National Scheme for Industrial Training Institute (ITI) Upgradation
Prelims: Economic Development| Social Sector initiatives | Current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
Recently, Cabinet approved National Scheme for Industrial Training Institute (ITI) Upgradation and Setting up of 5 National Centres of Excellence for Skilling.
- Launched by – Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Objectives – To position existing ITIs as government-owned, industry-managed aspirational institutes of skills, in collaboration with State Governments and industry.
Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) have been the backbone of vocational education and training in India since the 1950s, operating under State Governments.
- Funding pattern - Centrally Sponsored Scheme, includes Central share, State share and Industry share.
- It has co-financing to the extent of 50% of Central share by the Asian Development Bank and the World Bank, equally.
- Focus - Upgradation of 1,000 Government ITIs in hub and spoke arrangement with industry aligned revamped trades (courses).
- Capacity Augmentation of 5 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs).
- Target – Over a 5-year period, 20 lakh youth will be skilled through courses that address the human capital needs of industries.
- Ensuring alignment between local workforce supply and industry demand, thereby facilitating industries, including MSMEs, in accessing employment-ready workers.
- Implementation - For the first time, it seeks to establish deep industry connect in planning and management of ITI upgradation on a sustained basis.
- It will adopt an industry-led Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) model for an outcome-driven implementation strategy, making it distinct from previous efforts to improve the ITI ecosystem.
- Activities – Infrastructure upgradation for improved Training of Trainers (ToT) facilities will be undertaken in 5 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) like
- Bhubaneswar, Chennai, Hyderabad, Kanpur, and Ludhiana
- Additionally, pre-service and in-service training will be provided to 50,000 trainers.
- Significance - It will create a pipeline of skilled workers aligned with industry demand, addressing skill shortages in high-growth sectors such as electronics, automotive, and renewable energy.
- It aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision of Viksit Bharat (developed India) by 2047.
Reference
PIB| Approval for launch of NSTIs
Development and Welfare Board for the Denotified, Nomadic, and Semi-Nomadic Communities (DWBDNC)
Prelims: Social Development| Inclusion | Social Sector Initiatives
Why in News?
Recently, Union Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) reviewed the implementation of the SEED (Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs) programme of Development and Welfare Board for De-notified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Communities (DWBDNC).
- DWBDNC - It is a Society Registered under Societies Registration ACT 1860.
- Constituted in - 2019
- Head Quarter at - New Delhi
- Composition
- Chairperson – Appointed by the Government of India
- Member Secretary - Chief Executive Officer of the Board in the rank of Joint Secretary to the Government of India
- 3 Members - Joint Secretary, Department of Social Justice & Empowerment, a representative of Ministry of Tribal Affairs & a representative of Department of School Education
- Nominated members – 5 eminent persons working in the field of these communities to be nominated by the Government of India.
- Tenure – A period of 3 years extendable up to 5 years for Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
- Powers and Functions - To formulate and implement Welfare and Development programmes.
- To identify the locations/areas where these communities are densely populated and to assess and identify gaps in accessing existing programmes and entitlements.
- To collaborate with Ministries/implementing agencies to ensure the ongoing programmes meet the special requirements.
- To monitor and evaluate the progress of the schemes of Government of India and the States/UTs with reference to these communities.
- To do any other related work as may be assigned by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
|
Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs (SEED)
|
- Launched in – 2022, by Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Objectives - Providing quality coaching to DNT candidates for competitive examinations
- Providing health insurance to DNT communities,
- Promoting livelihood initiatives at the community level for small groups within DNT/NT/SNT communities,
- Providing financial assistance to DNT individuals for constructing houses.
- Beneficiaries – It targets families with an annual income of Rs 2.50 lakh or less, who are not availing benefits from similar schemes of the central or state governments.
|
References
- PIB| Reviewing SEED Scheme of DWBDNC
- DWBDNC| Development and Welfare Board of DNC
Air Defence Systems
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Mains (GS III): Security challenges and their management in border areas
Why in News?
Recently, India deployed a range of air defence systems in response to Pakistan’s drone and missile attacks, which were immediately tracked and destroyed.
- Primary objective – To take out threats from the skies like enemy fighter aircraft, unmanned drones, or missiles.
