7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
Thousands of Indians are flocking to these digital assets and pumping in crores of rupees and there comes a need to know about cryptocurrencies before joining them.
What is a cryptocurrency?
Satoshi Nakamoto is said to have conceptualised an accounting system in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis which has mooted the idea of blockchain.
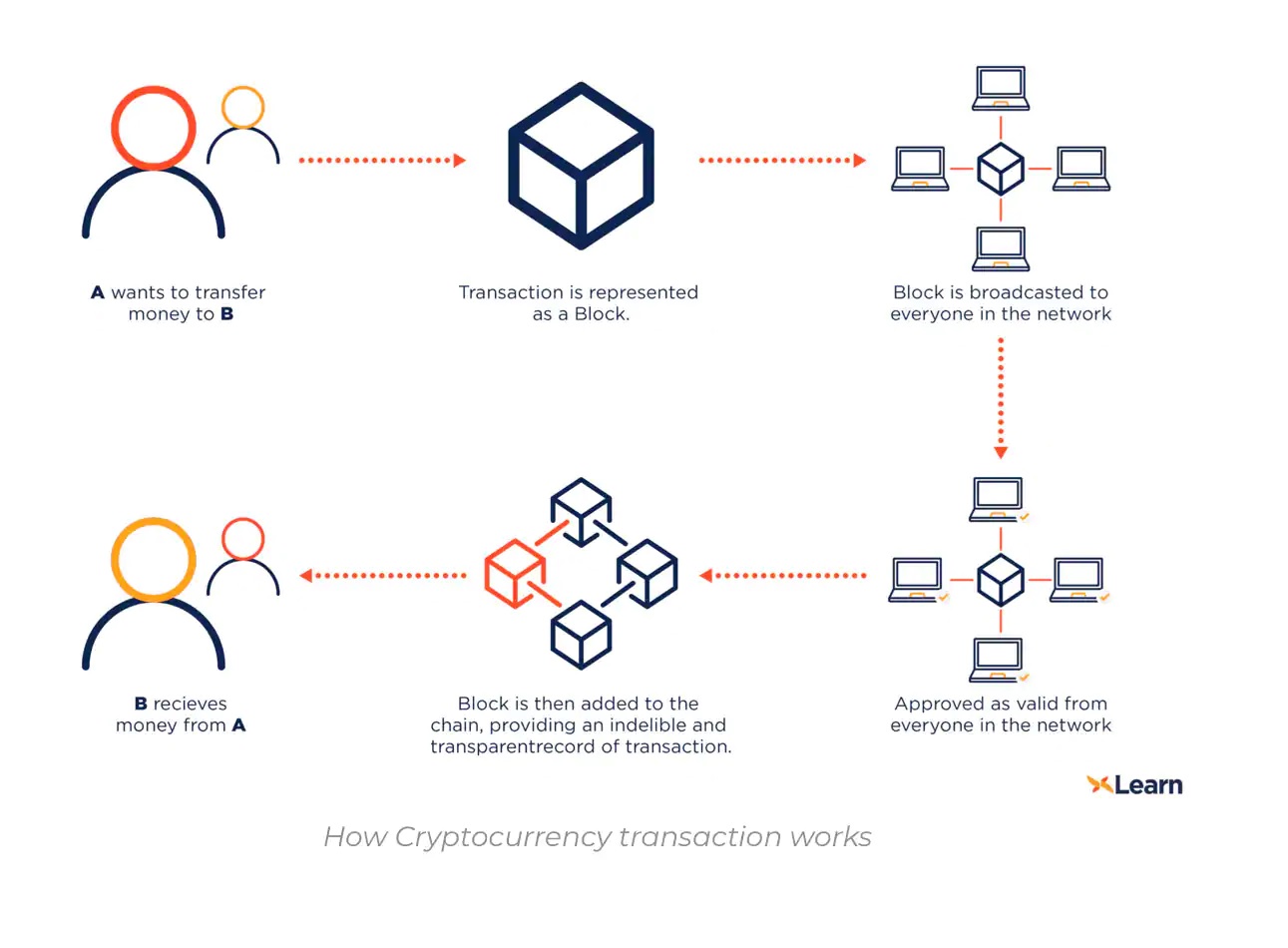
How does cryptocurrency work?
 How are cryptocurrencies bought?
How are cryptocurrencies bought?
How are the cryptos sold for INR?
What are the pros and cons of cryptocurrency?
Pros of cryptocurrency
Cons of cryptocurrency
What alternatives are available against volatile cryptocurrencies?
What are the risks in stablecoins?
How can this play out in India?
Reference