7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS II – Health
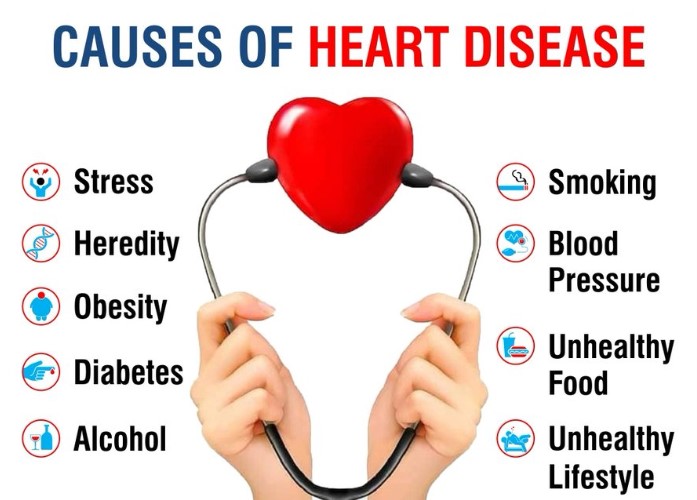
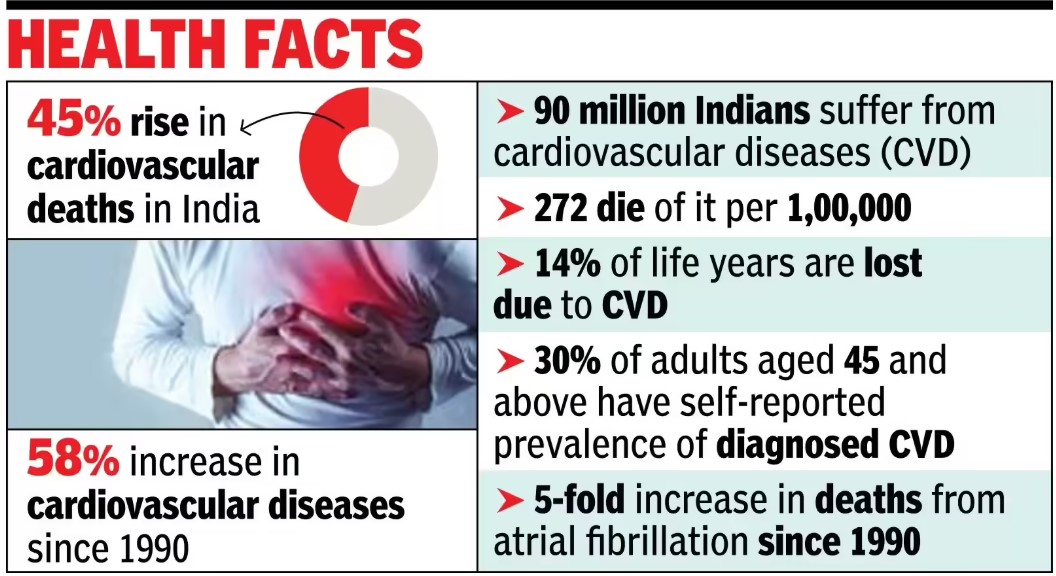
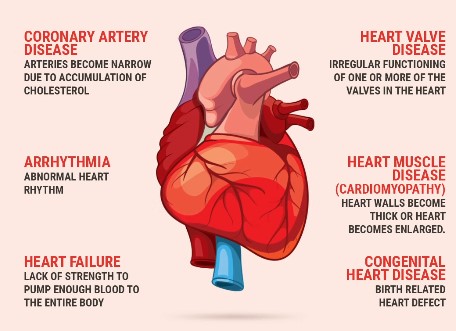
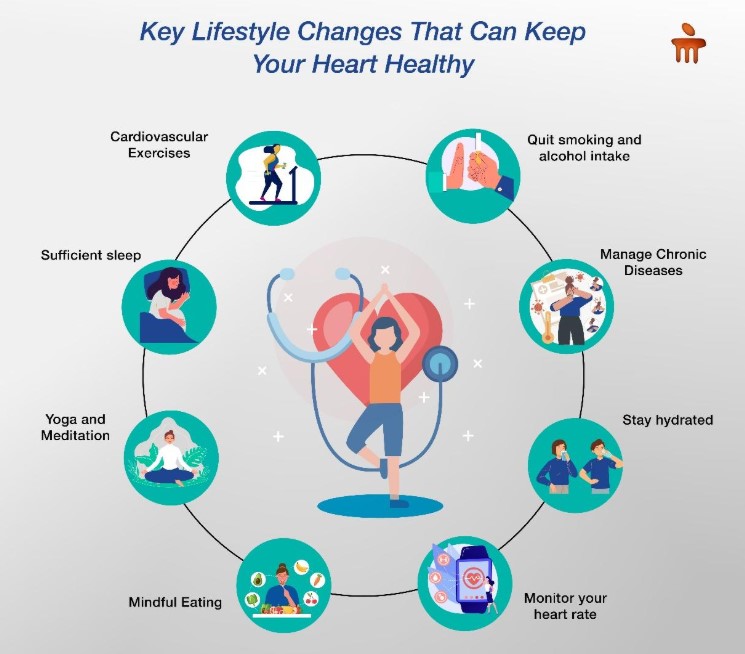
Recently, there has been a manifold increase in the cardiovascular disease and the world heart health day stresses the need to address the issue.