Prelims – History of India.
Mains – General Studies-I (Indian Heritage and Culture).
Why in news?
The Indian government has recently condemned an auction of ancient Indian gems and issued a legal notice to stop the “unethical” sale of the relics, stating that it should be treated as the sacred body of the Buddha.
William Peppe
The 1878 Indian Treasure Trove Act establishes the legal framework for buried wealth. Treasure is defined as "something of any value hidden in the soil, or in anything affixed thereto, “It only applies to riches that have been buried for less than 100 years.
Stance of the Indian Government
Reference
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance | Indian Polity and Governance | Economic and Social Development-Sustainable Development.
Mains – General Studies- II (Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources | Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance)
Why in news?
The Human Development Index (HDI), 2025 was recently released by the United Nations Development Programme.
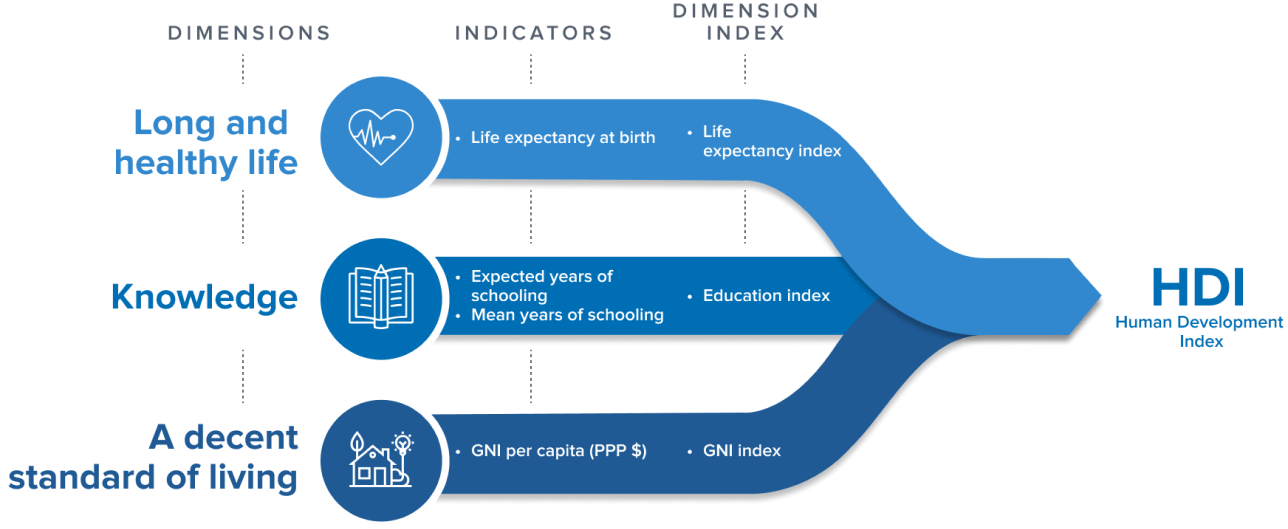
Key Findings of the 2025 Human Development Report on India
Reference
Prelims: Science and Technology | Current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
Recently, India has developed the world’s first-ever genome-edited rice varieties.
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes are made up of DNA. Some genes act as instructions to make molecules called proteins, which are needed for the body to function. However, many genes do not code for proteins, instead they help control other genes.
