7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS - II – International relations
Why in News?
Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps began a new round of military exercises in the Strait of Hormuz, the drills, launched on the eve of talks with the United States, were aimed at preparing for “potential security and military threats” in the strait.
Where is the location of the Strait of Hormuz?
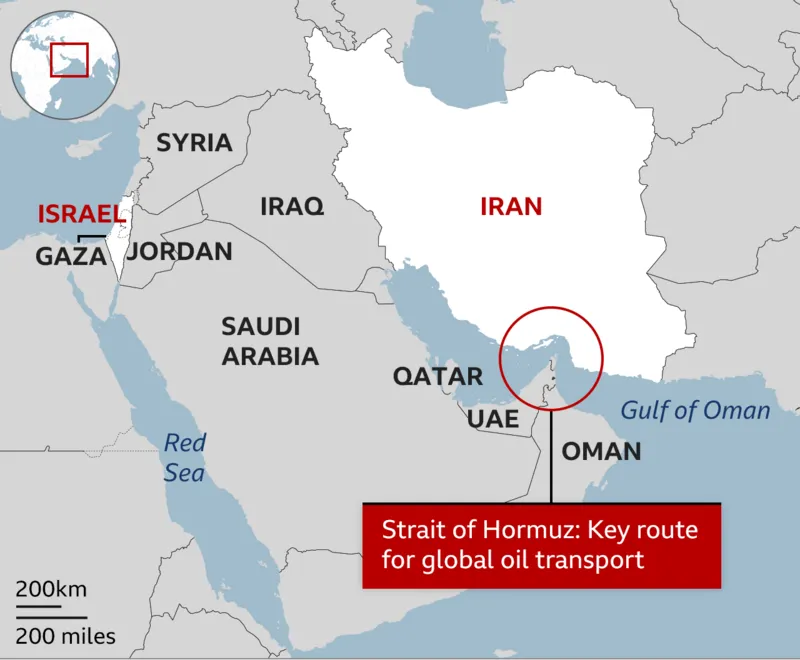
Why the Strait of Hormuz remains central to global energy security?
What is the strategic importance of the region with regards to Iran?
What is the global economic impact caused by the disturbances in this region?
What are the few alternatives?
What are the latest tensions?
What lies ahead?
Reference
The Hindu | Why the Strait of Hormuz remains central to global energy security?