- Technology used – It is done with the help of a complex system of radar, control centres, defensive fighter aircraft, and ground-based air defence missile, artillery, and electronic warfare systems.
- Working – It can be sub-categorised into 3 interlinked operations
- Detection
- Tracking
- Interception
- All these 3 aspects of an air defence system have to work together as a cogent whole called “C3” or a “command, control and communication” system.
- Detection – It is typically done by radar, although satellites may be used in certain circumstances, such as an enemy launching an Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM).
- Radar sends out beams of electromagnetic radio waves by a transmitter which are reflected by the objects that they hit.
- A receiver then collects the returning radio waves and makes inferences such as the distance of the threat, its speed, and its specific nature (what kind of aircraft/ missile).
- Tracking – It is typically done using a combination of radar and other sensors such as infrared cameras or laser rangefinders.
- The accuracy of tracking is crucial for effectively neutralising the enemy without targeting false threats.
- Interception – Depending on the challenges they foresee; nations utilize a wide assortment of weapons to neutralise aerial threats.
- Fighter Aircrafts
- Surface-to-Air Missiles
- Anti-Aircarft Artillery
- Electronic Warfare

|
Anti-Aircraft Artillery (AAA)
|
- They fire shells rapidly, at rates of over 1,000 rounds per minute.
- AAA shells are designed to explode at predetermined altitudes so as to disperse shrapnel over a wide area.
- This makes an AAA battery effective even if it does not achieve a direct hit.
- When augmented with automated fire-control systems, they remain crucial last-ditch defences, and are also used for specialised anti-unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) roles.
|
|
Fighter aircrafts
|
- These agile aircraft can be scrambled at a moment’s notice, and they climb quickly to altitude and neutralise an enemy aircraft before it deploys its weapons.
- Interceptors are equipped for air-to-air combat with cannon, rockets, a suite of visual-range and beyond-visual-range missiles, and electronic warfare systems.
|
|
Surface-to-Air Missiles
|
- They are more effective than anti-aircraft artillery (AAA), and do not put pilots in danger like interceptors.
- They are radar-, infrared-, or laser-guided. In addition to being operated from the ground, SAMs can also be launched from ships.
- Heavy long-range systems which are fixed or semi-mobile;
- Medium-range vehicle-mounted systems that can fire on the move
- Short-range man-portable air-defense systems (or MANPADS)
|
|
Electronic Warfare
|
- It is most often used to jam enemy radar and targeting systems, so as to impede its ability to accurately and effectively deploy its weapon.
- It can confuse attack drones or prevent enemy air-to-surface missiles from homing in on targets.
- These can operate from both land and air, including from specialised EW aircraft, such as the US Navy’s Boeing EA-18G Growler.
|
- Beyond the technical capabilities superior communication and decision-making capabilities are crucial for an effective air defence.
Reference
The Indian Express| Working of Air Defence System
Related News – S-400 System | Akash Missile
Arbitral Award
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance.
Mains – General Studies- II (Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary)
Why in news?
Recently, in a 4:1 majority ruling, a five-judge Bench of Supreme Court held that the Appellate Courts may exercise limited powers to modify arbitral awards under certain specific circumstances.
- Arbitral award – Is simply the final decision made by the arbitrator.
- It is binding on all parties involved, similar to a court judgment.
- Arbitration – Is an alternative dispute resolution mechanism where parties agree to resolve their disputes outside of courts through a neutral third party called an arbitrator.
- This process is governed by the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 in India.
- Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 – It does not expressly empower courts to modify or vary an arbitral award.
- Section 34 of the 1996 Act only confers upon courts the power to set aside an award.
Supreme Court Judgment (2025)
- A five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court delivered an important judgment in Gayatri Balasamy v. ISG Novasoft Technologies Ltd. clarifying courts' powers regarding arbitral awards.
- Modify arbitral awards – The courts can modify arbitral awards in limited circumstances in the following scenarios:
- When separating valid from invalid portions (severability).
- To correct obvious errors (clerical, computational, or typographical).
- To adjust post-award interest rates when necessary.
- Supreme Court's Special Powers – The Supreme Court can use its powers under Article 142 of the Constitution to modify awards, but must do so cautiously.
