7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in News?
September 20, 2024, marks the 100th anniversary of the announcement regarding the discovery of the Harappan Civilisation.

Harappa is an IVC site in located in present-day Pakistan.
|
Daya Ram Sahni ( Year 1921) |
Rakhal Das Banerji (1922) |
|
|
|
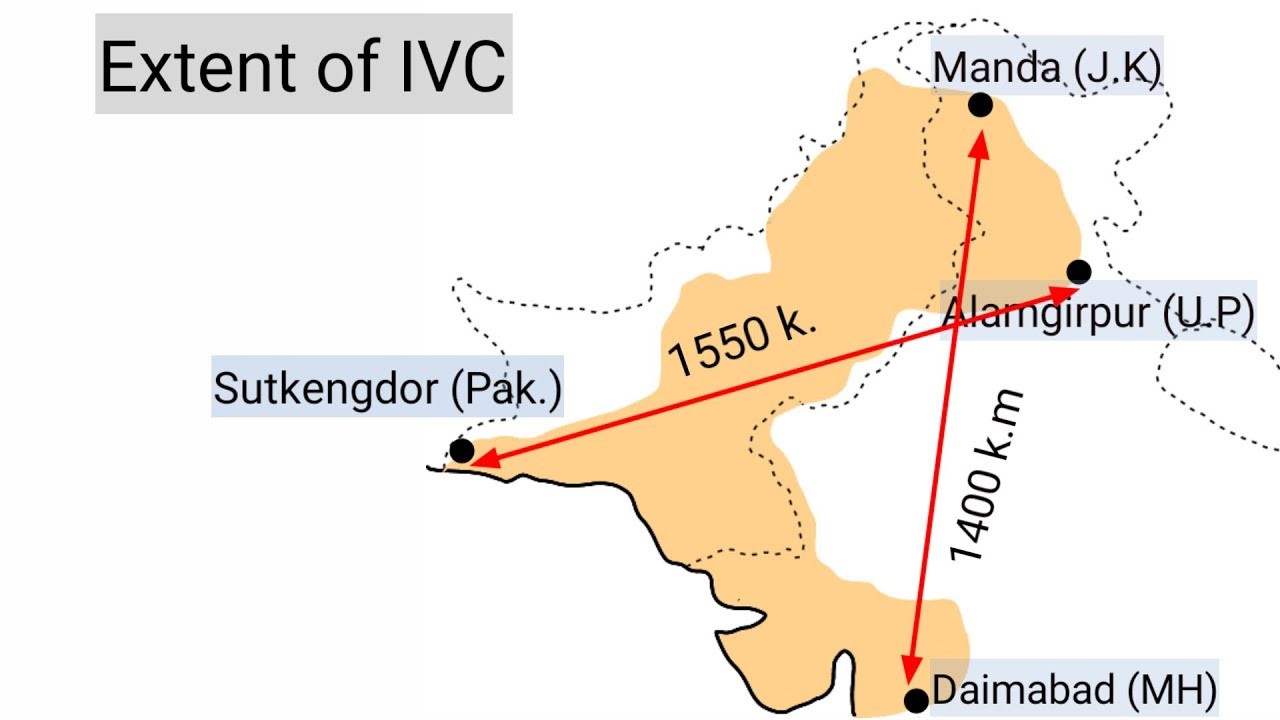
Boundaries |
Extension |
|
Western boundary |
|
|
Eastern boundary |
|
|
Northern Boundary |
|
|
South Boundary |
|
Remarkable similarities was observed between the artifacts from Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, despite their 640 km separation.