Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary
Prelims: Environment | Science and technology | Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
Recently Wildlife Institute of India experts collared three fishing cats in Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary in Andhra Pradesh to study the behaviour of the species.
- Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary – It is located in East Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh, India.
- Established – 1978 under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- It is situated at the Godavari River delta, rich in backwaters and estuarine systems.
- Mangrove forest – It is a significant mangrove forest ecosystem and is rich in flora and fauna adapted to brackish water ecosystems.
- Estuarine ecosystem – It supports a mix of freshwater and marine life due to tidal influences.
Key Fauna & Flora
- Endangered species – Fishing cat, Otters, Smooth-coated Otter and Small-clawed Otter.
- Birdlife – Over 120 species, including Pond Herons, Egrets, Flamingos, and Darters.
- Reptiles & Amphibians – It includes crocodiles, snakes, and frogs native to estuarine habitats.
- Aquatic & Avian Richness – It is a vital nursery for marine fish and crustaceans.
- Migratory birds – It is important stopover site for winter migratory species.
- Fish diversity – It includes estuarine and marine species adapted to salinity variations.
- Vegetation – Dominant mangrove species such as Avicennia, Rhizophora, Sonneratia.
- It also features dense mangrove thickets, tidal creeks, and mudflats.
|
Fishing Cat Collaring Project (2025)
|
- It is initiated by Wildlife Institute of India (Dehradun)to track endangered fishing cats.
- Fishing cats – It is found in Coringa and Krishna sanctuaries, primarily inhabiting mangrove ecosystems.
- Scientific name – Prionailurus viverrinus
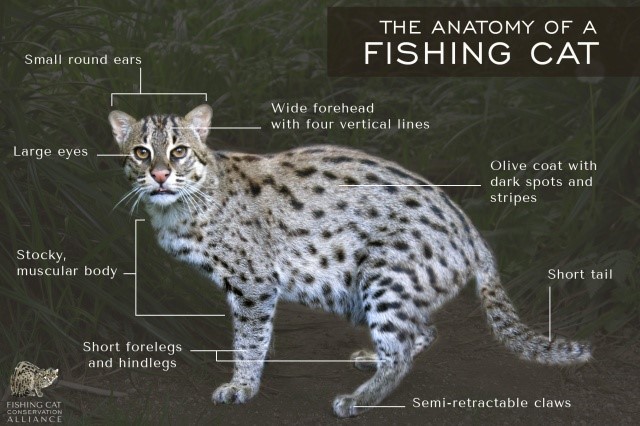
- It is aggressive, nocturnal, active near water bodies while hunting.
- It dwells deep within dense mangrove cover.
- It is one of the first of its kind in India to monitor home range and behaviour.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN – Endangered.
- CITES – Appendix II.
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 – Schedule I.
- Threats – Encroachment, pollution, and shrimp farming coastal erosion and climate change impacts.
- Three fishing cats collared in May 2025 using lightweight GPS-enabled collars.
- It will record environmental or human-induced threats that impact survival.
- Seven more fishing cats will be collared to study the home range, behaviour, feeding, breeding, and prey pattern of the endangered species
|
Reference
The Hindu| WII collar three fishing cats in Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary
ECI upgrades mechanism for Index Cards on Electoral Data
Prelims: Science and technology | Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI) announced that it had upgraded the mechanism for generating Index Cards, making it more technology-driven.
- Index Cards – They are non-statutory formats used after elections to compile detailed statistical data at the constituency level.
- These cards serve as a foundation for analytical reports about elections and are useful for researchers, policy analysts, and academics.
- Using the data from these cards, the ECI generates statistical reports for Lok Sabha (Parliamentary) and State Assembly elections, which includes,
Elector and Polling Information
- Details about electors broken down by state, parliamentary and assembly constituencies.
- Number and location of polling stations.
- Voter turnout percentages.
- Gender-wise participation, highlighting trends in women’s voting.
Candidate and Party Performance
- Total votes polled and counted
- Vote share of each candidate and political party
- Performance analysis of-
- National parties
- State parties
- Registered Unrecognised Political Parties (RUPPs)
- Details on winning candidates, including margins and voter base
- Summary and constituency-wise results for analytical purposes
|
Traditional method of Index card generation
|
Upgraded method of Index card generation
|
- The older system relied on manual data entry.
- Data was first written on physical cards at each constituency.
- These were later entered into an online system.
- This process had several drawbacks-
- It was slow and required multiple steps.
- It often led to delays in the release of reports.
- There was a risk of errors during transcription.
|
- The ECI has now introduced a technology-based system to automate the Index Card process.
- Automation and data integration allow-
- Faster and more accurate reporting.
- Reduced manual intervention, minimizing errors.
- Quicker data dissemination to the public and researchers.
|
- Significance – ECI aims to make electoral data more transparent, accessible, and research-friendly.
- A real-time voter turnout dashboard and it is planned to roll out before the Bihar elections.
Reference
The Hindu| ECI upgrades mechanism for Index Cards on electoral data
Nano Plastics Can Make E. Coli Infections Worse
Prelims: Science and technology | Current events of national and international importance
Why in news?
Recently, a new study from researchers at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, has revealed that nano plastics aren’t just risky on their own
- Nano plastics – It is extremely small plastic particles typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometres in size.