- Interest Modification – Courts cannot change interest awarded during arbitration proceedings.
- Courts can modify interest for the period after the award is given.
- Severance Power – All judges agreed that courts can "sever" or separate invalid portions of an award while keeping the valid parts intact.
Significance of Arbitral Awards
- Binding Decision – The arbitral award is binding on the parties, meaning they are legally obligated to comply with it.
- Finality – Generally, there is limited scope for challenging an arbitral award in courts to ensure the process remains efficient.
- Enforcement – An arbitral award can be enforced by a court in the same way as a decree of that court.
- Time and Cost Efficiency – Generally faster and less expensive than court litigation.
- Expertise – Arbitrators with specialized knowledge can be selected for complex disputes.
Reference
- Supreme Court Observer | Arbitral Award
- SSC Times | Arbitral Award
Gully Erosion
Prelims – Indian and World Geography
Mains – General Studies-I (Geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features)
Why in news?
A recent study published in Scientific Reports (February 2025) highlights gully erosion as a major and often overlooked driver of global land degradation, exacerbated by climate change and land-use changes.
- Gully erosion is the most severe form of soil erosion, characterized by deep incisions (several tens of meters) into soil, caused by surface and subsurface water runoff.
- It differs from other types of erosion due to its depth, higher specific soil losses, and unpredictable nature, often resembling the destructive impact of landslides.
Causes of Gully Erosion
- Gully erosion is a result of a complex interplay of natural and human factors.
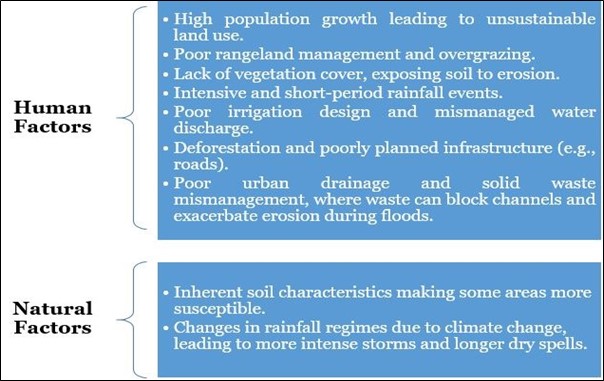
Consequences of Gully Erosion
- Loss of Fertile Topsoil – The most significant impact is the irreversible loss of topsoil, which can take centuries to rebuild, severely affecting agricultural productivity.
- Impact on SDGs – It directly undermines efforts towards zero hunger, clean water and sanitation and climate action.
- Damage to Infrastructure – Gullies can swallow farmland, roads, and buildings, disrupting livelihoods and connectivity.
- Increased Water Stress and Droughts – Degraded land loses its capacity to retain water, exacerbating water scarcity and drought conditions.
- Displacement and Migration – In severe cases, gully erosion can lead to village abandonment and forced migration.
- Agricultural productivity – Prolonged gully erosion leads to the formation of "badlands," severely impacting agricultural productivity.
Impact in India and world
- Globally, research has identified numerous locations where gully erosion has caused severe damage to life and property, with Nigeria being particularly affected.
- In India, gully landforms are present in 19 states and the National Capital Region, with at least 77 districts requiring urgent intervention.
- The most affected states in India are Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh, followed by Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
Gully erosion poses a significant challenge to India's commitment to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030 under the UN Convention to Combat Desertification.
Mitigation and Management
- Mitigating existing gullies is challenging and costly, and predicting their formation is difficult, limiting proactive interventions.
- The primary approach is often reactive land management after gully formation, including:
- Establishing vegetation cover to stabilize the soil.
- Implementing soil and water conservation measures like check dams and gully plugging.
- Runoff attenuation and/or diversion techniques.
- The appropriateness of these measures depends on local runoff characteristics and gully stability.
- An important aspect of mitigation is preventing the removal of eroded sediment, allowing for the formation of new wetlands that can further stabilize the land and support vegetation.
Reference
Down to Earth | Gully erosion
|
One Liners 09-05-2025.
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
Jenu Kuruba Return
Jenu Kuruba families are re-occupying ancestral homes in Nagarhole National Park.
- Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) Community - This PVTG mainly resides in Karnataka's Kodagu and Mysore districts.
