7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS III - Disaster and Disaster Management.
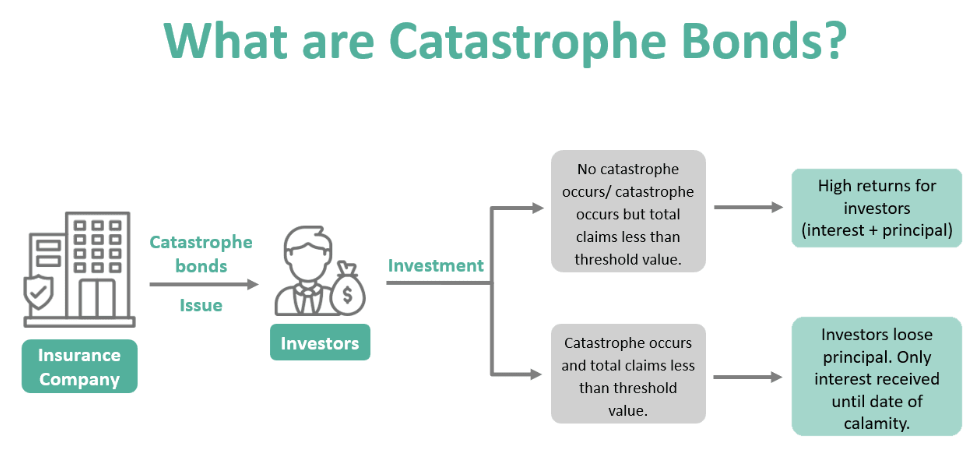
Recently, India is considering the use of catastrophic bonds for disaster resilience and management.
Nobel laureate Harry Markowitz’s emphasis on diversification aligns with the strategic rationale for including cat bonds in investment portfolios.
U.S., catastrophe bonds have seen over $180 billion in issuances globally, with approximately $50 billion currently outstanding, since their inception in the late 1990s following major hurricanes.