Click here for Part I.
What is the issue?
- FRDI bill is expected to be tabled in winter session of the parliament.
- But it has raised concerns among depositors on how they would be repaid in case of liquidation of banks.
What is the existing method?
- The Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) is an RBI subsidiary, established in 1971.
- In case a stressed bank had to be liquidated, the depositors would be paid through DICGC.
- It insures all kinds of bank deposits up to a limit of Rs.1 lakh.
- It is mandatory for banks to pay a sum to the DICGC as insurance premium.
What are the concerns in the proposed bill?
- The proposed Bill seeks closure of the DICGC, as the credit guarantee will be taken care of by the Resolution Corporation.
- The Resolution Corporation is empowered to monitor financial firms, calculate stress and take corrective actions in case of a failure.
- According to Section 52 of the proposed Bill, depositors will lose their rightful claim to retrieve their savings in case of liquidation of banks and insurance companies.
- It does not specify the fixed insured amount to be paid by the bank to the resolution corporation.
- It does not even specify the amount a depositor would be paid in case of liquidation.
- It is given that corporation may decide on the compensation in case of any bank failure, which could well be less than Rs. 1 lakh.
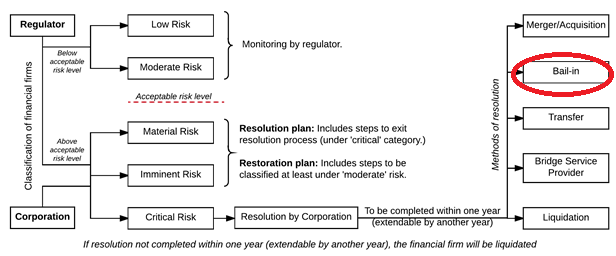
- Bail In - It also proposes 'bail-in' as one of the methods to resolution, where the banks issue securities in lieu of the money deposited.
- In the past, the bail-in efforts had largely worked against depositors.
- The ambiguities on how the depositors would be repaid needs to be addressed.
- Thus, there is a need to enhance insurance cover on deposits which should ideally continue to be managed by the RBI.
Source: BusinessLine
