Mains Syllabus: GS II - Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate; GS III- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc. & environmental pollution and degradation.
Why in the News?
Recently, International Maritime Organization (IMO) has approved net-zero regulations for global shipping
What are the importances of controlling global shipping emission?
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 13, "Climate Action," aims to take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
What are the measures taken by IMO to reduce shipping emission?
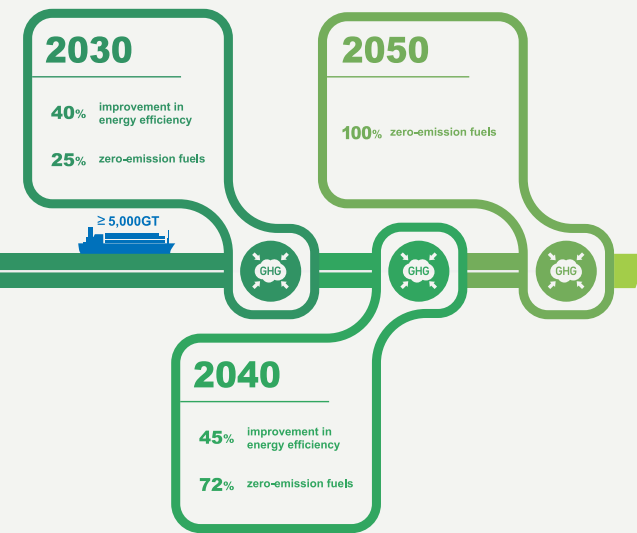
What is the IMO Net Zero framework?
What are the features of IMO framework?
What are the potential impacts for India?
India currently operates nearly 236 ships over 5,000 gross tonnage, with only 135 involved in international voyages.
Conclusion
Reference