7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS II – Important International Institutions, agencies and fora - their Structure, Mandate.
Recently, the 30th edition of the Conference of the Parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP30), the annual two-week climate talks, concluded in Belem, Brazil on 22nd November.
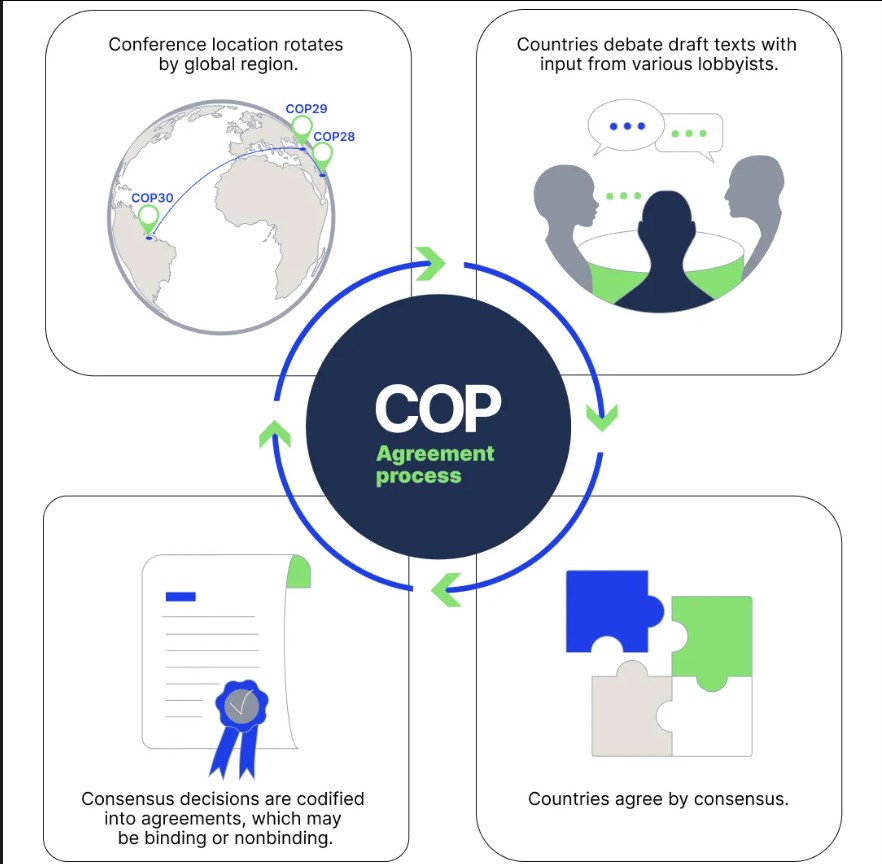
Mutirao is a Brazilian tradition of collective, community-driven mobilisation — a spirit the Presidency seeks to translate into global climate action.

The Indian Express| Outcomes of COP30