or disasters and who have not crossed an internationally recognized State border.
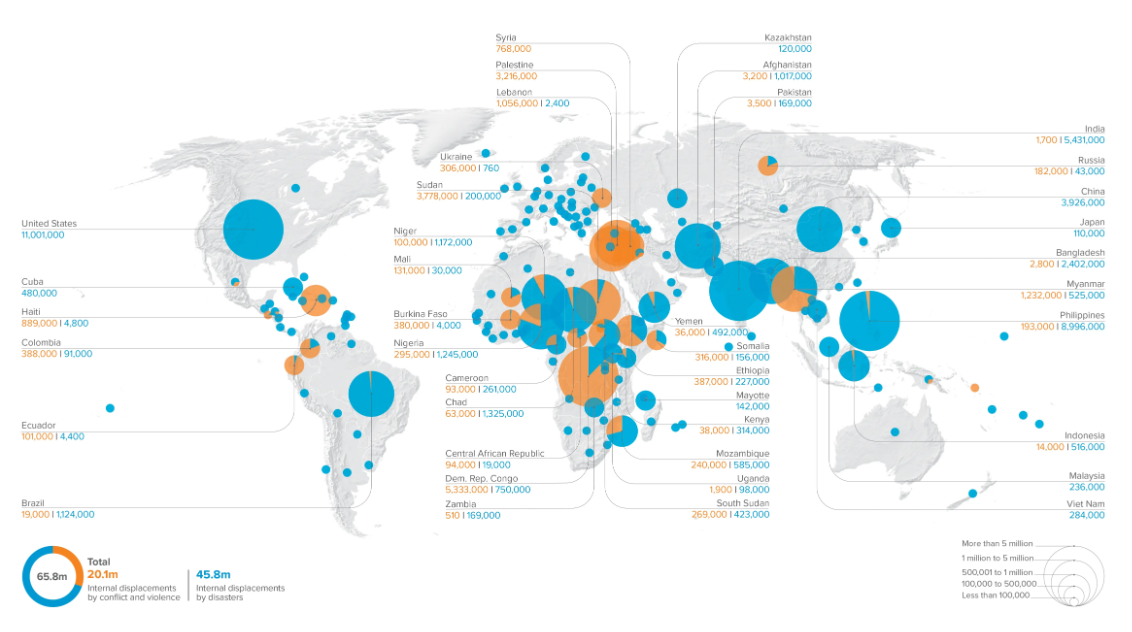
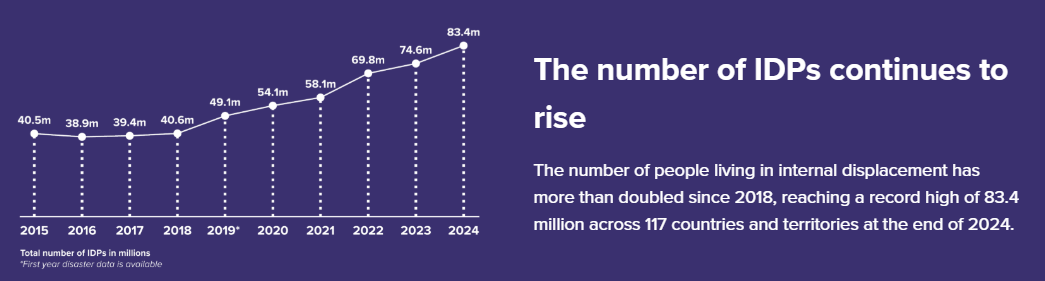
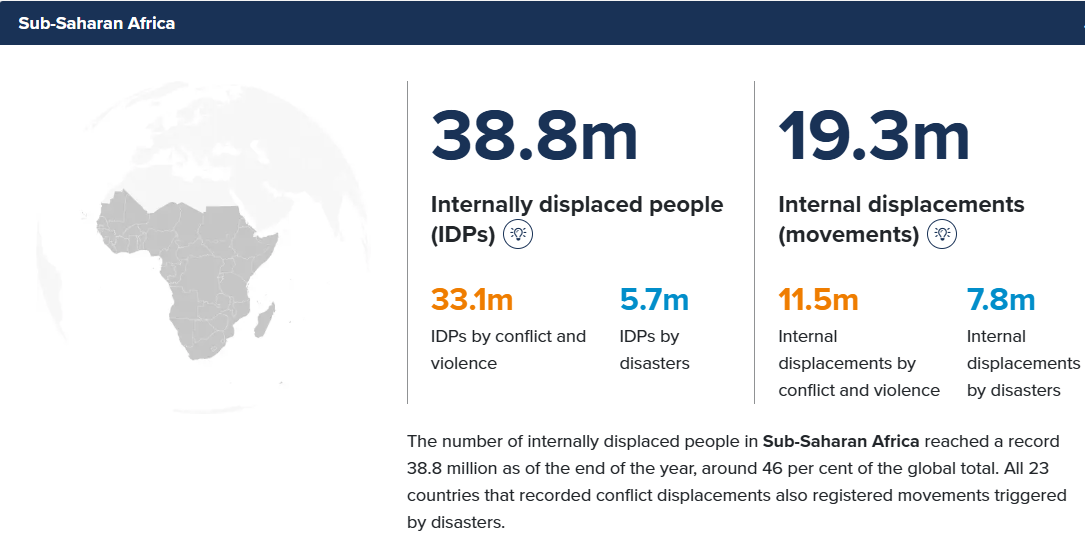
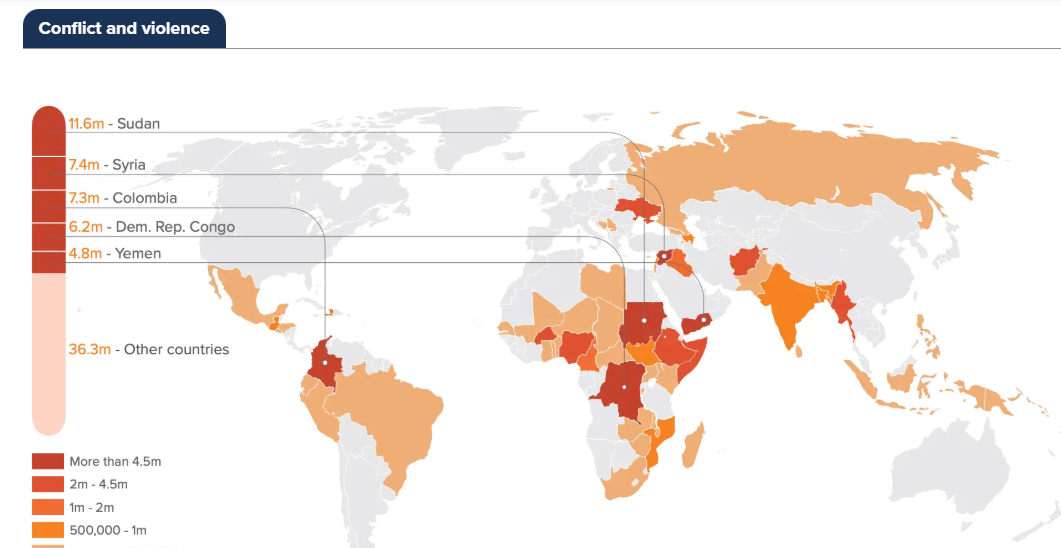
An internal displacement refers to each new forced movement of a person within the borders of the country of their habitual residence recorded during the year. This figure illustrates dynamics of displacement in a specific crisis.