- "Honey People" - Their name reflects their traditional honey collection and forest produce gathering.
- Social Structure - They live in Hadi settlements with headmen (Yajamana) and ritual heads (Gudda).
- Beliefs and Culture - They revere supernatural beings, and their culture includes songs and dances about their life.
- Significance - The re-occupation marks a crucial step for the Jenu Kuruba and their connection to their land.
|
|
Geography
|
|
Anak Krakatau Tsunami
Recent research indicates the deadly 2018 Anak Krakatau tsunami, triggered by a volcanic flank collapse, might have been predictable through years of detectable "silent slippage."
- The Catastrophic 2018 Eruption - Caused a flank of Anak Krakatau to slide into the ocean, generating a devastating tsunami that killed over 400 people and caused widespread destruction in Java and Sumatra.
- Detecting Silent Volcanic Slippage - Penn State research using satellite-based Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) revealed over a decade of gradual flank movement, with accelerated slippage preceding the eruption.
- Implications for Prediction - Highlights the potential of satellite monitoring to predict volcanic disasters by identifying instability. The absence of ground-based instruments hindered prediction in this case, revealing a critical monitoring gap.
- Acceleration as a Key Warning – Shows approximately 15 meters of slippage between 2006 and 2018, with periods of accelerated movement acting as potential early warning signs of the impending collapse.
- Future Monitoring Strategies - The research advocates for integrating InSAR technology for real-time monitoring of oceanic volcanoes, especially where ground-based systems are lacking, offering a crucial tool for early detection of hazardous volcanic activity.
|
|
Polity & Governance
|
|
CCI Modernizes Predatory Pricing Assessment
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has released draft CCI (Determination of Cost of Production) Regulations, 2025, to update its assessment of predatory pricing under the Competition Act, 2002, replacing the 2009 rules.
- Understanding Predatory Pricing - Predatory pricing, illegal under the Competition Act, involves a dominant firm pricing below production cost to eliminate rivals and later raise prices.
- Key Regulatory Changes - The 2025 draft shifts from market value to average total cost for assessments, focusing on average variable cost as a marginal cost proxy for more accurate evaluations, especially in digital markets.
- Sector-Agnostic Framework - The proposed regulations adopt a flexible, sector-agnostic approach to suit diverse industries, including the rapidly evolving e-commerce and quick commerce sectors.
- Stakeholder Feedback - While some stakeholders sought clarity on cost assessment across sectors, the CCI affirmed its commitment to a cost-based framework aligned with international best practices.
- Significance of the Update - Is vital for effectively addressing unfair practices, particularly in the digital economy, enhancing the CCI's ability to scrutinize predatory pricing and deep discounting. The regulations aim for global standards alignment.
|
|
Delhi's PRASHAST App for Early Disability Detection
Delhi's Directorate of Education has introduced the PRASHAST app to facilitate the early identification of students with disabilities, aligning with the National Education Policy 2020 and the Right to Education Act 2009.
- This aims to - Foster inclusive learning environments.
- Understanding Neurodiversity, Neurodiversity encompasses variations in brain functions like learning and sociability, including conditions such as ADHD and autism.
- PRASHAST App - Enables school-level screenings for 21 types of disabilities. Trained teachers observe students using structured checklists and refer those flagged for further assessment and support under the Samagra Shiksha initiative.
- Teacher Training and Observation - Teachers play a vital role, utilizing the app's checklists to observe both visible and subtle indicators of disabilities during classroom interactions.
- Challenges in On-Ground Implementation - Include large class sizes limiting individual attention, long waiting times for necessary therapy services, and potential parental resistance due to social stigma or lack of awareness.
- Support Systems - Special educators develop individualized learning plans for identified students. Government resource centers offer access to clinical psychologists and therapies, although bureaucratic processes can sometimes cause delays in service delivery.
|
|
Environment
|
|
Spiti Valley Snow Leopard Encounter
Tourists in Himachal Pradesh's Spiti Valley experienced a rare sighting of a snow leopard, a notoriously elusive predator.
- Snow Leopard - (Panthera uncia) is a medium-sized big cat inhabiting the rugged mountains of Central and South Asia. With an estimated wild population of 3,920 to 6,390 across a vast range, it's rarely seen, earning the moniker "ghost of the mountains."
