7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
In recent times, The Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) has launched a series of digital reforms to strengthen Gram Panchayats.
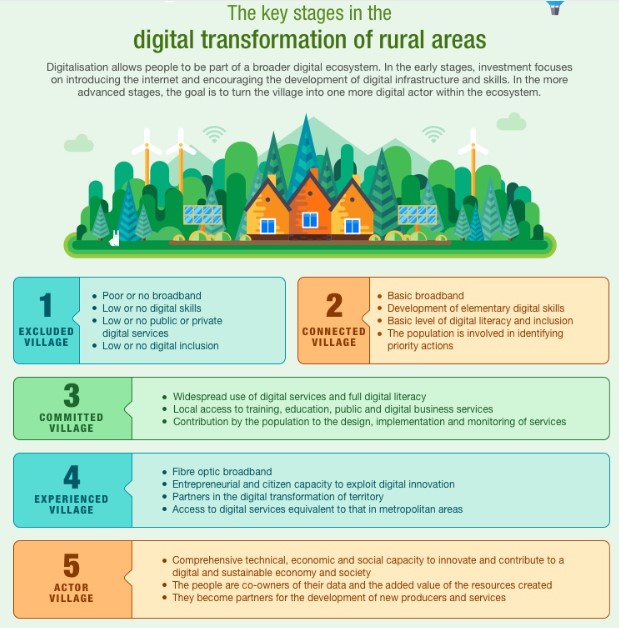
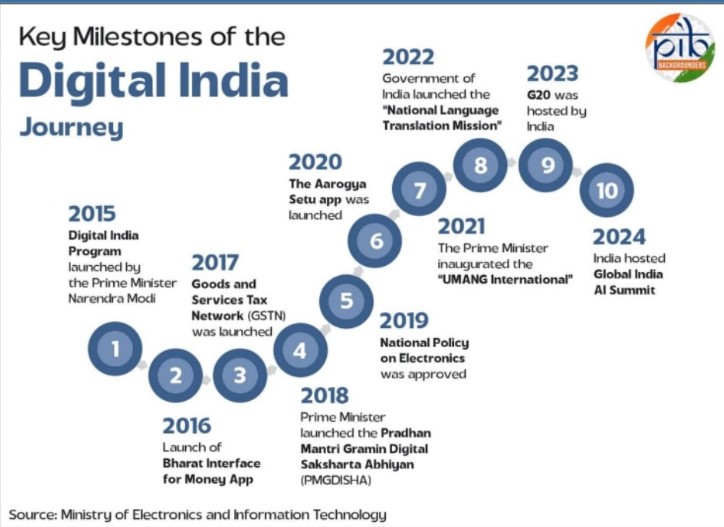

PIB| Digital Transformation of Rural India