Report on Performances of State Assemblies
Prelims: Indian Polity and Governance
Why in News?
According to a new report by PRS, a non-profit organisation, Indian state legislative assemblies continue to meet for less than 30 days on average.
- Lesser assembly meetings – Aftermath of 2020 pandemic, the number of meetings has remained close to 20 days a year including the year 2024.
- Odisha met for the highest number of days (42), followed by Kerala (38).
- While, some states have set a target for the minimum number of annual sitting days either through legislation or through Rules of Procedure, none of them have met these targets in any year.
- Duration of sitting - The average duration of each sitting was 5 hours.
- Timing for budget discussion - In 2024, states discussed budgets for 7 days on average.
- Vacancy in office of Deputy Speaker – It is vacant in 8 state Assemblies.
- Jharkhand has not elected one for over 20 years.
- Incidentally, the Lok Sabha too has not had a Deputy Speaker since June 2019.
Article 178 of the Indian Constitution requires Assemblies to choose two members as the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker as soon as possible.
- Bill passage – In 2024, states on average passed 17 of them.
- Of the over 500 bills passed, Karnataka passed the highest (49), followed by Tamil Nadu (45). Delhi passed just 1 bill, followed by Rajasthan with 2.
- About half of the bills passed relate to education, finance, and local governance.
|
Interesting Laws Enacted During 2024
|
- Uniform Civil Code by Uttarakhand.
- West Bengal Aparajita Act for stricter penalty for rape.
- Haryana’s law to regulate private coaching institutes.
- Madhya Pradesh’s laws to regulate private school fees.
- Tamil Nadu earmarked welfare spending for scheduled castes and scheduled tribes in proportion to population.
- Maharashtra provided 10% reservation for Marathas for education and government jobs.
- Gujarat passed laws banning black magic.
- Assam banned magical healing practices to treat diseases.
- Maharashtra increased the penalty for felling a tree without permission.
|
- Lesser discussion of bills – 51 % or over 250 of all bills passed, were passed within a day of introduction.
- 8 states passed all bills within a day of introduction.
- Jharkhand, Mizoram, Puducherry and Punjab had also passed all bills within a day in 2023 and 2022.
Reference
Down To Earth| Report on Performance of State Assemblies
Bar on Ex-Post Facto Environmental Clearances
Prelims: General issues on Environmental ecology | Public Policy | Current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
Recently, Supreme Court barred the Indian government from granting retrospective environmental clearances (ECs) in the future.
- Case – It arose from petitions challenging the legality of 2 Office Memorandums (OMs) that enabled environmental clearance to projects that had begun operations without prior approval under the Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification, 2006.
- The petitioners argued that the memorandums violated the fundamental requirement of prior clearance and weakened environmental protections.
2006 Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 had imposed certain restrictions and prohibitions on new projects or activities, on the expansion or modernization of existing projects and activities based on their potential environmental impacts.
Under EIA notification 2006, it is mandatory of getting for prior Environmental Clearance for certain new projects, expansion or modernization of existing projects based on their potential on environmental impact.
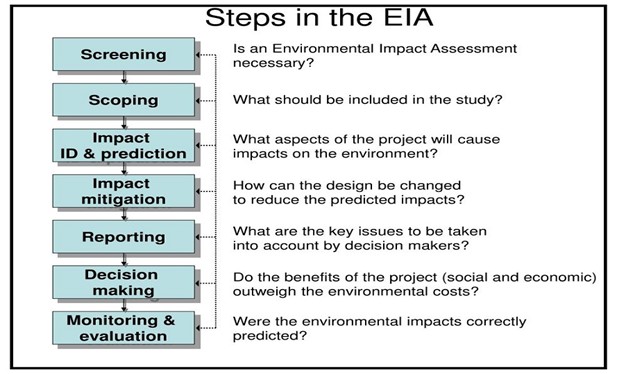
- Verdict – Supreme Court strikes down previous Office Memorandums (OMs) and notifications that permitted such approvals for mining and industrial projects.
- Supreme Court ruled that projects initiated without mandatory prior environmental clearance cannot later be legalised.
- No leniency should be shown to corporations, real estate developers, public sector undertakings and mining industries that deliberately ignored environmental laws.
- The bench explicitly prohibited the government from reintroducing any policy similar to the 2017 notification, which had allowed retrospective environmental clearances.
- However, it clarified that clearances already granted under these provisions would remain unaffected.
- Significance – The ruling strengthens the enforcement of prior environmental clearances, marking a significant step towards stricter ecological accountability.
Reference
Down to Earth| Bar on Ex-Post Facto Environmental Clearances
Surplus Transfer to Government from RBI
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance| Indian Economy
Why in news?
For the financial year 2024-25, the RBI is expected to transfer a record Rs 2.5-3 lakh crore, that exceeds the previous record of Rs 2.11 lakh crore transferred in 2023-24.
- RBI’s Surplus - Surplus is the excess of RBI’s income over expenditure, after provisioning for reserves and contingencies.
- It is not a dividend, as RBI is not a company but a statutory body owned by the government.
- Legal Basis - The transfer occurs under Section 47 of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, which mandates that after making necessary provisions, "the balance of the profits shall be paid to the Central Government.
- Evolution of Transfer Policy – Initially, the RBI transferred its surplus profits to the government without a structured framework.
