7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance | Space Technology
Why in News?
Recently, Blue Origin announced the suspension of its New Shepard suborbital space tourism programme for at least two years to focus on developing its lunar capabilities.
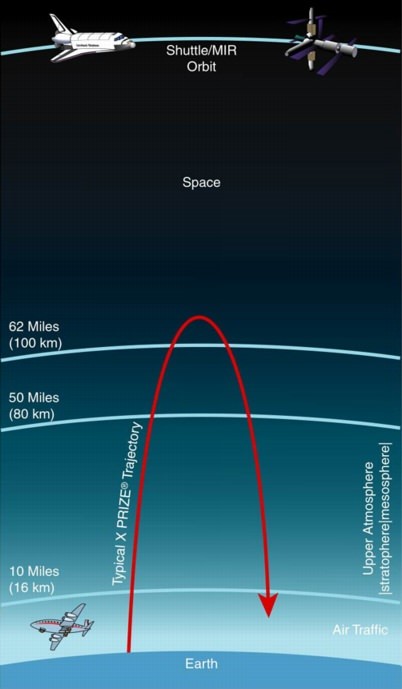
|
Quick Facts |
|
Reference