The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has recently released the images of Aditya L1 mission.
Aditya L1 shall be the first space based Indian mission to study the Sun.
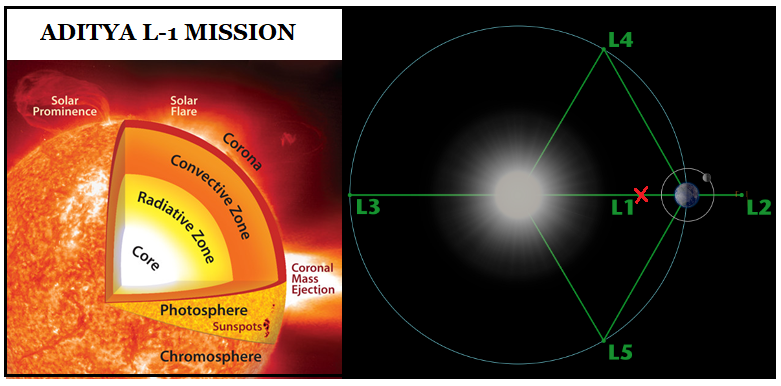
|
Lagrange point |
Home to |
|
L1 |
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite SOHO |
|
L2 |
Was the home to the WMAP spacecraft Current home of Planck Future home of the James Webb Space Telescope |
The science of studying the Sun and its influence throughout the solar system is called heliophysics.
|
INTERNATIONAL MISSIONS TO SUN |
|||
|
Mission |
Aim |
Country |
Year |
|
Helios 1 and 2 |
To study the solar wind from an orbit carrying the spacecraft inside Mercury’s orbit. |
US & Germany |
1970 |
|
Pioneer 9 |
To measure solar wind and solar magnetic field) |
U.S |
1983 |
|
SOHO |
Investigation of Sun's core, corona, and solar wind; comet discoveries |
Europe & U.S. |
1995 |
|
Yohkoh |
To observe the solar flares at X-ray wavelengths |
Japan |
1991 |
|
Hinode |
Exploring the Sun's magnetic field and outer atmosphere |
Japan |
2006 |
|
Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) mission |
To capture unseen images of Sun |
U.S. |
2006 |
|
Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) |
To study the solar atmosphere. |
U.S. |
2013 |
|
To unlock the mysteries of the Sun's corona and solar wind. |
U.S. |
2018 |
|
|
Aditya L1 |
Solar corona observation |
India |
Yet to be launched |
References