Sugar (Control) Order, 2025
Prelims Syllabus: Governance, Economic Development
Why in the News?
The Government of India has undertaken a comprehensive review of the Sugar (Control) Order, 1966, leading to the formulation of the Sugar (Control) Order, 2025.
- Aim - To simplify and streamline the regulatory framework governing the sugar sector in line with current industry dynamics and technological advancements.
- Objective - Building a more efficient, transparent, and accountable sugar ecosystem, fostering both domestic stability and global competitiveness.
Key Highlights of the Sugar (Control) Order, 2025
- Data integration and sharing - Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD) portal will be integrated with sugar mills Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)/ Systems, Applications, and Products (SAPAs).
- The process is already going on and more than 450 sugar mills are already integrated with the portal.
- Further, GSTN data related to sale of sugar-by-sugar mills is also integrated with the portal.
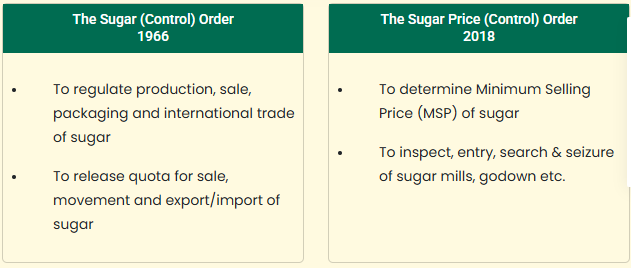
- Regulation of sugar price - Currently various provisions related to regulation of price of sugar have been mentioned in the Sugar Price (Control) Order, 2018.
- Now clause related to Sugar Price (Control) has been incorporated in the sugar control order, hence there will be no separate Sugar Price (Control) Order.
- Inclusion of raw sugar – Raw sugar is added in the control order and it will be considered in the total stock of sugar across the country.
- Currently, raw sugar is being sold by the name of khandsari/Organic; therefore, the change shall put a stop to misleading names of this product.
- Inclusion of khandsari sugar and khandsari sugar factory - Khandsari units having crushing capacity more than 500 TCD has been included in the Sugar Control Order, 2025.
- Inclusion will ensure payment of FRP to the farmers by Khandsari sugar factories & will help in the accurate estimation of sugar production.
A total of 373 No. of khandsari units (with total capacity of about 95000 TCD) are working in the country. Out of which, 66 (with total capacity of about 55200 TCD) are more than 500 TCD.
- Inclusion of various by-products - Different kinds of by-products as given below affecting sugar production from sugarcane included in the order.
- Cane bagasse, cane molasses, press mud cake or any other alternative product
- Including ethanol (produced from cane molasses, sugarcane juice, sugar syrup, sugar)
- Government will be able to regulate the diversion of sugar to ensure sufficient availability of sugar for domestic consumption.
- Inclusion of various definitions - Definitions for below items are updated to match with Food Safety Standard Authority of India (FSSAI) definitions to ensure uniformity.
- Sugar, Plantation White Sugar, Refined Sugar, Khandsari Sugar, Gur or Jaggery, Bura Sugar, Cube Sugar, Icing Sugar.
Sugar Industry Regulations
- Essential Commodities Act, 1955, - It confers the Directorate of Sugar & Vegetable Oils, Department of Food and Public Distribution to monitor the production, sale, export and stock availability of sugar in the country to ensure sufficient availability of sugar for domestic consumption at stable prices.
- Directorate is also the nodal Office to ensure sufficient capacity creation and production of ethanol in the country to meet target of 20% ethanol blending with petrol by 2025 in India.
