National Conference on “Good Governance Practices”
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance.
Why in the news?
Recently, the two-day national Conference on “Good Governance Practices” was Inaugurated in Bhubaneswar.
- Aim - To foster a spirit of collaborative learning and institutional innovation by bringing together public administration leaders from the national and state levels on a unified platform.
- Objective - It seeks to highlight exemplary governance initiatives recognized with the Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration.
- Theme - “Good Governance Practices”.
- Organized by - the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) in collaboration with the Government of Odisha.
- Recognition – The conference seeks to highlight with PM’s awards for Excellence in Public Administration.
- Representation - 400 delegates from across the country, comprising senior officials from the Central and State Governments
- More than 20 distinguished speakers, including District Magistrates and Secretaries.
- Key highlights - The conference highlighted that out of 41 Conferences held since Independence, an impressive 29 have been organized in the last 15 years.
- It also noted that 4 critical dimensions of the Modi-led reforms include
- Reforms as revolutionary, breaking away from outdated practices
- Far-reaching socio-economic impact.
- Instilling a new sense of self-esteem, confidence, and trust in the system.
- several initiatives—such as the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) and the Digital Life Certificate—have evolved into global models of innovative governance.
- Outdated and old laws have been repealed, emphasising a departure from the 'status quo' approach of the past, promoting greater efficiency in governance.
- India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which has now surpassed global payment systems like VISA in terms of usage.
- Odisha affirmed the State’s commitment to people-centric, technology-driven, and future-ready governance.
- Secretary of DARPG, emphasized that the conference has been in alignment with the theme of Civil Services Day 2025 i.e. “Holistic Development of India through Holistic Development of Districts and Blocks”.
- Significance – It is showcasing scalable and replicable models in public service delivery, digital governance, citizen engagement, and inclusive development.
Reference
PIB | Conference on “Good Governance Practices”
Capacity Utilization of Renewable Energy
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance.
Why in News?
India’s renewable energy capacity utilization stands at 30%, despite its contributing to a 50% share in India’s total energy capacity.
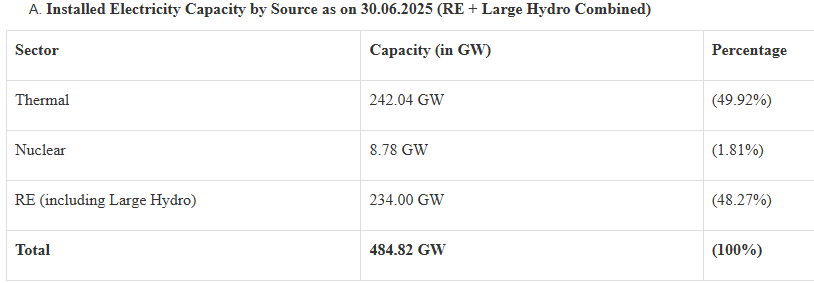
- Status of installed energy capacity – India’s renewable energy share is 50% of its total electric power capacity i.e. 484 gigawatts.
- Notable achievement - It is emphasizing that India is five years ahead of the target set under its Nationally Determined Contributions [NDCs] to the Paris Agreement.
|
Year
|
Share of Renewable energy in India’s installed electricity capacity
|
|
2014-15
|
30%
|
|
2024-25
|
50%
|
The quantum of clean energy (non-fossil) produced annually has risen quite significantly from 190 billion units in 2014-15 to 460 billion units in 2024-25.
- Importance -This underscores the country’s steadfast commitment to climate action and sustainable development, and signals India’s clean energy transition.
- Issue addressed – Despite the share of clean/renewable energy is 50%, its share of actual electricity supplied is below 30%.
- Causes - Lower capacity utilization factor - CUF values for clean energy have been lower than that of coal or nuclear sources.
Capacity utilization factor (CUF) is a measure of how much available energy was usable.
- Solar has CUF of approximately 20% and wind around 25-30%, compared to coal’s 60% or nuclear is 80%.
- This means despite high installed capacity, their contribution to actual generation remains limited.
- Major electricity contributor – Coal is the largest contributor to India’s Base load demand, or power that is available through the day.
- It shares about 75% of India’s energy mix.
- Measures -Grid flexibility i.e. grid needs to adapt quickly to changes in solar power supply, which can fluctuate based on weather and time of day.
- Improved battery storage - Advanced batteries are required to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods.
- Differential tariffs - Charging lower rates for electricity during solar-rich daytime hours encourages consumers to use more power when solar supply is highest, matching demand with supply.
- Develop ‘hybrid’ power projects - That combine solar, wind, hydro and storage elements to meet India’s growing peak and round-the-clock power.