What are the causes of internal displacement?
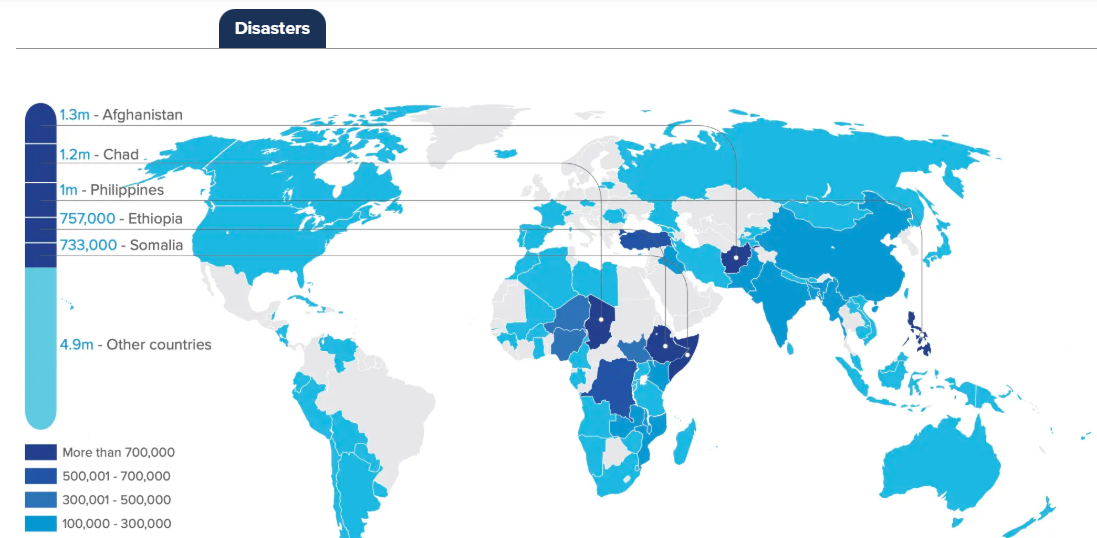
Hurricanes Helene and Milton were particularly destructive in the United States, leading to 11 million internal displacements—nearly a quarter of the global total for disaster-related movement.
What are the challenges in addressing internal displacement?
The new US government has significantly reduced global support ( U.S. foreign aid funding) for displaced populations.
What needs to be done?
Reference