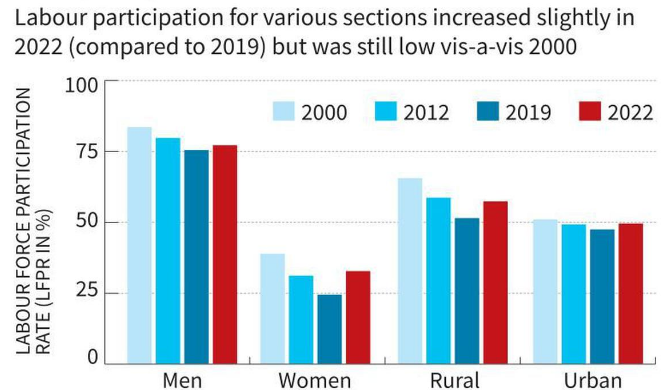
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
Art forms in Tamil Nadu
|
|
Folk Dances
|
Features
|
|
Poikkaal Kuthirai Aattam
|
- It involves a dummy horse with a gap in the middle for the dancer to fit into.
- It is also known as puravi attam.

|
|
Oyillattam
|
- It tells stories from mythology, and is traditionally performed by men wearing colorful handkerchiefs tied around their fingers and ankle bells.
- It is also known as the "Dance of Beauty" or the "Dance of Grace.

|
|
Karagattam
|
- It involves balancing pots on the head while performing intricate dance movements.
- The dance is performed to praise the rain goddess Mariamman.
- It is a mixture of multiple forms of Tamil dance forms like Bharatanatyam postures and mudras.

|
|
Mayilattam
|
- It is a traditional dance from south India that is performed by women in Hindu temples in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- The dance is performed in reverence to Lord Murugan.
- It is also known as the peacock dance.

|
|
|
Space science and Technology Awareness Training (START) 2024 programme
|
|
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will soon conduct the START 2024 programme.
- Aim- To attract the youngsters to the fields of space science and technology.
- Hosted in - Educational institutes, universities, colleges within India who are offering UG and PG courses in physical sciences and technology.
- Domains - The programme will cover various domains of space science, including Astronomy & Astrophysics, Heliophysics & Sun-Earth interaction, Instrumentation, and Aeronomy.
|
|
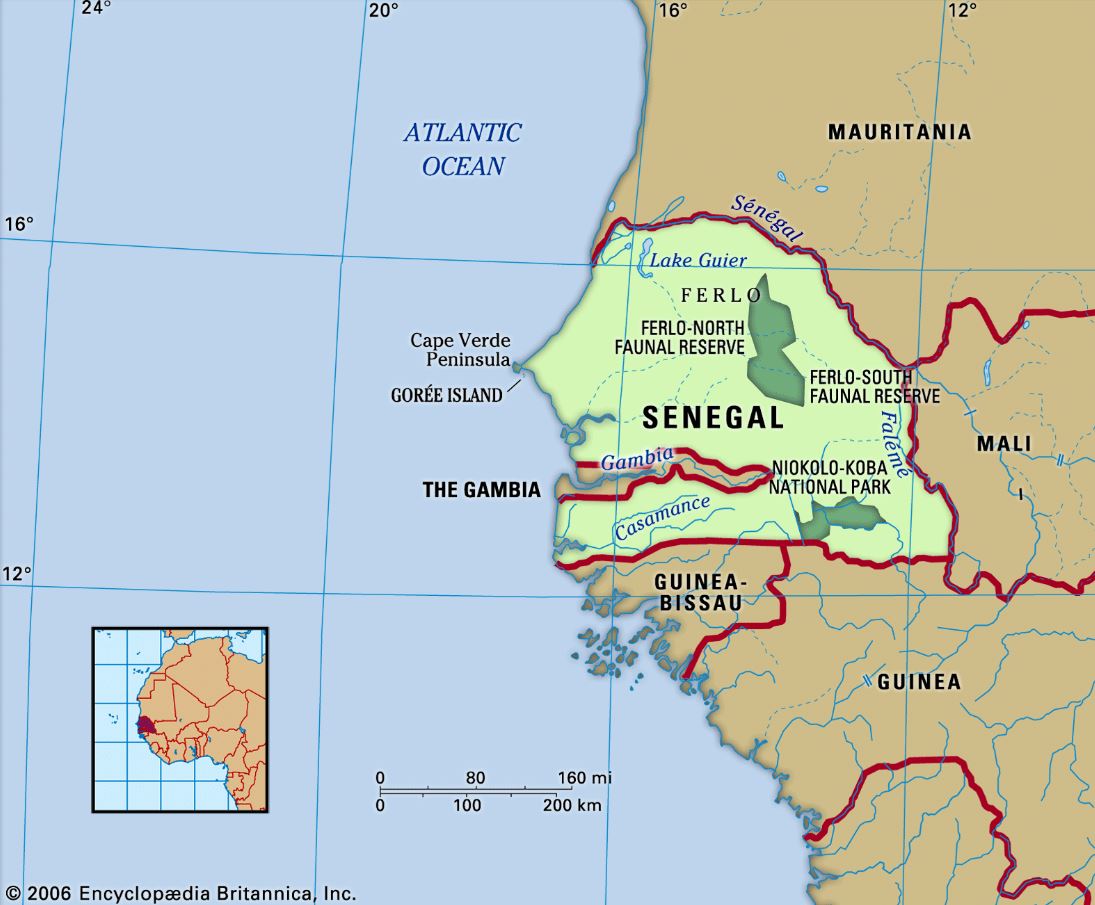
Senegal
|
|
Senegal’s Bassirou Diomaye Faye appears to have won the recent presidential election.
- Senegal is a West African country with Dakar as its capital.
- Senegal is bounded to the north and northeast by the Senegal River, which separates it from Mauritania; to the east by Mali; to the south by Guinea and Guinea-Bissau; and to the west by the Atlantic Ocean.
- Senegal is crossed by 3 westbound rivers - Senegal River, Gambia River, Casamance River.
- Senegal is known as the Gateway to Africa.
- The country lies at an ecological boundary where semiarid grassland, oceanfront, and tropical rainforest converge.
- The Cape Verde (Cap Vert) Peninsula is the westernmost point of the African continent.
|
|
Magnetofossils
|
|
Scientists have discovered a 50,000-year-old sediment, a giant and one of the youngest magnetofossil in the Bay of Bengal.
- Magnetofossils are the fossilised remains of magnetic particles created by magnetotactic bacteria, also known as magnetobacteria.
- They are found preserved within the geological records.
- The geologic record is a standard time scale that partitions the Earth's history into four eons and their subdivision of eras, periods, and epochs.
Magnetotactic bacteria
- These bacterias are mostly prokaryotic organisms that arrange themselves along the earth’s magnetic field to reach places that had optimal oxygen concentration.
- These unique creatures were 1st described in 1963, by Salvatore Bellini, an Italian doctor and then again in 1975 by Richard Blakemore of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Massachusetts.
- These magnetotactic bacteria create tiny crystals made of the iron-rich minerals magnetite or greigite.
|
|
Spiral galaxy NGC 1512
|
|

