7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance | Geography
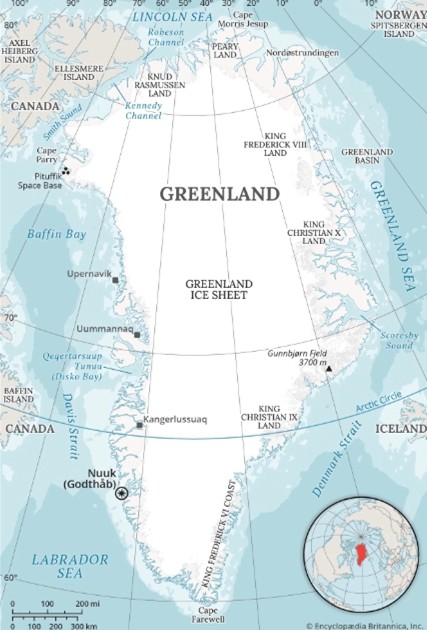
Why in News?
Recently, Greenland has been in focus after U.S. President Donald Trump called for immediate talks on acquiring the island.
References