7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS III – Conservation, Environment Pollution & degradation, Environment impact assessment
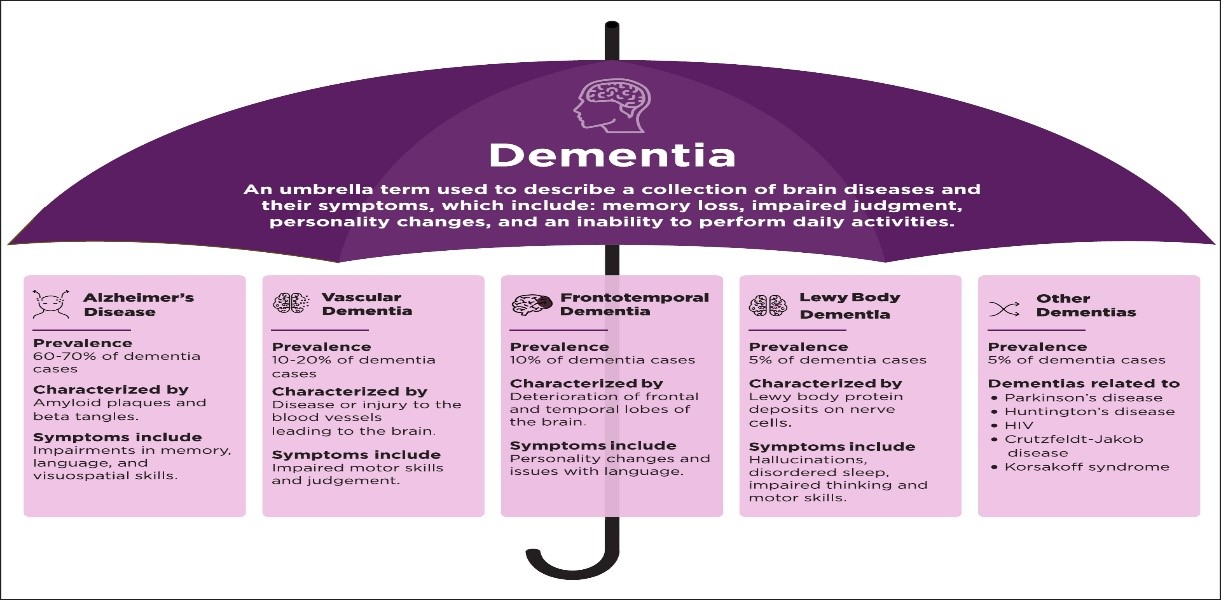
Recently, Cambridge University researchers have found that long-term exposure to air pollution is linked to an increased risk of developing dementia.
|
Primary pollutants |
|
|
Secondary pollutants |
|