Glucagon – Like Peptide 1 (GLP 1)
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
Recently, nearly 12% of Americans have used GLP-1 drugs for weight loss, including about one-fifth of women aged 50 to 64, according to a journal report.
Glucagon – Like Peptide 1 (GLP 1) – It is a naturally occurring peptide hormone.
It is water soluble molecules ranging for a few 200 amino acids in length.
It is incretin hormone and a neurotransmitter.
Incretin hormones are a group of gut hormones that play a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels after eating.
Neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that transmits signals between neurons or from neurons to other cells like muscle or gland cells.
Secreted from – The small intestine and from the hindbrain (regulating vital functions and coordinating movement).
It is produced in the gut by enteroendocrine L-cells after we eat a meal.
Features – Natural GLP-1 is so short-lived.
GLP-1 works for just a few minutes, so after you eat a meal and GLP-1 is secreted naturally, it gives an immediate effect that lasts maybe 30 minutes.
To last longer in the body, GLP-1 is attached to fatty acids, which help the drug stick to a blood protein (albumin), which carries
Carries it around the body
Protects it from being broken down too quickly.
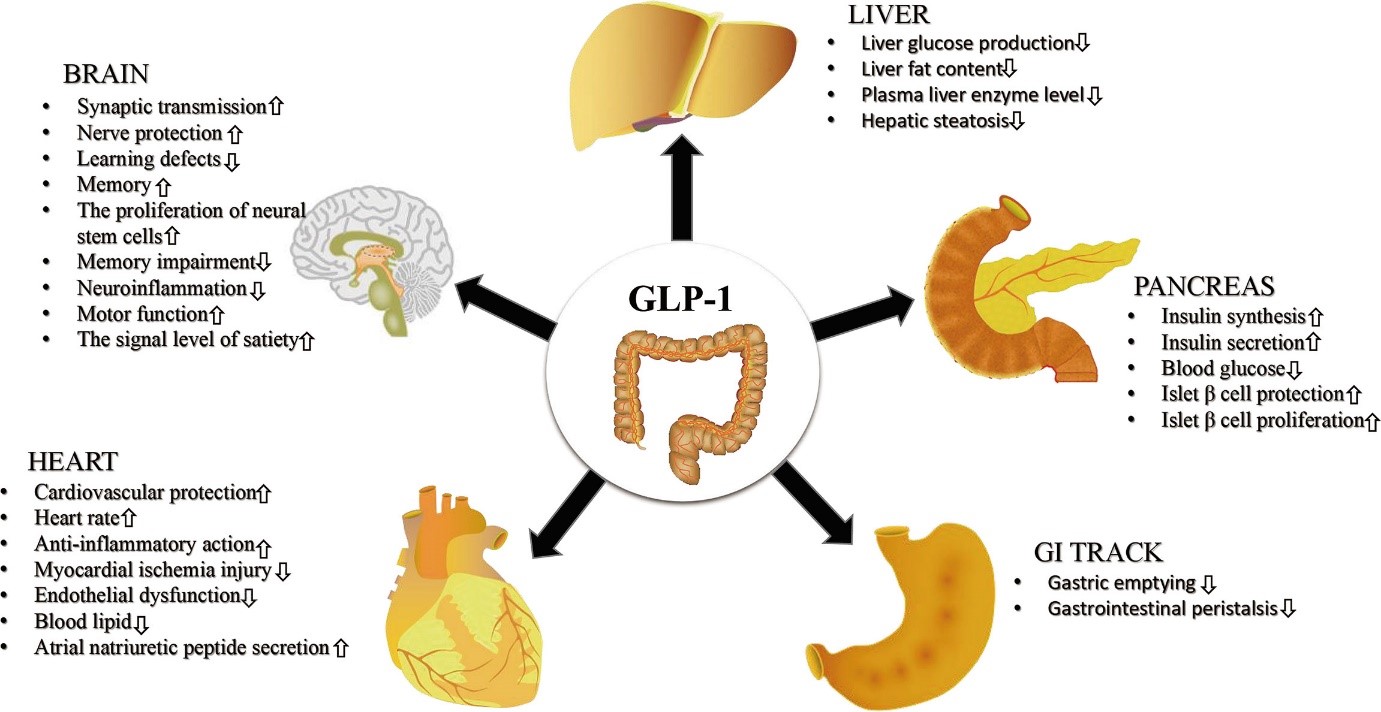
Functions - Travels to the pancreas, where it helps to regulate our blood sugar by increasing insulin and decreasing glucagon. It helps control body weight.
