7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS – II – Polity & Governance | Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector and Resources.
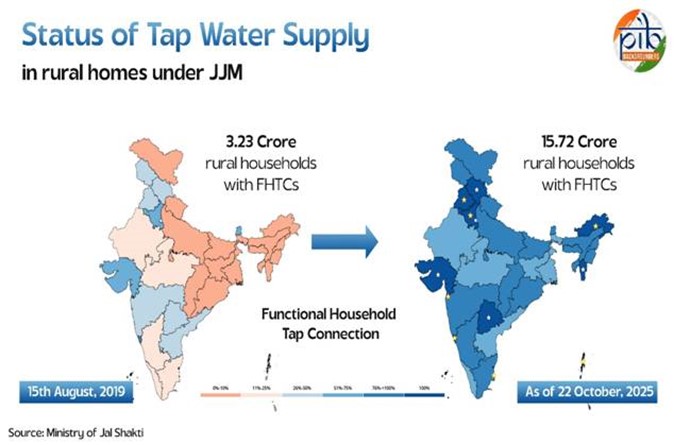
India has achieved a major milestone under the Jal Jeevan Mission (Har Ghar Jal), with over 81 % of rural households having access to clean tap water, marking a significant step towards universal water security in rural India.
|
Quality Assurance and Monitoring (QA&M) system under JJM |
|
The success of the JJM lies not only in infrastructure creation but also in the spirit of “Jan Bhagidari se Peyjal Prabandhan”, community-led water governance combined with innovative use of technology.