7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS III – Money-Laundering and its prevention
Recently, a report submitted by the Finance Minister in the Rajya Sabha states that Enforcement Case Information Reports (ECIRs) have been issued to initiate proceedings under the Prevention of money laundering act (PMLA) 2002.
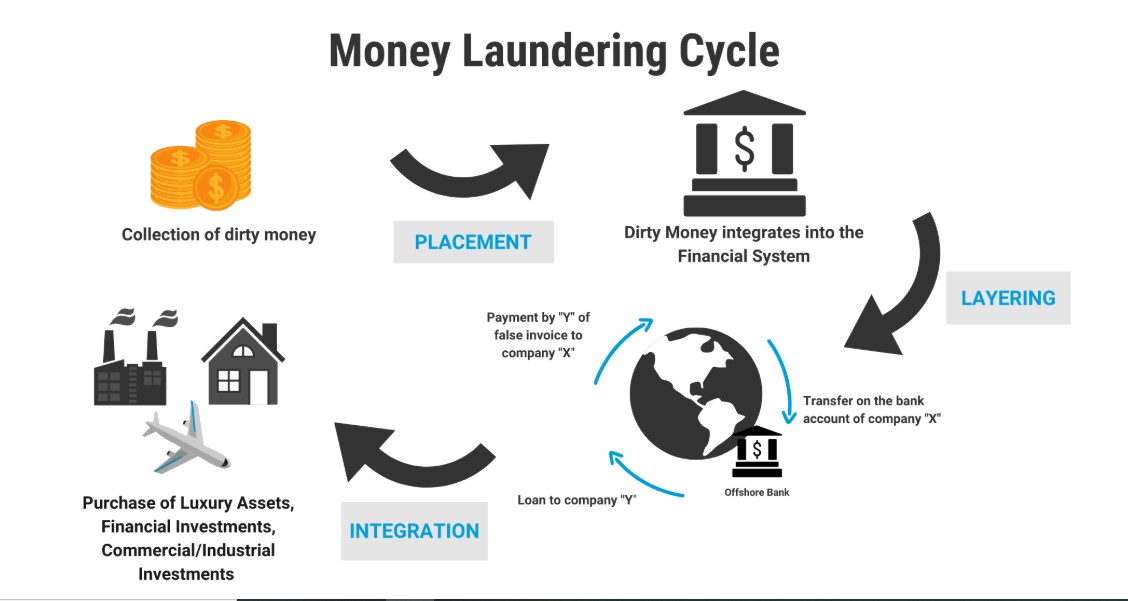
Smurfing is a process which involves breaking up large amounts of cash into smaller sums
The burden of proof in law refers to the responsibility of a party in a legal case to prove their claims.
|
Enforcement Case Information Reports (ECIRs) |
|