7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS II - Government Policies and Interventions for Development in various sectors and Issues arising out of their Design and Implementation
Recently, the Parliament passed the Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Bill, 2025.
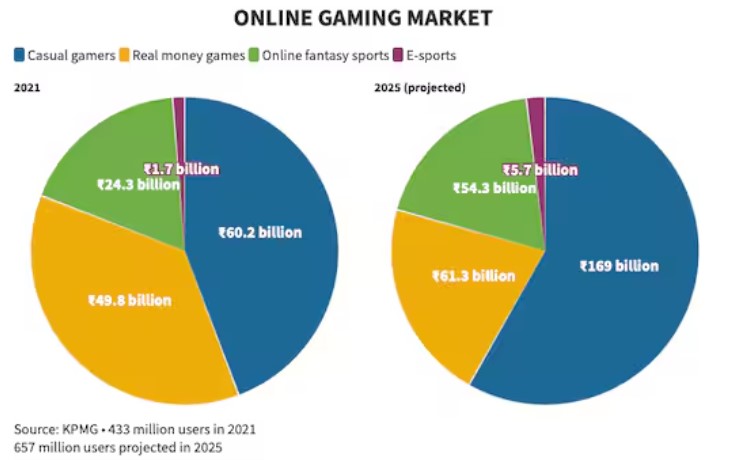
The Hindu| Regulation of Online Games in India