7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS III – Science and Technology- Effects of Liberalization on the Economy
Recently, Bank of England places limits on the transaction of stablecoin transactions.
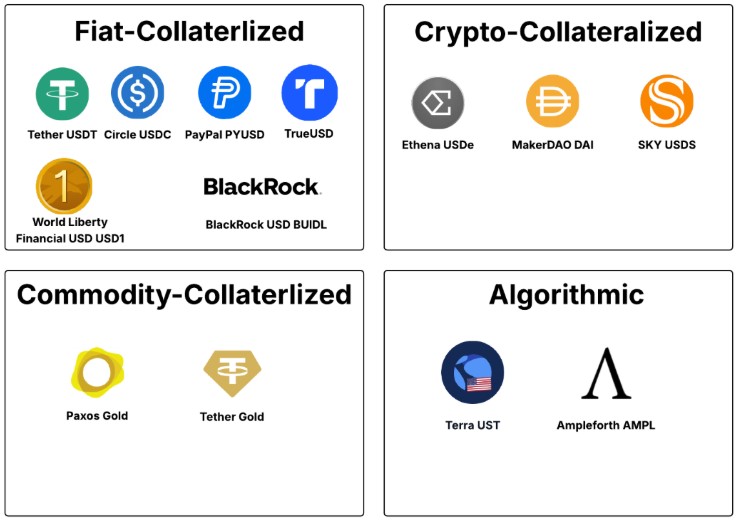
The Indian Express| Stablecoins