Prelims: Economic Geography of India | Agriculture
Why in News?
In last few decades times, both rice and wheat acreages across India was rising than other crops.
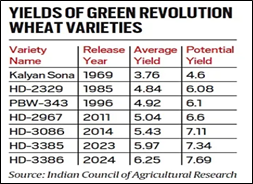
The HD-3385 variety of wheat released in 2023, for example, yields an average of 6 tonnes per hectare and potential of over 7.3 tonnes. It is, moreover, resistant to all major rusts – yellow (stripe), black (stem) and brown (leaf).
Quick Facts
|
|
Genome Edited Rice |
Genome Edited Wheat |
|
Variety |
Pusa DST Rice 1 |
Kamala |
|
Parent |
Cottondora Sannalu (MTU-1010) |
Samba Mahsuri |
|
Edited |
DST (drought and salt tolerance) gene, reducing its expression |
Gn1a’ gene - to reduce its expression |
|
Effect |
It becomes viable even under conditions of water, salinity and alkalinity stress. |
It promotes cytokinin accumulation, leading to higher grain numbers. |
Reference
The Indian Express| Preference for Rice and Wheat Cropping in India