Lokmanya Bal Gangadhar birth anniversary (23 July 1856)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak or Lokmanya Tilak was an Indian nationalist, social reformer and lawyer.
- The Britishers called him, ‘The Father of the Indian unrest’.
- He was given the honourary title of 'Lokmanya', which means admired (or accepted) by the people.
- He is known as the 'Father of Swarajya' and made 'Swaraj' as a part of the independence movement and he was the strongest advocates of ‘Swaraj’ (self-rule).
- He started the Swadeshi movement.
- He joined the Indian National Congress (INC) in the year 1890.
- He started two newspaper, ‘Kesari’ in Marathi and ‘Mahratta’ in English (referred as 'Maratha').
- He had a political regime with Bipin Chandra Pal and Lala Lajpat Rai and they were referred as 'Lal-Bal-Pal triumvirate'.
- He organised ‘Deccan Education Society’ along with Gopal Ganesh Agarkar, Mahadev Ballal Namjoshi and Vishnushastri Chiplunkar.
- It was set up to teach young Indians, the nationalist ideas through an emphasis on Indian culture.
- He founded the ‘All India Home Rule League’ in 1916 along with Joseph Baptista, Annie Besant and Muhammad Ali Jinnah.
- He transformed the household worshipping of Ganesha into a grand public event ‘Sarvajanik Ganeshotsav’ in 1894.
- Today, ‘Ganesh Chaturthi’, started by Tilak, is considered as the prime festival in Maharastra and adjacent states.
- Tilak was the poineer for the celebration of "Shiv Jayanti", the birth anniversary of Chhatrapati Shivaji.
- In 2007, the Government of India released a coin to commemorate Tilak on his 150th birth anniversary.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
- It is a flagship scheme of Ministry of Tourism.
- It is for an integrated development of theme based tourist circuits in the country.
- The following thematic circuits have been identified, for development namely,
- North-East India Circuit, Buddhist Circuit,
- Himalayan Circuit, Coastal Circuit, Krishna Circuit,
- Desert Circuit, Tirtankar circuit, Tribal Circuit,
- Eco Circuit, Wildlife Circuit, Rural Circuit,
- Spiritual Circuit, Sufi circuit, Ramayana Circuit and Heritage Circuit.
- Recently the sanctioned project in Andhra Pradesh, Kakinada Hope Island has been developed as a world Class Coastal & Eco Tourism Circuit.
- The Buddhist Circuit of Shalihundam in A.P and the Coastal Circuit of Sri Potti Sriramalu, Nellore are at stage of completion.
- The scheme would result in increased tourist inflow thereby creating employment opportunities for the local community.
- It is different from "PRASAD" scheme of Ministry of Tourism.
- PRASAD focus on holistic development, beautification and rejuvenation of the identified sites.
Sree Narayana Guru
- Sree Narayana Guru was a great saint, scholar, philosopher, poet and the forerunner of social renaissance in Kerala.
- He was born in 1856 in a peasant family of then untouchable Ezhava caste, in Thiruvananthapuram.
- He led a reform movement in Kerala, against the injustice in the caste-ridden society in order to promote social equality.
- He gave the universal message, “One caste, one religion, one God.”
- ‘Sahodaran Ayyappan’ (Pulaya Ayyappan), a social reformer from Kerala coined a rejoinder ‘No Caste, No Religion, No God for Mankind’.
- ‘Aravipuram Movement’ was launched by Narayana Guru.
- He defied the religious restrictions traditionally placed on the Ezhava community and consecrated an idol of Shiva at Aravipuram.
- He was a follower of Advaitha philosophy.
- He translated Tamil works like "Thirukkural" into Malayalam.
- He had written number of hymns to different gods and some of the notable ones are "Atmopadesa Sathakam" and "Darsanamala".
- He lent his support to the ‘Vaikkom Satyagraha’. Mahatma Gandhi met him during this time.
- ‘Sivagiri pilgrimage’ was conceived by three of the disciples, Vallabhasseri Govindan Vaidyar, T. K. Kittan and Muloor S. Padmanabha Panicker.
- The goal of the pilgrimage was the promotion of education, cleanliness, devotion to God.
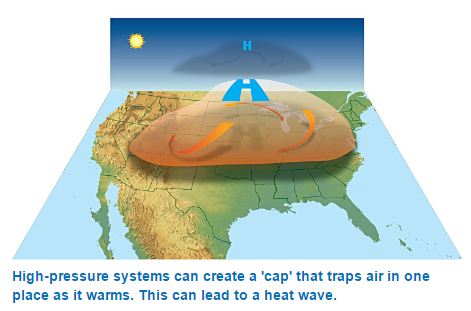
Prevention and Management of Heat-Wave - Action Plan
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) issued Guidelines for ‘Preparation of Action Plan – Prevention and Management of Heat Wave’.
- The ‘Ministry of Health and Family Welfare’ issued ‘Guidelines on Prevention and Management of Heat Related Illnesses’.
- It provides insights into heat-related illness and the necessary mitigative and response actions to be undertaken.
- Heat-wave is defined as the condition where maximum temperature at a grid point is 3˚C or more than the normal temperature, consecutively for 3 days or more.
- WMO defines it as, maximum temperature at a grid point is 5˚C or more than the normal temperature, consecutively for 5 days or more.
- This condition may leads to physiological stress, which sometimes can claim human life.
- Ahmedabad was among the first city to prepare a Heat wave Action Plan in 2015.
- It is expected that extreme heat waves will become more common worldwide because of climate change.
- India is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
- More than 2400 people died in the heat wave of 2015.
- Heat wave also caused death of cattle and wildlife besides affecting animals in various zoos in India.
- The guidelines serve as a tool for developing risk management plans, early warning systems, preparedness for health-related problems.
- Key strategies of the Plan –
- Establish Early Warning System and Inter-Agency Coordination.
- Capacity building and training programme.
- Public Awareness and community outreach.
- Collaboration with non government and civil society.
- Roles and Responsibilities for Managing Heat Wave –
- Preparation of Heat Wave Action Plan – NDMA
- Early Warning – IMD
- Mitigating Heat Wave - Ministry of Urban/Rural Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Transport.
- Monitoring and Response - Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Occupational Support and advisories - All Ministries.
- Media campaign and IEC activities - Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Documentation - Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
- Long Term Measures - Ministry of Urban Development, Ministry of Environment Forests and Climate Change.
- Heat wave is called as “Silent disaster” as it develops slowly and kills and injures humans and animals nationwide.
- The adverse impact of heat wave are preventable by educating the public on the preventive actions.
Source: PIB, The Indian Express
