|
One Liners 23-01-2026
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
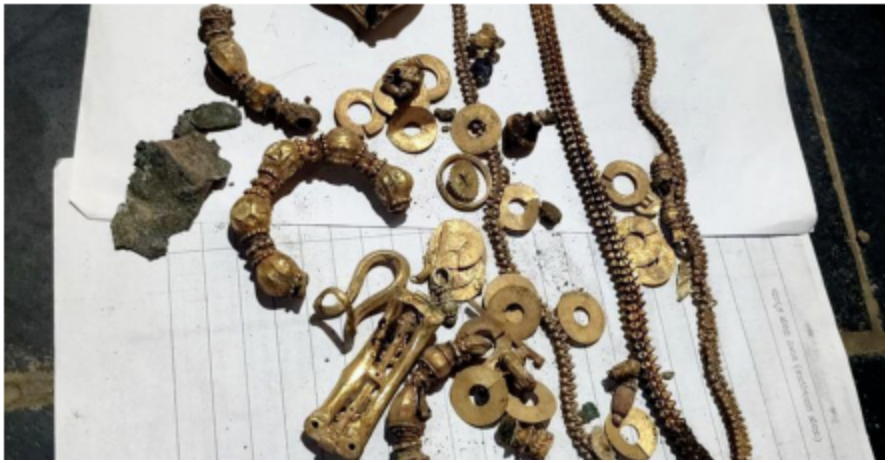
Excavation in Lakkundi village
A century-old treasure of gold ornaments and artifacts was unearthed in Lakkundi village, Gadag district.
- Discovered – Gold ornaments and other articles in a copper container.
- Location – Lakkundi village, Gadag district, Karnataka.
- Significance of Lakkundi – Known for ancient Chalukyan architectural monuments.
- Depth of Discovery – 5 feet during house foundation excavation.

|
|
Social Issues
|
|
Equality in society
Supreme Court's emphasis on schools as the starting point for societal equality, highlighting the transformative potential of the Right to Education (RTE) Act.
- Court's observation – Equality in society must start in school, where children from diverse backgrounds (rich/poor) sit together.
- Legal Basis – Right to Education (RTE) Act, 2009.
- RTE Act's Obligation – It ensures neighbourhood schools admit children from weaker and disadvantaged sections.
- Constitutional basis – Earnest implementation of Article 21A (Right to Free and Compulsory Education).
|
|
Polity & Governance
|
|
Section 17A of the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988