GLP-1 binds to in many organs in the body, also has beneficial effects in many of these organs, such as the kidney, liver, and cardiovascular system.
It is chopped up by metabolic enzymes known as DPP-4 and cleared by the kidneys.
Blood glucose-dependent – The GLP-1 start to act only if the blood glucose is elevated.
Impacts - The brain associated with control of hunger and satisfaction, to effectively tell us that we have had enough to eat and need to stop eating.
References
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Recent studies have shown that GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RA) can be used to treat Alzheimer’s and Diabetes.
Fatty acid acylation is drug molecule attached to a fatty acid, in this case, GLP-1. That will allow the drug to bind to a natural protein called albumin.
Albumin is a protein that plays a crucial role in transporting various substances throughout the body, including fatty acids.
Feature – It solves druggability problem of GLP-1, by attaching to albumin, that protect the drug from degradation, from being cleared by the kidneys.
Druggability is the ability of a protein to bind a modulator and produce a desired therapeutic effect.
Availability of GLP-1 RA –They are available in different forms, including injectable medications and, increasingly, oral formulations.
Uses – Stimulates insulin secretion to lower blood sugar.
Manages appetite and weight
Slows gastric emptying – Contribute to a feeling of fullness and reduce calorie consumption.
It may have neuroprotective effects, potentially improves conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease (as per National Institutes of Health)
It reduces overall inflammation in the body
Treatment – Type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Quick facts
|
Diabetes |
|
Reference
Prelims – Current events of National and International Importance | Bio-diversity.
Recently, Mizoram university and Guwahati based biodiversity conservation group, Help Earth, have recorded a new species of rain snake.
Scientific name – Smithophis leptofasciatus.
Genus – It is the third species in the genus, Smithophis to have been recorded from the northeastern State
Nomenclature – Leptofasciatus is a Greek and Latin hybrid, meaning ‘narrow-banded’, refers the snake’s distinctive dorsal markings.
Another name – Ruahrul in Mizoram.
Family – Natricidae.
Size – Small sized snake, reach up to 32 cm.
Morphology – Predominantly shiny dark or black, interspersed with distinct, narrow, creamish-white or yellowish-lime transverse bands, each covering only one or two dorsal scales.

Habitat –Semi-aquatic, close to small streams under leaf litter, and beneath rocks or decaying logs.
Distribution – Tropical wet montane and tropical semi-evergreen forests at elevations ranging from approximately 900–1,200 m in Mizoram, India. Endemic to tropical forest in Mizoram.
Behavioural traits - It is nocturnal and most commonly spotted during the monsoon season.
Reproduction - A gravid female observed in captivity laid 6 eggs, providing rare reproductive data.
Significance - The new species reinforces Mizoram’s importance as a biodiversity hotspot.
References
Taprobanica| Smithophis leptofasciatus
Scheme for Conservation, Development and Sustainable Management of Medicinal Plants
Prelims - Current events of national and international importance | Government policies and interventions.
Why in News?
Recently, government has approved projects under integrated Component of Scheme for Conservation, Development and Sustainable Management of Medicinal Plants.
|
Other Government Support for Medicinal Plants |
|
|
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) |
Provide financial assistance for area expansion of short duration medicinal plants. |
|
Ministry of Tribal Affairs |
It supports value addition, processing and marketing of forest and agricultural produce gathered by tribal communities under
|
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root & tuber crops, mushrooms, spices.
|
National Medicinal Plants Board (NMPB) |
|
References