7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance | Ecology & Environment
Why in news?
Recently, researchers studied how mangrove cells enable the plants to survive in saltwater.
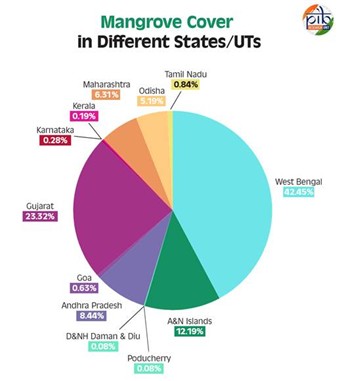
To know more about Mangrove Ecosystem, Click here
Quick Fact
|
How mangrove’s cells helps plants survive in saltwater? |
|
Key Insights
|
References