7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance | Health
Why in News?
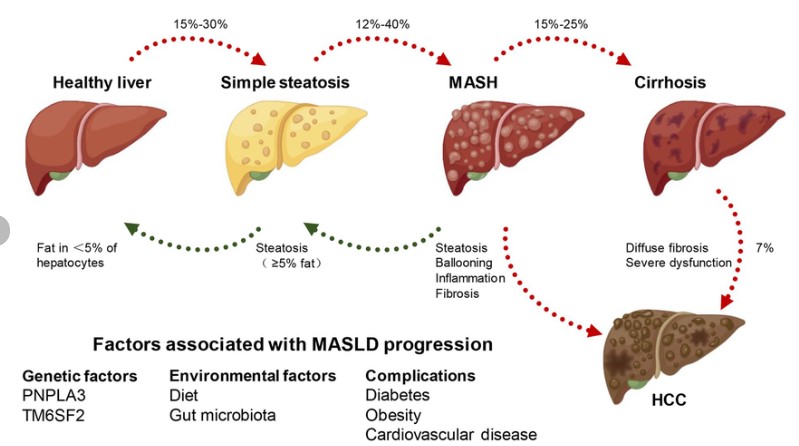
Recently, Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) has been emerging as a major public health concern in India.
References