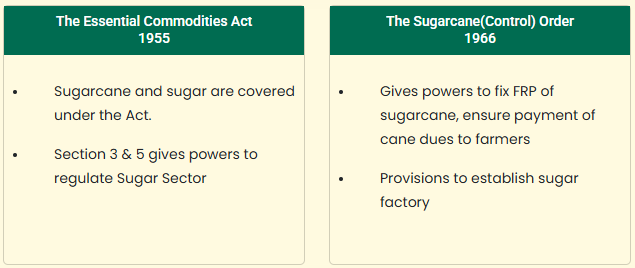
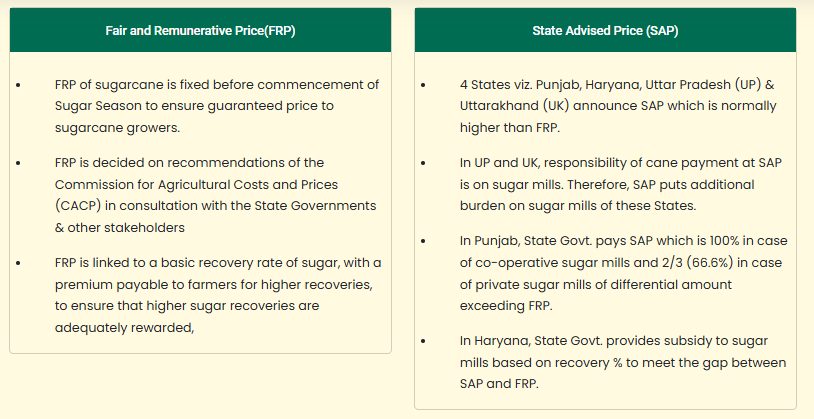
- Cane Price Payment to Sugarcane Farmers - Fair & Remunerative Price (FRP) is the minimum price that sugar mills are supposed to pay to the farmers for purchase of sugarcane.
- However, some States determine their own State Advised Price (SAP) which is generally higher than FRP and it is announced by key sugarcane producing States namely Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana &Uttarakhand.
References
- PIB | Sugar (Control) Order, 2025
- DFPD | Directorate of Sugar
Ancient Civilisation in Maharashtra
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance | History of India
Mains (GS-I): GS-I - Indian Heritage and Culture
Why in News?
Recently, Nagpur University researchers have unearthed a potentially 3,000-year-old Iron Age civilization in Maharashtra's Yavatmal district.
- Prime site of excavation – It was a mound that produced a cultural deposit measuring around 8.73 meters in thickness, indicating a multi-period and extensive occupation.
In archaeology, mounds commonly describe zones of long human settlement, in which soil and rubbish of a cultural nature accumulate over centuries or millennia.
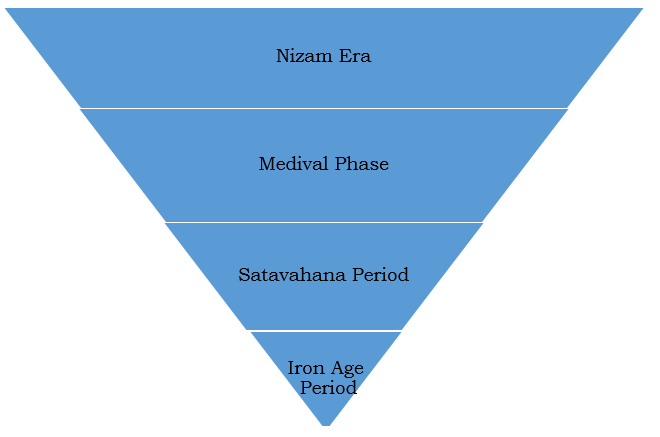
- Findings – It revealed a multi-layered settlement with distinct cultural periods.
|
1st Cultural Phase - Iron Age
|
- It represents the base layer of the settlement.
- Artefacts such as iron instruments and certain classes of pottery were found.
|
|
2nd Cultural Phase - Satavahana period
|
- It presents their inhabitation in the Deccan plateau, from about the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century CE.
- Artefacts of this era included ceramic shapes and other artefacts typical of this transformative period in history.
|
|
3rd Cultural Phase - Medieval phase
|
- Settlement contains evidence of reuse or reoccupation.
- Although it yielded fewer artefacts, their presence was sufficient to position it within the chronological sequence of the site.
|
|
4th Cultural Phase - Nizam period
|
- It is the highest occupation level.
- It indicates that the mound was subsequently reused as a watchtower during the 18th to 20th century.
|
- Architectural observation - Remains of round houses, a feature commonly used by early agrarian and tribal communities.
- The houses featured limestone floors, which indicate some planning and stability in building.
- Wooden posts has been inserted around the perimeter of the houses, probably to frame organic material roofs such as thatch and wood.
- There was a house plan with a chulha or mud oven suggesting that there was a dedicated cooking space in the house.
- Artefacts findings – Different styles and textures of pottery.
