7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims – Indian and World Geography
Mains – General Studies-I (Geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features)
Why in news?
A recent study published in Scientific Reports (February 2025) highlights gully erosion as a major and often overlooked driver of global land degradation, exacerbated by climate change and land-use changes.
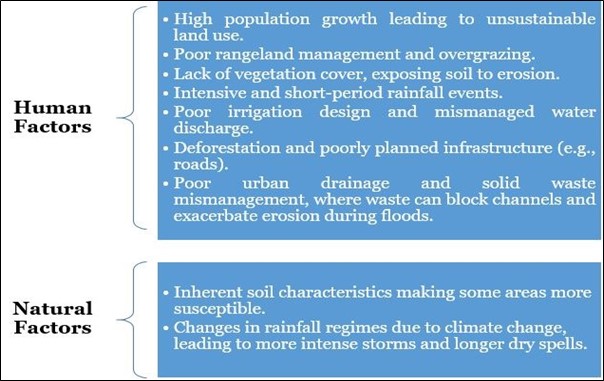
Causes of Gully Erosion
Consequences of Gully Erosion
Impact in India and world
Gully erosion poses a significant challenge to India's commitment to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030 under the UN Convention to Combat Desertification.
Mitigation and Management
Reference