Recently Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud addressed a unique ceremonial bench as the country's highest court turned 75 years.
Sir Elijah Impey was the first Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of Calcutta.
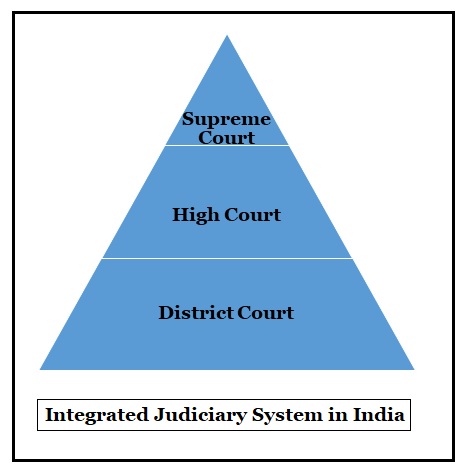
It is a single system of Courts which establishes both Centre laws and State laws.
Articles 124 to 147 in Part V of the Constitution deal with the organisation, independence, jurisdiction, powers, and procedures and so on of the Supreme Court.
The consultation with the chief justice is obligatory in the case of appointment of a judge other than Chief justice.
Both were declared unconstitutional and void by the Supreme Court as it affects the independence of judiciary.
|
Classification of jurisdiction |
About |
|
Original |
Between the Centre and one or more states. |
|
Between the Centre and any State or States on one side and one or more other States on the other side. |
|
|
Between two or more States. |
|
|
Writ |
The Supreme Court is empowered to issue writs including habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto and certiorari for the enforcement of the fundamental rights of an aggrieved citizen. |
|
Appellate |
The Supreme Court is primarily a court of appeal and hears appeals against the judgements of the lower courts. |
|
Advisory |
|
|
Court of Record |
|
|
Judicial Review |
|
|
Constitutional interpretation |
|
|
Election of President and Vice President |
|
|
Union Public Service Commission |
It enquires into the conduct and behaviour of the chairman and members of the Union Public Service Commission on a reference made by the president. |
|
Power to review |
|
|
Cases in High Court |
|
|
Decree and order of Supreme Court |
|
|
Judicial superintendence |
|
To know about Part II- Click here
References