|
|
International Relations and Issues
|
|
India – Iran Trade
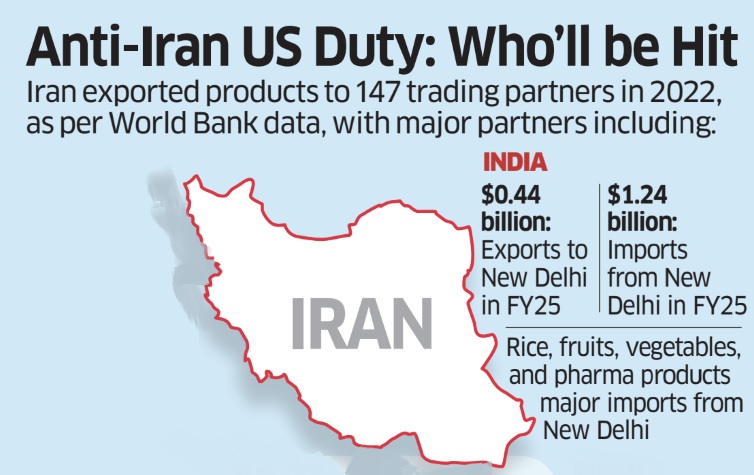
|
|
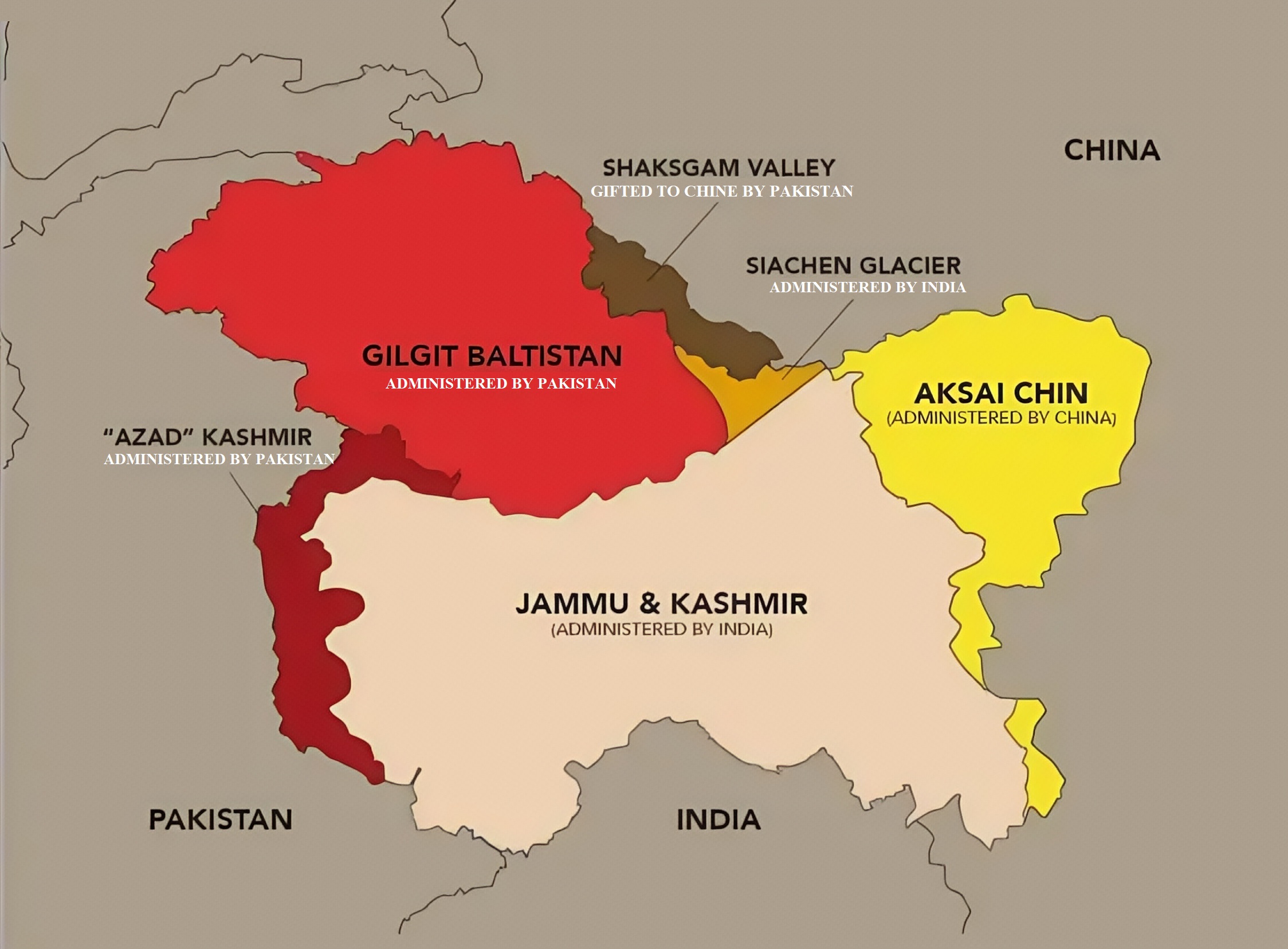
Shaksgam Valley Dispute (India-China-Pakistan Territory)
China-Pakistan signed the 1963 boundary agreement, granting China 5,180 sq.km (Shaksgam Valley); India continues to claim it.
- Key History
- Part of – A Larger Jammu & Kashmir dispute
- 1963 agreement – Pakistan ceded territory to China (controversial).
- Pakistan controls the ground; China shows interest via the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) infrastructure project.
- India's position – Invalidated the agreement.
- Current Status –
- CPEC running through the region which shows connectivity and military significance.
- India protest against unrecognised occupation; it has never acknowledged the agreement.
- Geographic reality – India has a long-standing claim but no ground control in the region.
|
|
Environment
|
|
Valley of Flowers
A forest fire in the Valley of Flowers, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, led Uttarakhand to seek Indian Air Force assistance.
- Location – Spread over an area of 87 sq.km in the Chamoli district, the Valley of Flowers National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and forms one of the two core zones (the other being the Nanda Devi National Park) of the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve.
- Altitude – 3,600 metres above sea level.
- Biodiversity – Around 600 exotic flower varieties like orchids, poppies, primulas, marigold, daisies and anemones are an eye-catching spectacle.
- Flora – Sub-alpine forests birch and rhododendron cover parts of the park's area.
- Fauna – Home to such rare and amazing wildlife species like the gray langur, the flying squirrel, the Himalayan weasel, and black bear, the red fox, the lime butterfly, the snow leopard and Himalayan monal, to name a few.
- Unusual Aspect – The forest fire occurred in early January, although such incidents generally reach their peak during May–June, likely due to minimal snowfall.
|
|
Environmental impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- GHG Emissions – ICT industry (including AI) estimated 1.8%-3.9% of global GHG emissions.
- Training a single Large Language Model (LLM) can generate 3,00,000 kg of carbon emissions.
- Water consumption – AI servers may use 4.2-6.6 billion cubic meters of water by 2027, leading to scarcity.
- Comparison – ChatGPT request consumes 10X more energy than a Google search.
- Global Response – UNESCO (Ethics of AI), US (AI Environmental Impacts Act), EU (harmonized AI rules).
|
|
Recommendations for India
Need for India to develop policies and standards to address AI environmental impacts.
- Expand EIA to cover AI’s environmental impacts.
- Develop measurement standards with input from tech firms, NGOs, and think tanks.
- Track sustainability metrics like GHG emissions, energy, water, and land use.
- Integrate AI’s footprint into ESG disclosures under MCA and SEBI.
- Encourage sustainable AI practices such as using pre-trained models and renewable-powered data centers.
|
|
Carbon Credit Monetisation Framework
Delhi government approved a 'Carbon Credit Monetisation Framework' to generate revenue from green initiatives.
- Objective – To generate revenue by scientifically measuring emission reductions and converting them into carbon credits.
- Mechanism – Sale of carbon credits in both national and international carbon markets.
- Sources of Credits – Electric buses, plantation drives, solar energy promotion, and enhancement of waste management practices.
- Revenue Usage – Funds are deposited into the Consolidated Fund of the State, used for public welfare schemes.
|
|
Science
|
|
Havana Syndrome

|