- In 2013, the Malegam Committee recommended increasing surplus transfers to support fiscal deficit reduction efforts.
- This led to a significant rise in transfers, with the RBI transferring 99.99% of its surplus in 2013-14, up from 53.4% in 2012-13.
- Earlier, part of the surplus was set aside for:
- Contingency Fund (CF) for unforeseen events.
- Asset Development Fund (ADF) for capital investments and subsidiaries.
- Economic Capital Framework (ECF) - In 2018, the Bimal Jalan Committee was formed to review the RBI's economic capital Framework.
The ECF provides a structured approach to determine the appropriate level of risk provisioning (CRB) and guides the surplus transfer to the government.
- The committee recommended maintaining a Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB) between 5.5% and 6.5% of the RBI's balance sheet.
- Any excess over this range could be transferred to the government.
- The ECF was adopted in August 2019, that provoide a structured approach to surplus distribution.
The RBI is exempt from paying income tax or any other tax on its earnings under Section 48 of the RBI Act.
- Global Practice - In countries like the US and UK, the surplus transfer is decided in consultation with the government.
- In Japan, the government unilaterally decides the transfer.
- Globally t*he surplus transfer typically averages around 0.5% of GDP.
Reference
The Indian Express| Surplus Transfer to Government from RBI
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
Recently International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), has said that there has been no radiation leak from any nuclear facility in Pakistan after the escalated military engagement with India.
- IAEA – It is a global nuclear watchdog organization.
- Established in – 1957
- Origin – It is proposed by U.S. President Dwight Eisenhower in his “Atoms for Peace” speech (1953).
- Headquarters – Vienna, Austria.
- Members – 178 countries
- Motto – Atoms for Peace and Development
- Function – It monitors nuclear facilities and activities worldwide and promote peaceful nuclear use & prevent military use.
- Incident and Emergency Centre (IEC) – It is established in 2009 by IAEA for coordinating response to radiation incidents.
- IAEA Safeguards – The legal agreements formed to verify that nuclear material is not diverted for military use and there are three types of safeguards agreements,
- Comprehensive Safeguards Agreement (CSA) – With non-nuclear-weapon NPT states. (India is not a member)
Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) is a treaty that signatories agreed not to develop or acquire nuclear weapon except U.S, Russia, U.K, France, and China.
-
- Voluntary Offer Agreement (VOA) – With nuclear-weapon NPT states (U.S, Russia, U.K, France, and China).
- Item-specific Agreement – With non-NPT states e.g., India, Pakistan, Israel (India is a member).
- They are nuclear weapon states but haven’t signed NPT.
- Additional Protocol (AP) – It strengthens IAEA's inspection rights on its member countries.
- India ratified AP in 2014 for its civilian nuclear facilities.
Quick Facts
|
Other Nuclear Export Control Regimes
|
Objective
|
India’s Membership Status
|
|
MTCR (1987)
|
Restrict missile tech with range >300 km & 500 kg payload
|
Member since 2016
|
|
Australia Group (1985)
|
Prevent export of materials used in chemical/biological weapons
|
Member since 2018
|
|
Wassenaar Arrangement (1996)
|
Control exports of conventional arms & dual-use goods
|
Member since 2017
|
|
NSG (1974)
|
Regulate nuclear materials/technology export
|
Not a member
|
Reference
The Indian Express| No radiation leak in any nuclear facility in Pakistan
Samudrayaan Mission
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
Recently the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) announced that, Samudrayaan, mission which is slated for launch by the end of 2026.
- Samudrayaan – It is the India's first manned ocean mission using self-propelled manned submersible Matsya-6000 to a depth of 6,000 meters.
- The mission is part of India’s Deep Ocean Mission, a flagship initiative to explore and harness deep-sea resources.
- Implementation - It is implemented by the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai, under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- Key Objectives – To explore India’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and continental shelf for:
- Polymetallic nodules
- Gas hydrates
- Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts
- Deep-sea biodiversity
- To strengthen India’s presence in the blue economy and oceanic research.
- To develop a manned submersible capable of diving to a depth of 6,000 meters.
Matsya-6000
- It is the indigenously developed submersible that is a specialized underwater vehicle designed to explore and conduct research in the deepest parts of the ocean.
- It is named after the fish incarnation of Lord Vishnu—Matsya.
- It is designed to carry 3 humans to a depth of 6,000 meters (6 km).
- It is made of Titanium alloy to withstand the extreme pressures (up to 720 bar) encountered at 6,000 m depth.
- Developed by - ISRO
- Operational endurance:
- 12 hours of continuous mission capability
- 96 hours emergency survival capacity
- Buoyancy and Ballast systems for submergence and resurfacing.
- Key features:
- Manoeuvring propellers for navigation.
- Power and control systems with onboard battery storage.
- Subsea intervention manipulators for sample collection.
- Communication systems by Ethernet and acoustic communication.
- Navigation and positioning devices.
- Safety systems for emergency support.
- Strategic Importance – It enhances India’s technological self-reliance in marine exploration.
- It supports India's commitment to sustainable ocean resource use.
- It strengthens India’s capabilities in,
- Resource extraction
- Scientific research
- Environmental conservation
Reference
India Today| Samudrayaan Mission