- Global Distribution - These majestic creatures inhabit high-altitude regions (1,800m to 5,500m) across 12 countries, including China, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Russia.
- Indian Habitat - Snow leopards are primarily found in the cold, arid, and rugged terrains of Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Distinctive Features - Their pale grey fur with dark rosettes provides excellent camouflage. A dense undercoat and long outer fur offer insulation and protection. Their long tails (almost half their 7-foot length) aid balance and warmth.
- Solitary Nature - Adult snow leopards are typically solitary animals, living alone except during mating season or when raising their young.
|
|
Security
|
|
INS Vikrant: Indigenous Milestone
India's first indigenously built aircraft carrier, INS Vikrant (IAC-1), marks a significant step towards self-reliance. It's India's largest warship.
- Design and Construction - Designed by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau (WDB) and built by (Cochin Shipyard Limited) CSL in Kochi, it's the first of its Vikrant-class.
- Power and Combat Systems - Propelled by four GE LM2500+ turbines (110,000 HP), it features a Combat Management System (CMS) developed by Tata Power and a Russian firm.
- Size and Performance - Measuring 262m long and displacing 43,000 tonnes, it reaches 28 knots with a 7,500 nm range.
- Crew and Capacity - It accommodates 1,600 personnel, including women officers. It has 18 floors and around 2,300 compartments.
- Onboard Infrastructure - Features include a 16-bed hospital, operation theatres, and pantries feeding 600 simultaneously.
|
|
S-400 Defense System Success
India's S-400 "Sudarshan Chakra" missile defense system reportedly thwarted a significant Pakistani attempt to attack 15 Indian cities.
- Details of the Attempted Attack - The attempted attacks, involving missiles and drones, occurred in the early morning of May 8, 2025, over Punjab, between approximately 1:10 AM and 1:20 AM.
- S-400 System Overview - Is a long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) system from Russia's Almaz Central Design Bureau, considered a world-leading air defense system.
- Threats Intercepted - It counters various aerial threats: stealth aircraft, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, and drones/UAVs.
- S-400 Squadron Composition - A typical S-400 squadron includes 2 batteries (each with 6 launchers), command-and-control units, surveillance and engagement radars, and can carry/launch up to 128 missiles.
- India's S-400 Acquisition - India's Rs 35,000 crore deal with Russia (2018) was for five squadrons. Three are operational as of 2025, with two more expected by 2026. They are deployed along strategic borders.
|
|
Science
|
|
E-Passport Rollout in India
India has launched chip-based e-passports nationwide, enhancing travel security and efficiency with RFID and biometrics.
- Significance of the Move - This aligns India with global standards, modernizing travel documentation under the Passport Seva Programme 2.0.
- E-Passport Key Features - Embedded chips securely store personal and biometric data; barcodes allow digital address access.
- Goals of the Initiative - Aims to boost security, streamline immigration, combat fraud, and support digital governance.
- Implementation Status - Launched April 1, 2024, e-passports are now issued in cities like Chennai through select offices.
- 2025 Passport Rule Changes - New rules include mandatory birth certificates (post-Oct 2023 births) and digitally embedded addresses.
|
|
International Relations
|
|
Quad Concludes Logistics Network Simulation
The Quad nations – Australia, India, Japan, and the USA – recently concluded an Indo-Pacific Logistics Network (IPLN) simulation exercise in Honolulu, Hawaii.
IPLN Initiative - The IPLN is a Quad-led initiative designed to enhance the partners' ability to jointly utilize their logistics capabilities across the Indo-Pacific region.
Primary aim of - The IPLN is to facilitate a more rapid and efficient civilian response to natural disasters affecting countries within the Indo-Pacific.
Leveraging Shared Capabilities - By enabling the Quad partners to leverage their combined logistics resources, the IPLN seeks to streamline aid delivery and support during humanitarian crises.
Broader Quad Commitment - The IPLN, alongside the Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness, underscores the Quad's dedication to a free and open Indo-Pacific.
Strengthening Practical Cooperation - These initiatives highlight the Quad's focus on strengthening practical cooperation among its member nations to effectively address shared regional challenges.
|

