7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains: GS III – Science and technology
Recently, Starlink Company has decided to launch the satellite based internet services in India.
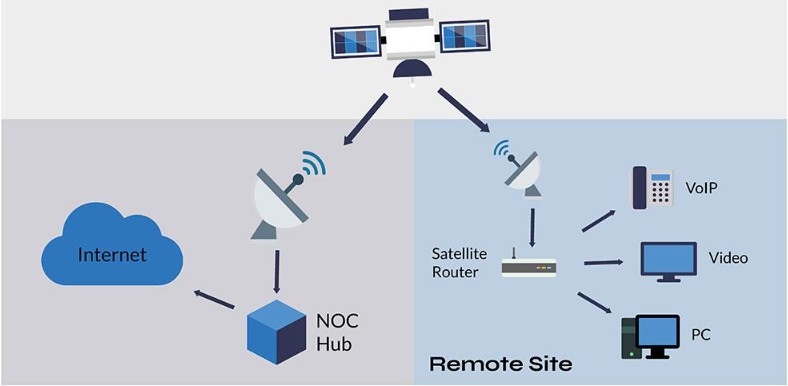
User terminal is the device that is used by an end user to access the services provided by the wireless networks.
Starlink Internet Project
|
|
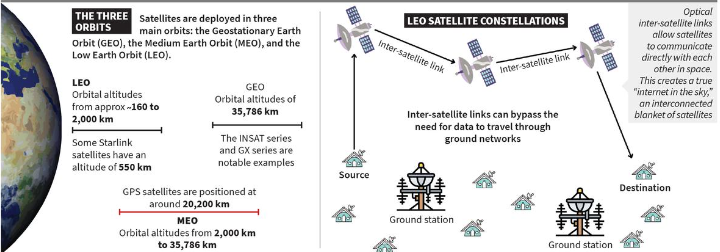
The Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) |
Viasat, is a global communications company specializing in satellite-based internet and networking systems for both commercial and government sectors.
Latency refers to the delay, or time it takes, for data to travel from one point to another on a network.
|
|
The Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) |
|
|
The Low Earth Orbit (LEO) |
|