7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance | Polity & Governance
Why in News?
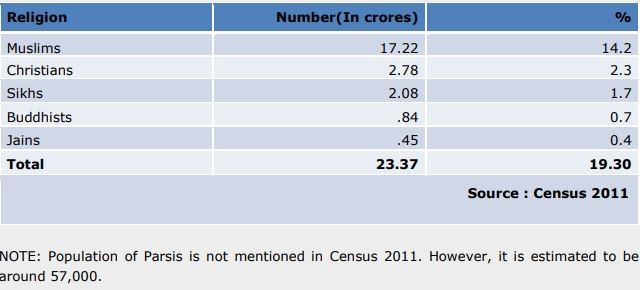
Over a month after the Delhi High Court sought the Centre’s response on delayed appointments in the National Commission for Minorities, Union Ministry for Minority Affairs remained non-committal.
References