7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG)
Areas where Groundwater meets the Oceans
Maritime Heritage Museum
Sagarmala Programme
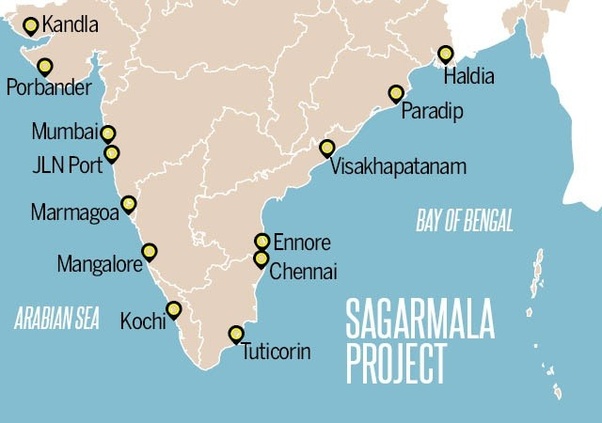
Lothal
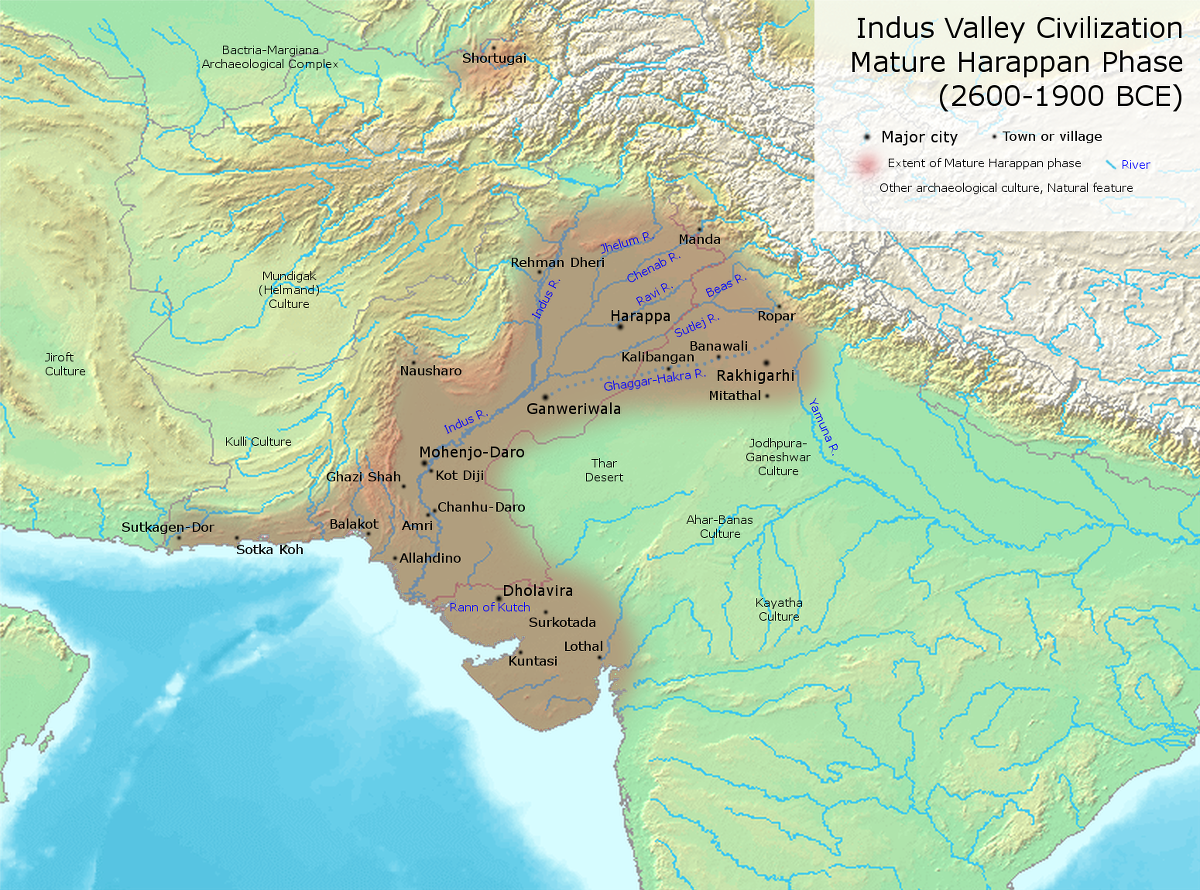
Source: PIB, the Hindu
Shivam Agrahari 7 years
Very awesome information