7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
United Nations has released Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group (MMEIG) 2020 report which provides global estimates of MMR.
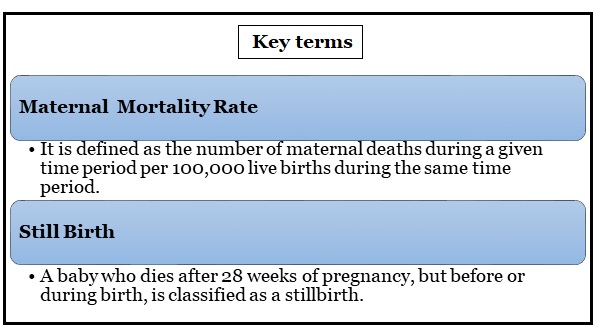
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 3.1) reduce global MMR to less than 70 maternal deaths per 100 000 live births by 2030
|
MMR |
2000 |
2020 |
Average annual rate of reduction |
|
Global |
339 |
223 |
2.07% |
|
India |
384 |
103 |
6.36% |
References