|
Gene Editing by Bacteria |
|
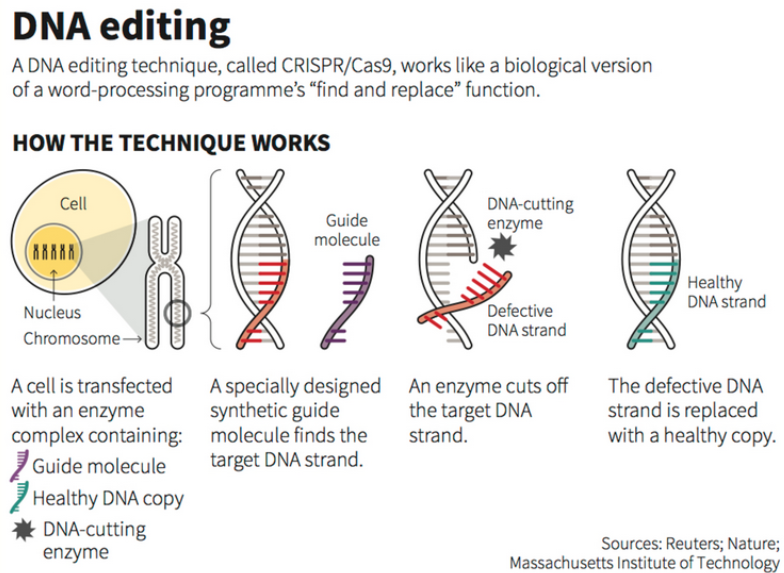
Gene Modification
Reference
PIB| Gene Editing using CRISPR Technology
Prelims: Bio-diversity | Current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
The National Biodiversity Authority has released a new set of rules to manage sharing of benefits generated through the use of biological resources.
Biological Diversity Regulation 2025 replaces ‘The Guidelines on Access to Biological Resources and Associated Knowledge and Benefits Sharing Regulations 2014’, which did not include digital sequence information in the ambit of genetic resources.

Quick facts
References
Down to Earth| Notification of Access and Benefit Sharing Regulation 2025
Why in News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved grant of fresh coal linkages to Thermal Power Plants of Central Sector/State Sector/ Independent Power Producers (IPPs) through revised SHAKTI policy.
Central Sector Thermal Power Projects (TPPs) shall continue to get coal linkage on nomination basis on the recommendation of Ministry of Power, whereas, the linkages earmarked to the States on nomination basis on the recommendation of Ministry of Power may be utilized by the States in the State Generating Company.
The revised SHAKTI Policy, besides supporting Brownfield expansion, will promote setting up of Greenfield Thermal Power Projects primarily at pithead sites (nearer to the coal source).
Reference
PIB| Notification of Revised SHAKTI Policy
|
One Liners 08-05-2025 |
|
History, Art and Culture |
|
Commemorate the 300th birth anniversary of Ahilyabai Holkar, Recently, Maharashtra announced it will produce a multilingual biopic on Ahilyabai Holkar's life for her 300th birth anniversary, showcasing her governance and welfare contributions on Doordarshan and OTT.
About Ahilyabai Holkar
|
|
World Red Cross Day (WRCD) annually on May 8th, honoring the global humanitarian network and its dedicated volunteers and staff.
|
|
Geography |
|
Poonch Pakistan's retaliation after India's Operation Sindoor struck Poonch civilians, killing 12 and destroying property including a Gurudwara. "All Eyes on Poonch" reflects rising LoC tensions and calls for peace.
|
|
Ancient Wildfire Evidence in Godavari Basin Scientists recently discovered palaeofire (ancient wildfire) evidence from the Permian Period (250 million years ago) in India's Godavari Basin.
|
|
National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) Flags Damage in KLIP Barrages NDSA has reported "irreparable damage" to three barrages within Telangana's Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP).
|
|
Polity & Governance |
|
Haryana's Artist Support Scheme Launched Recently,Haryana government has introduced the “Pandit Lakhmi Chand Kalakar Samajik Samman Yojana” to provide financial assistance to senior artists and art scholars.
|
|
Environment |
|
Trespassing Threatens Bhimgad Sanctuary Recently uncontrolled public trespassing into the ecologically vital Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) in Khanapur taluk raises serious conservation concerns.
|
|
Yangtze Porpoise Decline Evidenced by Poetry Recent research utilizing classical Chinese poetry reveals a significant decline in the distribution of the critically endangered Yangtze finless porpoise.
|
|
Security |
|
Operation Abhyas Following a Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) directive, recently Bengaluru held a significant civil defence mock drill, ‘Operation Abhyas’.
|
|
Science |
|
World Thalassaemia Day 2025 May 8th, marks World Thalassaemia Day.
|