Mains: GS3 - Science and Technology: Developments and their applications and effects in everyday life | Infrastructure - Energy
The recent global shift towards renewable energy sources, Biofuels have emerged as a promising alternative to fossil fuels, leaving the questions about its efficiency in net energy consumption.
|
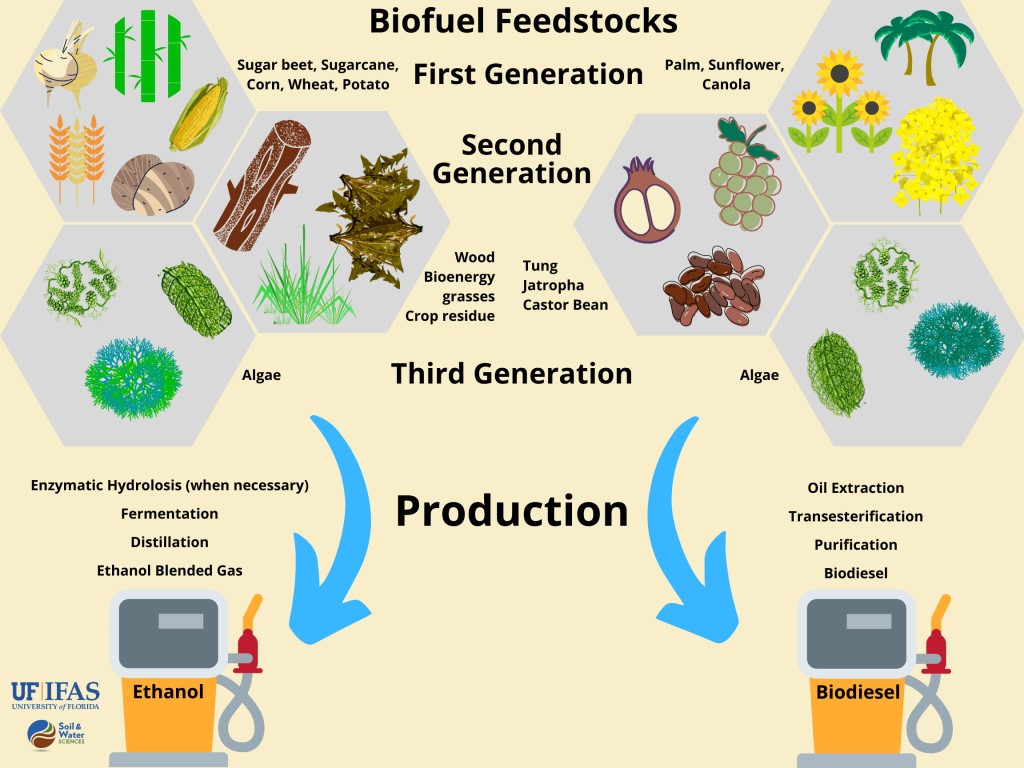
Generation |
Source |
Example |
|
First generation (1G) |
Food sources - corn, sugarcane, and vegetable oils. |
Bioethanol, biodiesel, biogas |
|
Second generation (2G) |
Non-food sources and the waste left from the food resources - Municipal solid waste, wood chips etc., |
Cellulose ethanol, biodiesel |
|
Third generation (3G) |
Algae - It consists of 40% of lipids which can be converted to biodiesel or synthetic petroleum. |
Butanol, Gasoline, Jet fuel |
|
Fourth generation (4G) |
Produced from genetically engineered bio algae |
Humans directly manage around 0.5 % of global biomass, mostly as food crops.
Aerobic Respiration uses oxygen to fully extract energy from glucose, releasing CO₂ and water for cellular work. Anaerobic Respiration is faster but less efficient, producing energy-rich byproducts like ethanol and lactic acid.
Sugarcane ethanol reduces greenhouse gas emissions, but most biofuels do not.
|
Biofuel-Ethanol |
|