7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS-III – Economy - Infrastructure: Energy.
India is reducing fossil fuel dependence and ramping up domestic clean energy production, in line with its vision of achieving Net Zero by 2070. In this transition, Green hydrogen is emerging as a scalable, clean fuel to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors.
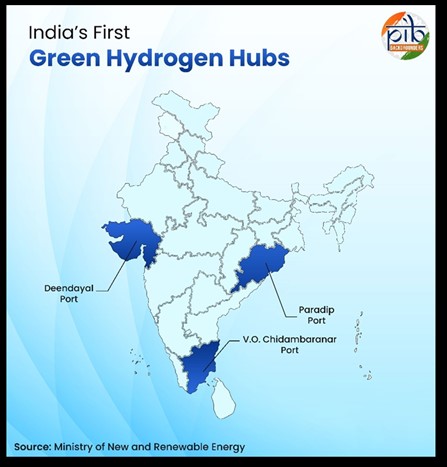
PIB | Unlocking India’s Green Hydrogen Production Potential