7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS II – Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
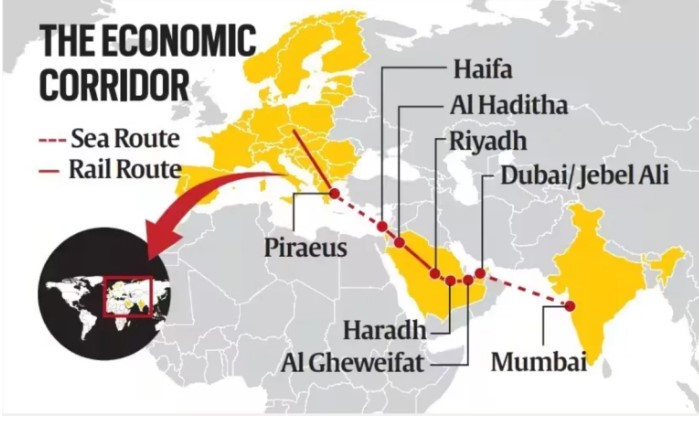
Recently, India’s National Security Council Secretariat hosted envoys and officials to discuss progress on the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
Reference