- Iron tools, beads made of semi-precious stones, terracotta beads and bone artifacts were also found.
- Significance – It offer insights into the daily lives and technological advancements of the ancient inhabitants.
- Excavated artefacts reveal that they were also involved in craft, trade, and perhaps ritualistic practices.
- The findings of beads can be seen to reflect involvement in broader trading circles or cultural exchange with the outside world.
- Future prospects – Organic samples were sent to the Inter University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) in New Delhi to reach a correct timeline.
- Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) dating, a highly precise technique employed to estimate the age of ancient materials by measuring carbon isotope decay, will be carried out by the IUAC.
Reference
Times of India| Discovery of Multi-cultural Settlement in Maharashtra
Supreme Court Judgment Regarding Modification of Arbitral Awards
Prelims (GS I) – Indian Polity and Governance.
Mains (GS II) – Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary.
Why in news?
Recently, five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court headed by Chief Justice Sanjiv Khanna ruled (4:1) that courts have limited power to modify arbitral awards.
Majority Opinion (4:1)
- The majority opinion held that courts are judicially empowered under Section 34 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 to alter arbitral awards on restricted grounds.
- The Supreme Court affirmed it can use its inherent powers under Article 142 to do complete justice in arbitration cases with great care and caution and not in derogation or suppression of the Arbitration Act's objectives.
- Modifications that are allowed under Section 34 are,
- Power to set aside invalid portions of an award from valid parts.
- To correct obvious typographical, computational or clerical errors.
- To change interest calculations post-award.
|
Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996
|
- The Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 governs arbitration and conciliation, provides a framework for resolving disputes through alternative dispute resolution (ADR) mechanisms.
- It was enacted to modernize India's arbitration framework based on the UNCITRAL Model Law.
The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) established by the in 1966 is a subsidiary body of the U.N. General Assembly (UNGA) responsible for helping to facilitate international trade and investment.
- It covers both domestic and international commercial arbitration, as well as the enforcement of foreign arbitral awards.
- The Act aims to make arbitration a fair, efficient, and capable procedure, while also minimizing the role of courts in resolving disputes.
- It ensures that arbitral awards are enforced in the same manner as court decrees.
- Section 34 Provisions – Section 34 of the act allows a party to seek setting aside of an arbitral award if,
- It is against public policy
- It is contrary to the fundamental policy of Indian law
- It was induced by fraud or corruption
- It conflicts with basic notions of morality and justice
|
Minority Opinion
- Justice K V Viswanathan who has dissented the majority opinion held that arbitral awards cannot be modified unless expressly permitted by the arbitration statute.
- His view was that courts do not have the power to modify an arbitral award under Section 34.
- This opinion aligned with the Centre's position who was represented by Solicitor General Tushar Mehta.
- He also said that power to modify is not a lesser power than the power to set aside as the two operate in separate spheres.
Reference
The Hindu| SC upholds courts’ power to modify arbitral awards
Digital Access as a Fundamental Right
Prelims (GS I) – Indian Polity and Governance.
Mains (GS II) – Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary| Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Why in news?
In a recent judgement the Supreme Court held that inclusive digital access to e-governance and welfare delivery systems is part of the fundamental right to life and liberty.
- The judgement addressed the concerns of the petitioners that disabled people find it nearly impossible to complete digital KYC processes.
Digital KYC is a process of verifying a customer’s identity using digital means, like e-documents, biometric data, or Aadhaar authentication, rather than traditional paper-based methods.
- The court interpreted the right to digital access as a fundamental right under the Article 21 (right to a dignified life) of the constitution.
Key observations and orders by the Court
- Bridging the digital divide is not merely policy discretion but a constitutional imperative.
- Digital transformation must be both inclusive and equitable.
- The unfriendly digital atmosphere has further marginalized vulnerable populations rather than integrating them into mainstream society.
- Revision of digital Know Your Customer (KYC) – To proactively design and implement inclusive digital ecosystems to make it accessible to persons with disabilities and other marginalized section of the society.
- It also asked the RBI to issue guidelines to all regulated entities to adopt alternative modes for verifying the liveness or capturing a live photograph to ensure inclusivity and user-convenience.
- Ensuring accessibility standards – The court asked various ministries to direct all the regulated entities, government or private, to follow accessibility standards.