|
|
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO)
|
|
The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) has expressed concern over some States not compiling living and deceased donors’ data.
- It is an apex organisation situated in New Delhi.
- It works under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Aim - To provide for an efficient and organised system of organ procurement and distribution in the country, and maintain a national registry of donors and recipients of organs and tissues.
- It was established under the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act (THOTA), 1994.
- NOTTO also has a National Organ Transplant Program (NOTP) that aims to improve access to transplantation for needy citizens by promoting deceased organ donation.
- Organ and tissue transplantation –
- It is a surgical procedure that involves removing an organ, tissue, or group of cells from one person (the donor) and transplanting it into another person (the recipient), or
- Moving it from one site to another site in the same person.
|
|
Tamil Isai Movement
|
- The Tamil Isai movement is a fight to establish Tamil as a musical language.
- The movement began in 1939 to promote Tamil songs and give them a prominent role in music concerts, instead of making them the end result.
- The movement also aims to oppose the dominance of Sanskrit and Telugu compositions.
- It gained momentum with the establishment of Tamil Isai Sangam, which was established in 1943 by Annamalai Chettiar.
|
|
Animal Birth Control (ABC) programme
|
- The Animal Birth Control (ABC) program aims to control the population of stray dogs in India without cruelty.
- The program involves catching dogs, sterilizing them, vaccinating them against rabies, and releasing them back to their original location.
- The rules for the ABC program announced in April 2023 will replace the 2001 rules.
- It will be implemented by local bodies, municipalities, municipal corporations, and panchayats.
India accounts for 36% of the world's rabies deaths and 65% of rabies deaths in Southeast Asia.
|
|
Francis Scott Key bridge
|
|
Baltimore's Francis Scott Key Bridge collapsed after a container ship with all Indian crew members smashed into the bridge’s tower.
- The Francis Scott Key Bridge is situated in Maryland, U.S.
- The bridge spanned across the Patapsco River and Baltimore harbour.
- It was opened in 1977 in honour of Francis Scott Key, a 19th Century Maryland poet who wrote the words for the US national anthem, the Star Spangled Banner.
- It is described as a continuous truss bridge, and it is the 3rd longest bridge of its type in the world.
|
|
T Coronae Borealis (tau Coronae Borealis)
|
|
T Coronae Borealis, or T CrB, last exploded in 1946 and astronomers believe it will do so again between February and September 2024.
- T Coronae Borealis is a binary star system comprised of a cool red giant and a hot white dwarf star 3,000 light years away in the constellation Corona Borealis.
- The smaller white dwarf has been stealing matter from the red giant and appears to be getting ready to emit a burst of energy, making it visible for at least a few days.
- It is known as a recurring nova where matter, mostly hydrogen, is collected by the white dwarf until enough mass is reached, creating a fusion reaction.
- That will then emit a burst of energy, which includes visible light.
|