- These hybrids can store surplus energy and release it during peak demand hours, particularly in the evening.
- Challenges - Land-aggregation issues
- Lack of coordinated transmission planning
- High cost of storage components.
Reference
The Hindu| Capacity Utilization of Renewable Energy
PIB | India’s Renewable Rise
Accountability For Safety UN peacekeepers
Prelims: current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
In a recent high-level meeting of the Group of Friends (GoF) at the UN Headquarters, India's Permanent Representative to the UN, underscored the significant challenges that UN peacekeepers encounter in their work.
- Established in - Officially established in December 2022 during India's presidency of the UN Security Council, building on the historic Security Council Resolution 2589 (2021).
- Co-chaired by - India along with other key nations.
- Dedicated to - The group's mission is focused on advancing legal frameworks, promoting investigations, and supporting initiatives to ensure accountability for crimes committed against UN peacekeepers.
- Primary goal – To deter future assaults and secure justice for peacekeepers and their families.
- India's expression - India has reiterated its strong dedication to ensuring accountability for crimes against United Nations peacekeepers, describing this as a "strategic necessity" essential for global peacekeeping missions.
- Need - UN peacekeepers operate in increasingly perilous environments and face significant challenges, with many crimes remaining unpunished.
- This absence of accountability greatly undermines international peace initiatives by instilling greater confidence in perpetrators.
- Critical imperative - The emphasis is that accountability is more than just a matter of justice for individuals.
- It is fundamental for the effectiveness, credibility, and future of UN Peace Operations around the world.
- In a strong display of global unity, aim to discuss better strategies, operational frameworks, and increased international cooperation to ensure safety of peace keepers.
- Emphasis - Peacekeepers are facing rising threats in highly unstable conflict areas, with hostile attacks and fatalities increasing.
- Indian contributions - India stands as the largest troop-contributing country to the United Nations, having deployed over 300,000 peacekeepers throughout its history.
- The Permanent Mission of India to the UN – It has noted that "Indian peacekeepers have served with valor and honor in nearly every major UN mission, making significant sacrifices, with 182 Indian peacekeepers having given their lives in service.
- Significance - Understanding these complex relationships is vital, necessitating a comprehensive approach along with a steadfast political commitment from all involved parties.
Reference
The Hindu| Accountability For Safety UN peacekeepers
Rare Diseases in India
Prelims - Current events of National & International importance and General Science.
Why in News?
Indian Organization for Rare Diseases (IORD) reported that out of 300 million people with rare diseases in the world, about 90 million are in India.
- Definition – According to WHO, Rare disease is a lifelong disease with a prevalence of 10 or fewer per 10,000 population.
- According to Organization of Rare Diseases India (ORDI) defined rare disease is defined as a disease that affects 1 in 5,000 people.
- Rare disease in children - 80% of these conditions are genetic in origin and predominantly affect children, about 30% of the children don’t live to see their 5th birthday.
- Fewer than 5% of rare diseases have treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- More than 95% of these conditions don’t have a therapy or it may be impossibly expensive.
- Reason for rare disease in India - Real number is likely to be higher since our social practices include endogamy, the practice of marrying within a community.
- Genetic condition in that community, endogamous marriages will tend to preserve that condition instead of letting it die out.
- Consequences – Expensive treatment, non-suitable insurance policies,
- Compensatory treatment by companies (not a feasible way of obtaining treatment), forced to get crowd funding.
- Creating awareness - Premarital counselling - Scientists and health advocates have collaborated with communities to discourage marriages between carriers of the same genetic mutation.
- This helps reduce the risk of passing on hereditary conditions to children.
- Awareness among doctors - Doctors may never have encountered them and are often unaware of these diseases.
- Inform registry – often medical problem is not reported, which would be essential to help draft suitable policies to support patients.
- Needed to help patients connect with each other, and so that industry identifies market opportunities to develop suitable therapies.
- GenTICS - Developed by Tata Institute for Genetics and Society, Bengaluru, a gene database on rare genetic disorders”.
- This is a valuable resource, since a user can choose from a list of symptoms to predict the possible rare disease.
- The patient’s family can then take the information to their doctor and seek support from a patient group.
- Molecular Diagnostics Counselling Care and Research Centre (MDCRC) in Coimbatore – Working on Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a disorder that affects only male children, with females being the carriers.
- MDCRC has done large-scale genetic screening across several districts of Tamil Nadu intending to detect the relevant mutations early and eventually eradicating DMD from the State.
- Similar efforts are required for many disorders around the country.
Reference
The Hindu| Rare diseases have a lot to gain from greater awareness
