GS – III – Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Why in news?
In the 56th GST Council meeting, chaired by Union Finance Minister, the Next-Gen Goods and Services Tax (GST) reforms have been approved.
What are the features of current GST 1.0?
What is the performance of GST so far?
What are the features of GST 2.0?

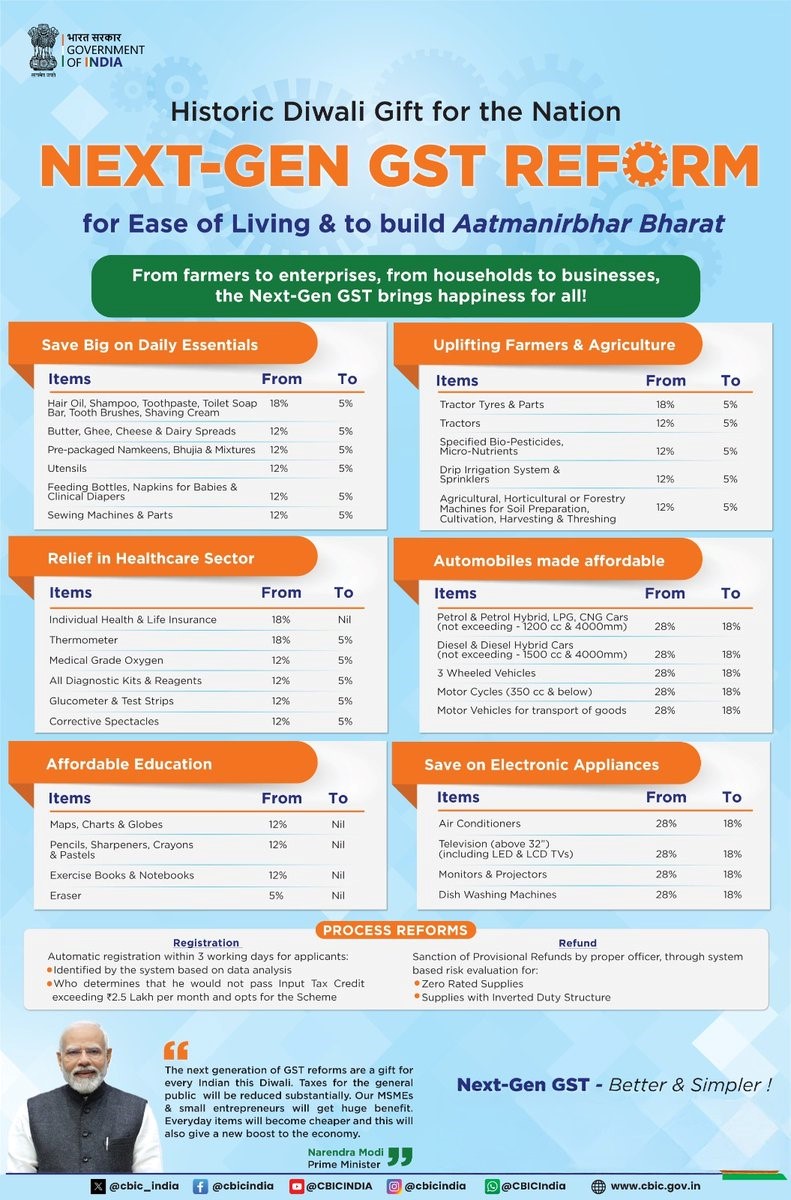
What are the potential benefits GST 2.0 reforms?
What are the challenges in implementing GST 2.0?
What lies ahead?
Conclusion:
Reference
harrystyles7117 2 days
While they might look simple, Papa's Games actually help improve time-management skills and attention to detail.
nytwordlehints 25 days
Great insights on GST reforms! The pips shift to a simplified two-tier structure and reduced rates on essentials is commendable, promising affordability and economic growth. Thank you for sharing this detailed overview!
Brad Pitt 2 months
This is a clear and balanced overview of GST 2.0. The potential benefits of a simpler rate structure and support for MSMEs are promising, but—much like Slope Game, where balance and precision matter—the concerns around revenue loss for states and the impact on lower- and middle-income groups are equally important. Successful implementation will really depend on stronger GSTN infrastructure and ensuring that the benefits actually reach consumers.