- They are found everywhere- in mountaintops, deep-sea trenches, human bloodstream, tissues, and even newborns.
- It is known for toxic effects including damage to cells and genetic material.
- E. coli (Escherichia coli) – It is a group of bacteria that usually lives in your gut without hurting you.
- It is a gram-negative bacillus foodborne pathogen and is a causative agent of many diarrheal illnesses.
Gram-negative bacteria appear pink or red under a microscope during lab test because they have a thin cell wall and an outer membrane that prevents the primary stain (crystal violet) from being retained.
Findings of the study
- Impact of Nano plastics – Researchers found that nano plastics make E. coli (Gram-negative) can be more virulent.
- The charged nano plastics increases stress on E. coli, prompting it to produce more Shiga-like toxins — proteins responsible for causing disease.
- The charged nano plastics initially inhibited bacterial growth.
- But over time, some E. coli cells adapted, resumed growth, and showed genetic changes.
- Both positively and negatively charged nano plastics led to these effects, although positive charges had more severe outcomes.
- Significance – Nano plastics can exacerbate bacterial infections by enhancing virulence
- It also poses indirect threat by making microbes more dangerous and resistant to antibiotics.
Reference
The Hindu| Nanoplastics can make E. coli infections worse
Rising black carbon heating the Himalayan snow
Prelims : Current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
A recent study by the think-tank Climate Trends stated that Levels of black carbon-ultra-fine particles of carbon in the Himalayas have been rising.
- The study analysed satellite-based measurements of black carbon and changes in snow temperature between 2000 and 2023.
- Findings - Eastern Himalaya records warmest snow surfaces, followed by the central and western Himalayas.
- This is contributing to warmer snow, increasing the risk of unseasonal flooding by glacier-fed rivers.
- Sources – Biomass combustion, fossil fuel use, Fertiliser, Vehicle exhaust, and open burning, particularly in the Indo-Gangetic plain, which acts as a hotspot for emissions.
- Effects - Light-absorbing particles like black carbon reduces the snow’s ability to reflect sunlight, accelerating surface heating.
- Aerosols particulate matter emissions from a variety of sources, from fertiliser to vehicle exhaust, clog the atmosphere, deflecting sunlight away from the carbon and mask the heating effect of greenhouse gases.
- Continued temperature rise in snow-covered areas can shorten snow season duration and advance melting onset, impacting hydrological systems and water security for millions downstream.
- Thus, temperature increases, in conjunction with black carbon presence, are significantly altering the snow thermal regime in the Himalayas.
- Black carbon is different in that it absorbs sunlight and, if it settles on the surface, can thus heat the ground.
Black carbon is considered as a catalyst to global warming, even though it is relatively short-lived in the atmosphere, unlike carbon dioxide, the most pervasive greenhouse gas.
Reference
The Hindu | Black carbon’ heating Himalayan snow
Ayush Nivesh Saarthi portal
Prelims : Current events of national and international importance | Governance
Why in News?
The Government of India has launched the Ayush Nivesh Saarthi portal during the Ayush Stakeholder/Industry Interaction meet held at Vanijya Bhawan recently.
- It is an investor-centric digitalised platform in the Ayush sector.
- Created by - Ministry of Ayush in partnership with Invest India, is focused on attracting investors.
- Aim - To transform India's traditional wellness systems into a significant economic force.
- It is designed to support both domestic and global investors.
- It consolidates policy frameworks, incentive structures, and investment-ready projects into a single user-friendly interface.
- It provides real-time data, clear policy guidance, and access to a dynamic and growing market, reinforcing India's aspiration to be a premier destination for investments in traditional medicine.
The sector is experiencing a 17% annual growth rate from 2014 to 2020 and has seen a rising global interest in natural and preventive healthcare.
- This portal is poised to be a crucial driver for foreign direct investment, empowering entrepreneurs and highlighting India's leadership in the field of traditional wellness.
Reference
The Print | Ayush Nivesh Saarthi Portal
Waste Picker Enumeration App
Prelims : Current events of national and international importance | Governance
Why in News?
Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) launches a Nationwide Digital Application for Profiling Waste Pickers under the NAMASTE Scheme.
- It is a digital platform designed to catalog, recognize, and assist waste pickers through social security measures and livelihood support initiatives under the NAMASTE Scheme.
- Involved Ministries - Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJE), Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs (MoHUA) & Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DoDWS).
- Implemented by - National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC).
- Objectives - Acknowledge waste pickers as vital contributors to India's solid waste management framework.
- Ensure they receive proper identification and protection.
- Facilitate their integration into formal urban systems for improved recognition and support.
- It offers health insurance through the Ayushman Bharat initiative.
|
NAMASTE Scheme
|
- NAMASTE is a central sector scheme for improving the living standards of sanitation workers in urban areas.
- It is a joint initiative of Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE), Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) and Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
- The scheme focuses on preventing hazardous cleaning practices, promoting safe cleaning through trained and certified workers, and formalizing/rehabilitating those involved in hazardous sewer and septic tank cleaning.
- The intended outcome is to eliminate direct contact with human faecal matter, achieve zero fatalities, and empower sanitation workers through various means.
|
Reference
PIB | NAMASTE Scheme|