Some members of the shompen tribes voted in the 2024 election amidst fears that their forests on the Great Nicobar island will be destroyed by a proposed project.
References
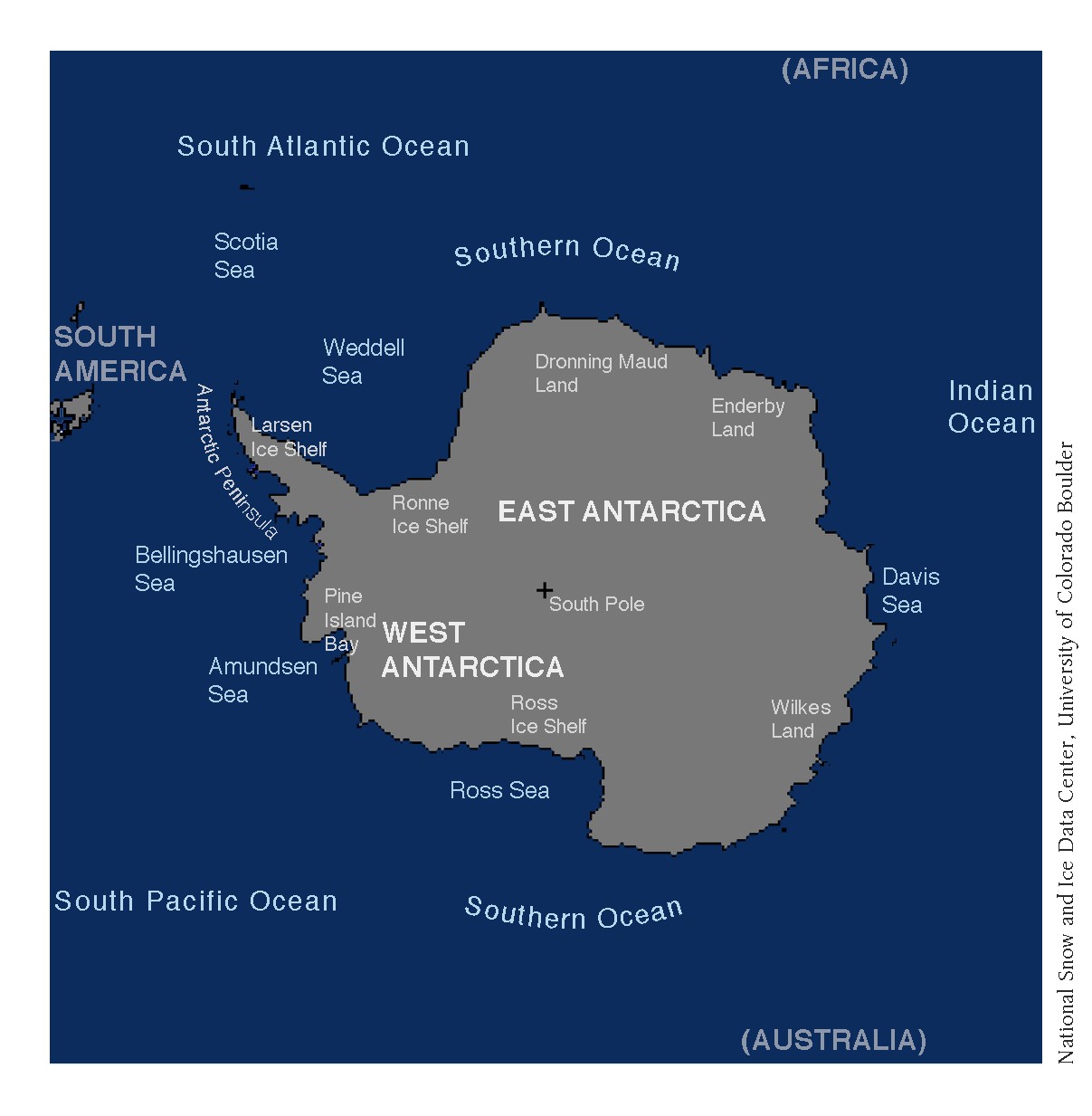
Antarctic Peninsula showed 10-fold greening since 1986 according to the archive study of National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Landsat satellite mission between 1986 and 2021.
