Why in news?
FRDI Bill was introduced in Parliament during Monsoon Session 2017.
What are financial firms?
- Financial firms include banks, insurance companies, and stock exchanges, among others.
- Since they transact with each other, their failure may have an adverse impact on financial stability and result in consumers losing their deposits and investments.
- e.g In 2008, the failure of a Lehman Brothers impacted the financial system across the world.
- Currently, there is no specialised law to resolve financial firms.
- Provisions to resolve are found scattered across different laws.
What are the highlights of the bill?
- The Bill seeks to create a consolidated framework for the resolution of financial firms.
- It repeals the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1962 and amends 12 other laws.
- Resolution Corporation - The central government will establish a Resolution Corporation.
- The Corporation will have a Chairperson and its members will include representatives from the Finance Ministry, RBI, and SEBI, among others.
- The Corporation will-
- Provide deposit insurance to banks
- Classify service providers based on their risk, and
- Undertake resolution of service providers in case of failure.
- It may also investigate the activities of service providers, or undertake search and seizure operations if provisions of the Bill are being contravened.
- Risk based classification - The Corporation, in consultation with the respective regulators specify criteria for classifying service providers based on their risk of failure.
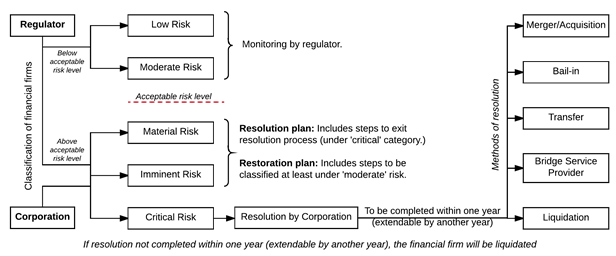
- A service provider categorised under the ‘imminent’ or ‘critical’ category will submit a restoration plan to the regulator, and a resolution plan to the Corporation. These plans will contain information, including: (i) details of assets and liabilities, (ii) steps to improve risk based categorisation, and (ii) information necessary for resolution of the service provider.
- Administration - The Corporation will take over the management of the service provider from the date when it is classified as ‘critical’.
- Resolution - The resolution of a service provider classified under the ‘critical’ category can be done by using
- Transfer of its assets and liabilities to another person,
- Merger or acquisition, and
- Creating a bridge financial,
- Bail-in and
- Liquidation
- Time limit - The service provider will automatically be liquidated if its resolution is not completed within the maximum time period of two years.
- Liquidation and distribution of assets - The Corporation will require the approval of the National Company Law Tribunal to liquidate the assets of a service provider.
- Offences - The Bill specifies penalties for offences such as concealment of property, and destruction or falsification of evidence.
Does the Bill guarantee the repayment of bank deposits?
- Currently, the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) provides deposit insurance for bank deposits up to 1 lakh rupees per depositor.
- The Bill proposes to subsume the functions of the DICGC under the Resolution Corporation.
- It will guarantee the repayment of a certain amount to each depositor in case the bank fails.