- Appointing a nodal officer in every department responsible for digital accessibility compliance.
- Periodical audit – All regulated entities must mandatorily undergo periodical accessibility audit by certified professionals.
Reference
The Indian Express| Right to digital access part of right to life
Green Municipal Bonds
Prelims (GS I) – Economic and Social Development.
Mains (GS II) – Government policies and interventions for development.
Why in news?
Recently, Ghaziabad Nagar Nigam (GNN) issued India's first Certified Green Municipal Bond and successfully raised Rs 150 crore.
- Green Municipal Bonds – They are debt securities issued by local governments or municipalities specifically to finance projects with positive environmental or climate benefits.
- These bonds must allocate proceeds exclusively to green projects, assets, or business activities.
- They follow the same financial structure as conventional municipal bonds but with environmental commitments.
According to Council on Energy, Environment and Water report India’s Municipal Green Bonds Market Could Mobilise up to Rs 20,000 crore.
- The funds from the bonds are earmarked only for climate and environmental projects.
- Terms usually range from 5-30 years, similar to traditional municipal bonds.
- It offers tax exemptions similar to regular municipal bonds.
- Significance – The green municipal bonds help Urban financing and promotes sustainable infrastructure and urban resilience
- Regulatory framework – The guidelines are issued by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) under the Framework for Sovereign Green Bonds.
Projects Funded under Green Municipal Bonds
- Renewable energy infrastructure (solar, wind)
- Energy efficiency improvements in public buildings
- Clean transportation (electric buses, metro systems)
- Water management and conservation projects
- Sustainable waste management facilities
- Climate adaptation and resilience infrastructure
- Green public spaces and urban forestry
To know more about Municipal Bonds, click here
Ghaziabad Nagar Nigam Green Munipal Bond
- The Green Municipal Bonds was issued by Ghaziabad municipal corporation and funds raised were specifically allocated for a Tertiary Sewage Treatment Plant (TSTP).
- The initiative was developed under the Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban framework.
- Tertiary Sewage Treatment Plant utilizes advanced Membrane Filtration Technologies, including Microfiltration, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, Reverse osmosis (RO).
Reference
PIB| Ghaziabad Nagar Nigam Green Municipal Bonds
|
One Liners 03-05-2025
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
Raghuji Bhosale I of Nagpur’s
Recently, Maharashtra government acquired Maratha warrior Raghuji Bhosale I of Nagpur’s iconic sword from London for Rs 47.15 lakh. This historic purchase repatriates a symbol of Maratha valor and heritage. The sword, adorned with Mulheri hilt and gold inlay.
- Background- With Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj's support in 1728, Raghuji Bhonsale I of Nagpur ascended to prominence in the early 18th century.
Nagpur Bhonsles
- They were one of the Maratha Sardhars and a significant part of the Maratha Empire.
- They asserted descent from the Sisodia Rajputs of Udaipur.
- They played a crucial role in the expansion of Maratha territories.
- They had connections to the Hinganikar clan, with origins in the Pune district.
- Raghuji Bhosale, I founded their dynasty.
|
|
Maharashtra Diwas: State Formation Day
Maharashtra Diwas, celebrated annually on May 1st, commemorates the formation of Maharashtra state in 1960.
- Linguistic Division of Bombay State - The state's creation followed the linguistic division of the former Bombay State, honoring Marathi speakers' aspirations.
Historical Context
- Bombay State - Before 1960, Maharashtra was part of the larger, linguistically diverse Bombay State, including Gujarat and parts of Madhya Pradesh.
- States Reorganisation and the 1960 Act -The 1953 States Reorganisation Commission advocated for linguistic state divisions, leading to the Bombay Reorganisation Act, 1960, and the birth of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Significance of the Day - Maharashtra Diwas celebrates Marathi language, identity, and culture, acknowledging the struggle for statehood and reinforcing linguistic harmony.
- Maharashtra's Achievements - The day also highlights Maharashtra's growth as a cultural, industrial, and financial powerhouse over the past decades.
|
|
Geography
|
|
Uturuncu volcano
Bolivia's dormant Uturuncu volcano shows unrest due to subsurface magma and gas movement, as revealed by Oxford and Cornell University studies analyzing over 1,700 earthquakes. High-resolution imaging suggests a low risk of immediate eruption.