Recent Findings
Antarctic Peninsula
Reference
Down to Earth | Antarctic Peninsula is dramatically greening
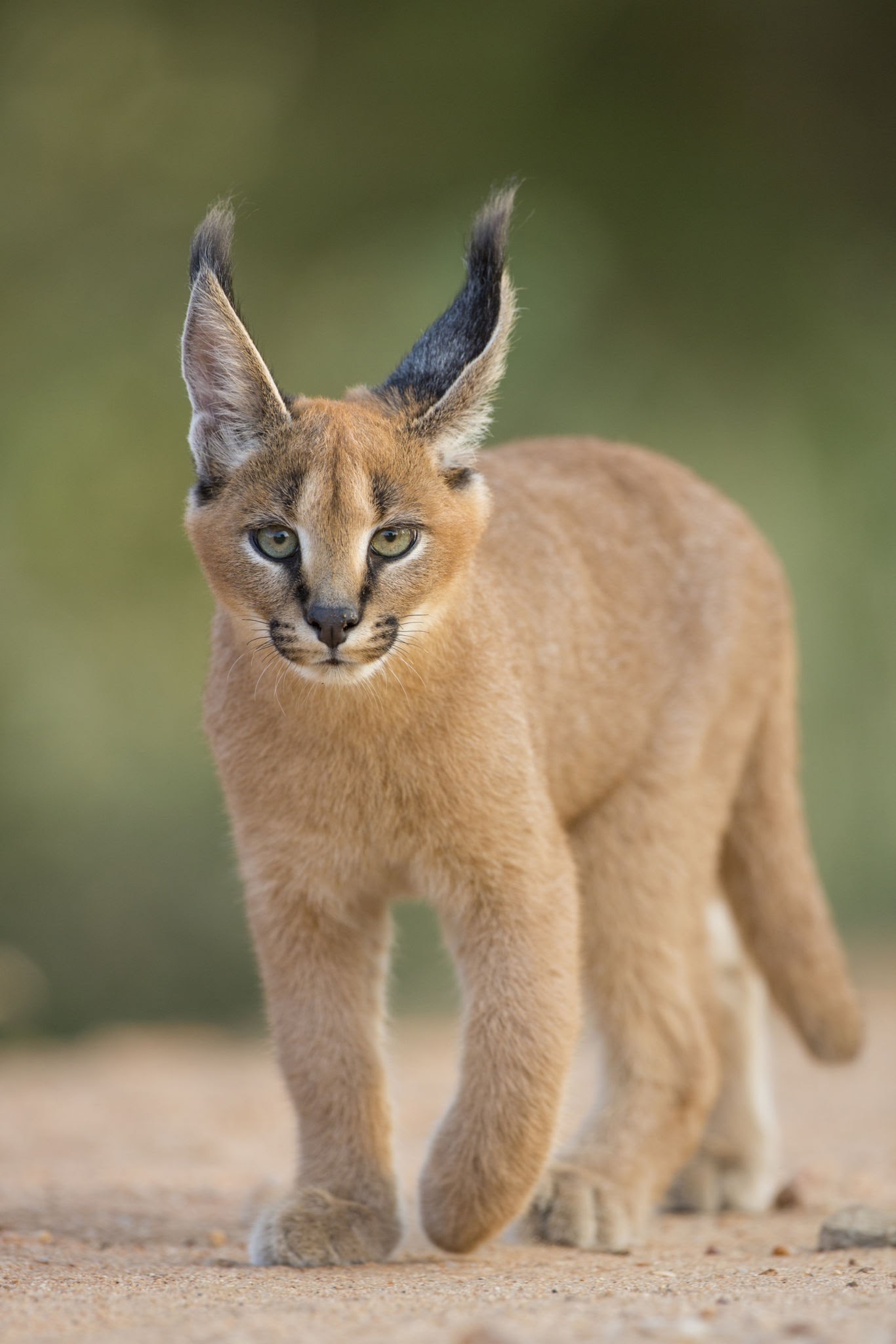
Gujarat government allocates Rs 10 crore for Caracal conservation and breeding recently.

Reference
Ani News | Gujarat allocates Rs 10 crore for Caracal conservation
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) recently announced the completion of the development trials of the ingeniously developed 4th Generation miniaturised VSHORAD.
References
Govt looking to align some indicators of India’s BRAP 2024 index with the World Bank’s B-READY index recently.
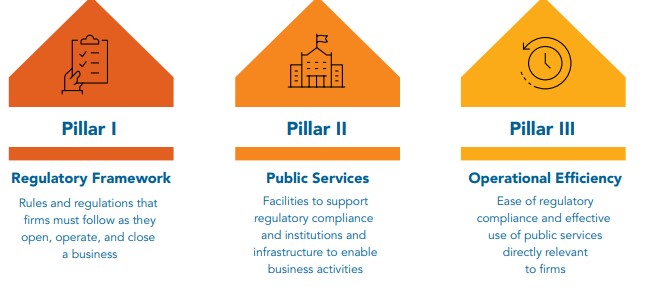

The government had recently announced the BRAP 2022 rankings, which were topped by Andhra Pradesh and Kerala.
References