7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains Syllabus: GS III – Infrastructure , Road
Recently Union Ministry of Road Transport and Highway announced the setting up of driving training centres and vehicle fitness centres in every district.

|
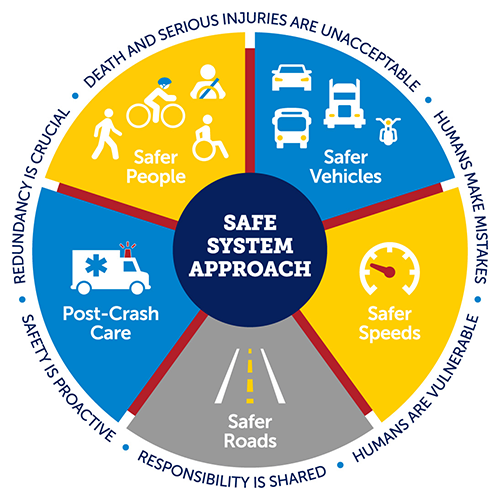
Key principles of the Safe System approach |
|
|
Four Key Elements of a Safe System
|
|
Government Measures on Road Safety |
|