- Stratovolcano Features - Uturuncu is a stratovolcano characterized by dacitic lava domes and flows.
- Impressive Elevation - Rising to approximately 6,008 meters, it stands as the tallest peak in southern Bolivia.
- Long Dormancy, Current Activity - Last erupting 250,000 years ago, Uturuncu remains seismically active within a 70 km uplifted area.
- Underneath: Vast Magma Reservoir -It sits atop the massive and deep Altiplano-Puna Magma Body (APMB).
- The "Zombie" Volcano - Known as a "zombie" volcano for its persistent non-eruptive activity.
|
|
International Relations and Issues
|
|
Fall of Saigon 50th Anniversary
Vietnam solemnly and grandly celebrated the 50th anniversary of the fall of Saigon on April 30, 2025.
- "Day of Southern Liberation" - Known as the "Day of Southern Liberation for National Reunification," it signifies the end of the Vietnam War.
- Commemorative Events - The anniversary featured significant military parades, an air show, and diplomatic engagements with China and the U.S.
- Historical Conflict - The Vietnam War (1955-1975) pitted communist North Vietnam (backed by USSR and China) against U.S.-supported South Vietnam.
- Fall of Saigon and Casualties - The fall of Saigon on April 30, 1975, led to Vietnam's reunification, but the war caused immense loss: ~3 million Vietnamese and ~60,000 American deaths.
- Significance of Celebrations - The events aimed to commemorate reunification, honor war heroes, and showcase Vietnam's growing military and diplomatic strength.
|
|
Environment
|
|
World Tuna Day (WTD)
WTD sponsored by the UN, is observed annually on May 2.
- Aims- To promote awareness about the importance of sustainable science-based fishing practices and marine conservation.
- Ensure long-term availability of tuna stocks.
- Support efforts aligned with the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially SDG 14 – Life Below Water.
- Importance - Tuna is vital for global food security, drives economic development, and is a key part of marine biodiversity.
- WTD Addresses - The dangers of overfishing and promotes responsible fishing methods.
- About Tuna - Are a genus of saltwater fish (Thunnus) belonging to the mackerel family (Scombridae).
- They are ocean-dwelling, ray-finned bony fish known for their streamlined bodies and powerful swimming abilities.
|
|
Security
|
|
National Security Advisory Board (NSAB).
Following the recently Pahalgam terror attack and escalating tensions with Pakistan, India has revamped its National Security Advisory Board (NSAB)
- New Appointment – PM Modi has appointed Alok Joshi, the former head of the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW), as the new NSAB Chairman.
- About NSAB - NSAB offers independent, non-partisan perspectives and policy options to the National Security Council (NSC), which is headed by the PM.
- Focuses - On long-term analysis of national security issues and provides strategic guidance on evolving threats and national interests.
- Functions - Provides policy perspectives and recommendations to the NSC.
- Offers strategic guidance on evolving threats and national interests.
- Focuses on research, foresight, and independent analysis to support government decision-making.
- Aids in formulating comprehensive security doctrines.
- Recommends defense, cyber, diplomatic, and internal security measures.
- Helps prepare key strategic documents such as the Nuclear Doctrine and National Security Reviews.
|
|
Science
|
|
Phthalates
2025, recent New York University studies have increasingly highlighted the risks associated with phthalates, common chemicals in household plastics.
- Global Impact on Cardiovascular Health - Study linked phthalate exposure to over 356,000 cardiovascular-related deaths globally in 2018, with the Middle East, South Asia, East Asia, and the Pacific being most affected.
- About Phthalates - Phthalates are chemicals used to increase the flexibility of plastics, earning them the moniker "everywhere chemicals" due to their presence in food containers, medical devices, and personal care items.
- Mounting Health Concerns - Beyond cardiovascular issues, concerns are growing about phthalates' potential links to obesity and ADHD.
- Phthalates as Endocrine Disruptors - Phthalates are identified as endocrine disruptors, capable of interfering with the body's hormonal systems, potentially causing reproductive problems and pregnancy complications.
- Cardiovascular Risks and Inflammation - Research suggests that daily phthalate exposure is associated with inflammation in heart arteries, thereby elevating the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
|



